Related Research Articles

Irssi is an IRC client program for Linux, FreeBSD, macOS and Microsoft Windows. It was originally written by Timo Sirainen, and released under the terms of the GNU GPL-2.0-or-later in January 1999.
In computing, traceroute and tracert are computer network diagnostic commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The history of the route is recorded as the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host in the route (path); the sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure of the total time spent to establish the connection. Traceroute proceeds unless all sent packets are lost more than twice; then the connection is lost and the route cannot be evaluated. Ping, on the other hand, only computes the final round-trip times from the destination point.
A chroot on Unix and Unix-like operating systems is an operation that changes the apparent root directory for the current running process and its children. A program that is run in such a modified environment cannot name files outside the designated directory tree. The term "chroot" may refer to the chroot(2) system call or the chroot(8) wrapper program. The modified environment is called a chroot jail.

UEFI is a set of specifications written by the UEFI Forum. They define the architecture of the platform firmware used for booting and its interface for interaction with the operating system. Examples of firmware that implement these specifications are AMI Aptio, Phoenix SecureCore Tiano, TianoCore EDK II and InsydeH2O.
Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE) is a software interface for Unix and Unix-like computer operating systems that lets non-privileged users create their own file systems without editing kernel code. This is achieved by running file system code in user space while the FUSE module provides only a bridge to the actual kernel interfaces.
Unix-like operating systems identify a user by a value called a user identifier, often abbreviated to user ID or UID. The UID, along with the group identifier (GID) and other access control criteria, is used to determine which system resources a user can access. The password file maps textual user names to UIDs. UIDs are stored in the inodes of the Unix file system, running processes, tar archives, and the now-obsolete Network Information Service. In POSIX-compliant environments, the command-line command id gives the current user's UID, as well as more information such as the user name, primary user group and group identifier (GID).

rm is a basic command on Unix and Unix-like operating systems used to remove objects such as computer files, directories and symbolic links from file systems and also special files such as device nodes, pipes and sockets, similar to the del command in MS-DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows. The command is also available in the EFI shell.

Git is a distributed version control system that tracks changes in any set of computer files, usually used for coordinating work among programmers collaboratively developing source code during software development. Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows.
The following tables compare general and technical information between a number of notable IRC client programs which have been discussed in independent, reliable prior published sources.

strace is a diagnostic, debugging and instructional userspace utility for Linux. It is used to monitor and tamper with interactions between processes and the Linux kernel, which include system calls, signal deliveries, and changes of process state. The operation of strace is made possible by the kernel feature known as ptrace.
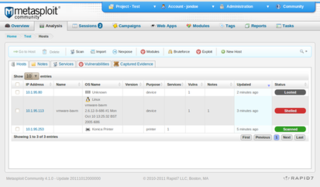
The Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development. It is owned by Boston, Massachusetts-based security company Rapid7.

Wireless network cards for computers require control software to make them function. This is a list of the status of some open-source drivers for 802.11 wireless network cards.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of file systems.
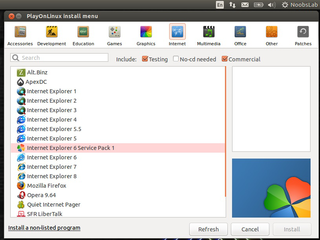
PlayOnLinux is a graphical frontend for the Wine software compatibility layer which allows Linux users to install Windows-based video games, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer, as well as many other applications such as Apple iTunes and Safari.
Rsyslog is an open-source software utility used on UNIX and Unix-like computer systems for forwarding log messages in an IP network. It implements the basic syslog protocol, extends it with content-based filtering, rich filtering capabilities, queued operations to handle offline outputs, support for different module outputs, flexible configuration options and adds features such as using TCP for transport.
Kqueue is a scalable event notification interface introduced in FreeBSD 4.1 in July 2000, also supported in NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD, and macOS. Kqueue was originally authored in 2000 by Jonathan Lemon, then involved with the FreeBSD Core Team. Kqueue makes it possible for software like nginx to solve the c10k problem.
The Ident Protocol, specified in RFC 1413, is an Internet protocol that helps identify the user of a particular TCP connection. One popular daemon program for providing the ident service is identd.

Void Linux is an independent Linux distribution that uses the X Binary Package System (XBPS) package manager, which was designed and implemented from scratch, and the runit init system. Excluding binary kernel blobs, a base install is composed entirely of free software.
Zstandard, commonly known by the name of its reference implementation zstd, is a lossless data compression algorithm developed by Yann Collet at Facebook. Zstd is the reference implementation in C. Version 1 of this implementation was released as open-source software on 31 August 2016.
doas is a program to execute commands as another user. The system administrator can configure it to give specified users privileges to execute specified commands. It is free and open-source under the ISC license and available in Unix and Unix-like operating systems.
References
- ↑ "oidentd Releases". GitHub . August 16, 2021. Retrieved July 4, 2022.
- ↑ "oidentd README". GitHub . March 8, 2018. Retrieved March 8, 2018.
- ↑ "oidentd License". GitHub . December 3, 2002. Retrieved March 8, 2018.