Environmental finance is a field within finance that employs market-based environmental policy instruments to improve the ecological impact of investment strategies. The primary objective of environmental finance is to regress the negative impacts of climate change through pricing and trading schemes. The field of environmental finance was established in response to the poor management of economic crises by government bodies globally. Environmental finance aims to reallocate a businesses resources to improve the sustainability of investments whilst also retaining profit margins.
Carbon neutrality is a state of net zero carbon dioxide emissions. This can be achieved by ending the use of coal, oil and gas to the extent that there is dramatically reduced emissions of carbon dioxide and removal carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The term is used in the context of carbon dioxide-releasing processes associated with transport, energy production, agriculture, and industry.
This glossary of climate change is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to climate change, global warming, and related topics.
The Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) is a United Nations-run carbon offset scheme allowing countries to fund greenhouse gas emissions-reducing projects in other countries and claim the saved emissions as part of their own efforts to meet international emissions targets. It is one of the three Flexible Mechanisms defined in the Kyoto Protocol. The CDM, defined in Article 12 of the Protocol, was intended to meet two objectives: (1) to assist non-Annex I countries achieve sustainable development and reduce their carbon footprints; and (2) to assist Annex I countries in achieving compliance with their emissions reduction commitments.
A carbon footprint (or greenhouse gas footprint) is a "certain amount of gaseous emissions that are relevant to climate change and associated with human production or consumption activities". In some cases, the carbon footprint is expressed as the carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) which is meant to sum up the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions caused by an individual, event, organization, service, place or product. In other cases, only the carbon dioxide emissions are taken into account but not those of other greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases, including the carbon-containing gases carbon dioxide and methane, can be emitted through the burning of fossil fuels, land clearance, and the production and consumption of food, manufactured goods, materials, wood, roads, buildings, transportation and other services. Beyond calculating carbon footprints for whole countries, it is possible to calculate the footprint of cities and smaller regions like neighborhoods but even sectors, companies and products.

A carbon offset is a reduction or removal of emissions of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases made in order to compensate for emissions made elsewhere. A carbon credit or offset credit is a transferrable financial instrument (i.e. a derivative of an underlying commodity) certified by governments or independent certification bodies to represent an emission reduction that can then be bought or sold. Both offsets and credits are measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO2e). One carbon offset or credit represents the reduction or removal of one ton of carbon dioxide or its equivalent in other greenhouse gases.
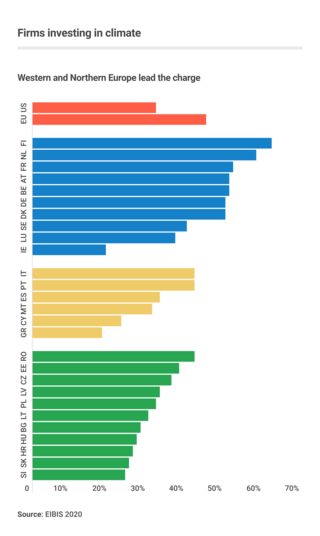
Business action on climate change includes a range of activities relating to climate change, and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of climate change, especially in the United States, through lobbying of government and funding of climate change deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of climate change, through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.
Flexible mechanisms, also sometimes known as Flexibility Mechanisms or Kyoto Mechanisms, refers to emissions trading, the Clean Development Mechanism and Joint Implementation. These are mechanisms defined under the Kyoto Protocol intended to lower the overall costs of achieving its emissions targets. These mechanisms enable Parties to achieve emission reductions or to remove carbon from the atmosphere cost-effectively in other countries. While the cost of limiting emissions varies considerably from region to region, the benefit for the atmosphere is in principle the same, wherever the action is taken.
Carbon finance is a branch of environmental finance that covers financial tools such as carbon emission trading to reduce the impact of greenhouse gases (GHG) on the environment by giving carbon emissions a price.

Carbon accounting is a framework of methods to measure and track how much greenhouse gas (GHG) an organization emits. It can also be used to track projects or actions to reduce emissions in sectors such as forestry or renewable energy. Corporations, cities and other groups use these techniques to help limit climate change. Organizations will often set an emissions baseline, create targets for reducing emissions, and track progress towards them. The accounting methods enable them to do this in a more consistent and transparent manner.

The CDP is an international non-profit organisation based in the United Kingdom, Japan, India, China, Germany, Brazil and the United States of America that helps companies and cities disclose their environmental impact. It aims to make environmental reporting and risk management a business norm, driving disclosure, insight, and action towards a sustainable economy. In 2022, nearly 20,000 organizations disclosed their environmental information through CDP.
The Investor Network on Climate Risk (INCR) is a nonprofit organization of investors and financial institutions that promotes better understanding of the financial risks and investment opportunities posed by climate change. INCR is coordinated by Ceres, a coalition of investors and environmental groups working to advance sustainable prosperity.

The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person. However, the IEA estimates that the richest decile in the US emits over 55 tonnes of CO2 per capita each year. Because coal-fired power stations are gradually shutting down, in the 2010s emissions from electricity generation fell to second place behind transportation which is now the largest single source. In 2020, 27% of the GHG emissions of the United States were from transportation, 25% from electricity, 24% from industry, 13% from commercial and residential buildings and 11% from agriculture. In 2021, the electric power sector was the second largest source of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for 25% of the U.S. total. These greenhouse gas emissions are contributing to climate change in the United States, as well as worldwide.

ClimateCare is a profit for purpose environmental and social impact company known for its role providing carbon offset services, with a particular focus on using carbon and other results based finance to support its 'Climate+Care Projects'. It also provides businesses and governments with sustainable development programmes, environmental and social impact measurement and project development.

Emission trading (ETS) for carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHG) is a form of carbon pricing; also known as cap and trade (CAT) or carbon pricing. It is an approach to limit climate change by creating a market with limited allowances for emissions. This can lower competitiveness of fossil fuels and accelerate investments into low carbon sources of energy such as wind power and photovoltaics. Fossil fuels are the main driver for climate change. They account for 89% of all CO2 emissions and 68% of all GHG emissions.
EcoSecurities is a company specialised in carbon markets and greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation projects worldwide. EcoSecurities specialises in sourcing, developing and financing projects on renewable energy, energy efficiency, forestry and waste management with a positive environmental impact.
Although it is a worldwide treaty, the Kyoto Protocol has received criticism.
Pedro Moura Costa is an entrepreneur involved in environmental finance with a focus on the international efforts for greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reductions. Of particular relevance, he was the founder and President of EcoSecurities Group Plc., one of the leading project developers for the international carbon markets, and has written widely about the policy and science of climate change mitigation, including contributions to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports.
Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) is an integrated approach to managing landscapes to help adapt agricultural methods, livestock and crops to the effects of climate change and, where possible, counteract it by reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, at the same time taking into account the growing world population to ensure food security. Thus, the emphasis is not simply on carbon farming or sustainable agriculture, but also on increasing agricultural productivity. "CSA ... is in line with FAO’s vision for Sustainable Food and Agriculture and supports FAO’s goal to make agriculture, forestry and fisheries more productive and more sustainable".

The European Green Deal, approved in 2020, is a set of policy initiatives by the European Commission with the overarching aim of making the European Union (EU) climate neutral in 2050. The plan is to review each existing law on its climate merits, and also introduce new legislation on the circular economy, building renovation, biodiversity, farming and innovation.







