
Low-alcohol beer is beer with little or no alcohol by volume that aims to reproduce the taste of beer while eliminating or reducing the inebriating effect, carbohydrates, and calories of regular alcoholic brews. Low-alcohol beers can come in different beer styles such as lagers, stouts, and ales. Low-alcohol beer is also known as light beer, non-alcoholic beer, small beer, small ale, or near-beer.

Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage, transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic beverages. The word is also used to refer to a period of time during which such bans are enforced.

The temperance movement is a social movement promoting temperance or complete abstinence from consumption of alcoholic beverages. Participants in the movement typically criticize alcohol intoxication or promote teetotalism, and its leaders emphasize alcohol's negative effects on people's health, personalities and family lives. Typically the movement promotes alcohol education and it also demands the passage of new laws against the sale of alcohol, either regulations on the availability of alcohol, or the complete prohibition of it.
A dram shop is a bar, tavern or similar commercial establishment where alcoholic beverages are sold. Traditionally, it is a shop where spirits were sold by the dram, a small unit of liquid.
A local option is the ability of local political jurisdictions, typically counties or municipalities, to allow decisions on certain controversial issues within their borders, usually referring to a popular vote. It usually relates to the issue of alcoholic beverage, marijuana sales, and now mask wearing.

Alcohol Justice is a San Rafael, California-based non-profit advocacy, research and policy organization describing itself as "the industry watchdog." The Marin Institute was renamed and re-branded as Alcohol Justice in 2011; it was originally named The Marin Institute for the Prevention of Alcohol and Other Drug Problems.

Alcoholic beverage control states, generally called control states, less often ABC states, are 17 states in the United States that have state monopolies over the wholesaling or retailing of some or all categories of alcoholic beverages, such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits.
An alcohol-free or non-alcoholic drink, also known as a temperance drink, is a version of an alcoholic drink made without alcohol, or with the alcohol removed or reduced to almost zero. These may take the form of a non-alcoholic mixed drink or non-alcoholic beer, and are widely available where alcoholic drinks are sold.

A temperance bar, also known as an alcohol-free bar, sober bar, or dry bar, is a type of bar that does not serve alcoholic beverages. An alcohol-free bar can be a business establishment or located in a non-business environment or event, such as at a wedding. Alcohol-free bars typically serve non-alcoholic beverages, such as non-alcoholic cocktails known as mocktails, alcohol-free beer or low-alcohol beer, alcohol-free wine, juice, soft drinks and water. Popular temperance drinks include cream soda, dandelion and burdock, sarsaparilla, and Vimto, among others. Various foods may also be served.
Foundation for Advancing Alcohol Responsibility (Responsibility.org), formerly known as the Century Council, is an American not-for-profit organization founded in 1991 and funded by a group of distillers that aims to fight to eliminate drunk driving and underage drinking and promotes responsible decision-making regarding alcohol use.

An alcoholic beverage is a beverage containing alcohol (ethanol). Alcoholic drinks are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and spirits—and typically their alcohol content is between 3% and 50%.

The Prohibition era was the period from 1920 to 1933 when the United States prohibited the production, importation, transportation, and sale of alcoholic beverages. The alcohol industry was curtailed by a succession of state legislatures, and Prohibition was formally introduced nationwide under the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified on January 16, 1919. Prohibition ended with the ratification of the Twenty-first Amendment, which repealed the Eighteenth Amendment on December 5, 1933.
The alcohol industry, also known as Big Alcohol, is the segment of the commercial drink industry that is involved in the manufacturing, distribution, and sale of alcoholic beverages. The industry has been criticised in the 1990s for deflecting attention away from the problems associated with alcohol use. The alcohol industry has also been criticised for being unhelpful in reducing the harm of alcohol.

Religion and alcohol have a complex history. The world's religions have had different relationships with alcohol, reflecting diverse cultural, social, and religious practices across different traditions. While some religions strictly prohibit alcohol consumption, viewing it as sinful or harmful to spiritual and physical well-being, others incorporate it into their rituals and ceremonies. Throughout history, alcohol has held significant roles in religious observances, from the use of sacramental wine in Christian sacraments to the offering and moderate drinking of omiki in Shinto purification rituals.

The 17 November 2010 United States ban on caffeinated alcoholic drinks is a ban which prevents the marketing and distribution of any prepackaged caffeinated alcoholic drink.

In the United States, the temperance movement, which sought to curb the consumption of alcohol, had a large influence on American politics and American society in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, culminating in the prohibition of alcohol, through the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, from 1920 to 1933. Today, there are organizations that continue to promote the cause of temperance.

The Canberra Hotel was a temperance hotel on the western corner of Ann and Edward Streets, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia.
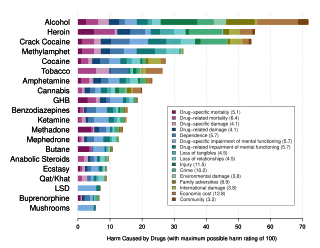
A managed alcohol program is a program meant to reduce harm for chronic alcoholics. The program involves providing a regular dose of alcohol to individuals with alcohol addiction, typically at a shelter-based harm reduction centre.

Alcohol packaging warning messages are warning messages that appear on the packaging of alcoholic drinks concerning their health effects. They have been implemented in an effort to enhance the public's awareness of the harmful effects of consuming alcoholic beverages, especially with respect to foetal alcohol syndrome and alcohol's carcinogenic properties. In general, warnings used in different countries try to emphasize the same messages. Such warnings have been required in alcohol advertising for many years, although the content of the warnings differ by nation.
This page is a list of terms related to the psychoactive drug alcohol.












