The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and north. The northeast corner is the Shelikhov Gulf. The sea is named after the Okhota river, which is in turn named after the Even word окат meaning "river".

Vitus Jonassen Bering, also known as Ivan Ivanovich Bering, was a Danish cartographer and explorer in Russian service, and an officer in the Russian Navy. He is known as a leader of two Russian expeditions, namely the First Kamchatka Expedition and the Great Northern Expedition, exploring the north-eastern coast of the Asian continent and from there the western coast on the North American continent. The Bering Strait, the Bering Sea, Bering Island, the Bering Glacier, and Vitus Lake were all named in his honor.

Okhotsk is an urban locality and the administrative center of Okhotsky District of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located at the mouth of the Okhota River on the Sea of Okhotsk. Population: 4,215 (2010 Census); 5,738 (2002 Census); 9,298 (1989 Census).

The North Pacific right whale is a very large, thickset baleen whale species that is extremely rare and endangered.

Kitami is a city in Okhotsk Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the most populous city and the commercial center in the subprefecture, although the subprefecture capital is Abashiri.

Abashiri is a city located in Okhotsk Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan.

Monbetsu is a city located in Okhotsk Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan; on the Sea of Okhotsk. The name comes from Ainu Mopet, Ainu "-pet" would be interpreted "-betsu" in Japanese as well of other city names in Hokkaido.

Dall's porpoise is a species of porpoise endemic to the North Pacific. It is the largest of porpoises and the only member of the genus Phocoenoides. The species is named after American naturalist W. H. Dall.

Drift ice, also called brash ice, is sea ice that is not attached to the shoreline or any other fixed object. Unlike fast ice, which is "fastened" to a fixed object, drift ice is carried along by winds and sea currents, hence its name. When drift ice is driven together into a large single mass, it is called pack ice. Wind and currents can pile up that ice to form ridges up to dozens of metres in thickness. These represent a challenge for icebreakers and offshore structures operating in cold oceans and seas.

The KamchatkaPeninsula is a 1,250-kilometre-long (777 mi) peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about 270,000 km2 (104,248 sq mi). The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the 10,500-metre-deep (34,449 ft) Kuril–Kamchatka Trench.
Chumikan is a rural locality and the administrative center of Tuguro-Chumikansky District of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located at the mouth of the Uda River. Population: 1,344 (2002 Census); 1,748 (1989 Census).

Michael Franzevich von Reinecke, better known as Mikhail Reyneke, was a Russian vice-admiral and hydrographer. During his service in the Imperial Russian Navy, Reinecke extensively documented the White Sea, the Baltic Sea, and the Barents Sea for the Russian Hydrographic Service, and determined the sea level measurement that became standardized throughout Russia.

The Okhotsk Coast is an informal name for the northwest coast of the Sea of Okhotsk. Although it was never an administrative unit there is some reason to treat it as a distinct region. Here in 1639 the Russians first reached the Pacific Ocean. From here, beginning in 1716, Russian ships sailed east to the Kamchatka Peninsula, the Aleutian Islands and Alaska.

Shantar Islands National Park covers both the terrestrial and maritime surroundings of the Shantar Islands, a group of 15 currently uninhabited islands that lie close to the coast of Khabarovsk Krai, in the Sea of Okhotsk in the Russian Far East. Most of the islands are moderately mountainous, with rugged cliffs; the highest point is 720 m (2,375 ft). The area around the islands is an important area for marine mammals - including Steller Sea Lions, seals, and many species of cetacean - plus spawning salmon and very large colonies of birds. The park was formerly a state nature reserve, but re-established as a federal national park in 2013 with the stated purpose of protecting the habitat of vulnerable species, and supporting the scientific study and ecological tourism of the area. The Shantar Islands are located in the Tuguro-Chumikansky District of Khabarovsk Krai. The park is overseen by the Russian Ministry of Natural Resources.
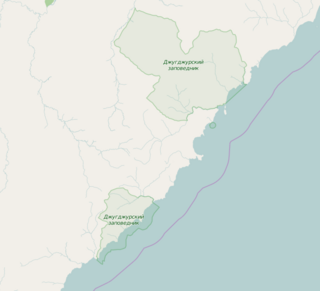
Dzhugdzursky Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' on the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk, on the territory of Ayano-Maisky region of the Khabarovsk Territory in the Russian Far East. With over 8,000 km2 of land area and over 500 km2 of marine area, it is the largest of the six nature reserves in Khabarovsk Krai. It supports spawning streams into the Okhotsk Sea for chum, pink salmon and coho salmon.

Komsomolsk Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik', encompassing the confluence of the Gorin River and the Amur River in the Russian Far East. The reserve protects a meeting zone of multiple ecoregions in the lower Amur, including the northernmost reach of Manchurian taiga. It is located about 50 km downstream (east) of Komsomolsk-on-Amur, in the Komsomolsky District of Khabarovsk Krai. The reserve was created in 1963, and covers an area of 64,278 ha (248.18 sq mi).

Poronaysky Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' covering Cape Patience, on the eastern side of Sakhalin Island in the Russian Far East. A specific purpose of the reserve is to protect rookeries for arctic birds on Cape Patience, which is a 65 km peninsula extending into the Okhotsk Sea. The reserve includes the southern part of the East Sakhalin Mountains, and the widest part of the Tym-Poronaisk dale. The reserve is situated in the Poronaysky District of Sakhalin Oblast, 50 km east of the regional city of Poronaysk. It was formally established in 1988, and covers 56,695 ha (218.90 sq mi).

The Okhotsk-Manchurian taiga ecoregion is an area of coniferous forests in the Russian Far East, covering the Amur River delta, the west coast of the Okhotsk Sea, and the rugged extension of the northern Sikhote-Alin Mountains that run southwest-to-northeast through the Primorsky and Khabarovsk regions. It is the southernmost taiga forest in Eurasia. The ecoregion is distinguished from surrounding ecoregions by the slightly warmer climate due to the maritime influence and the shield of the mountains to the west, and by the mixing of flora and fauna species from Okhotsk-Kamchatka communities to the north and Manchurian species from the south. The forest at lower altitudes is "light taiga", and "dark taiga" at higher altitudes.

The South Sakhalin-Kurile mixed forests ecoregion is split between the southwest region of Sakhalin Island, and the southern three islands of the Kurile Islands chain in the Russian Far East. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm, with a Humid Continental climate. It covers 12,432 km2 (4,800 sq mi).