Related Research Articles

Constance Nevlin Johnson is an American politician from the U.S. state of Oklahoma. She served in the Oklahoma Senate, representing District 48, which encompasses portions of northeastern and northwestern Oklahoma County until 2014. She was first elected to the state senate in a special election in September 2005.
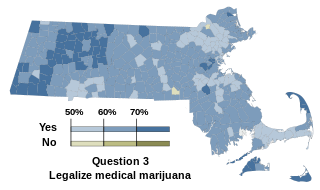
The Massachusetts Medical Marijuana Initiative, appeared as the third question on the state's 2012 ballot as an indirect initiated state statute. The measure allows cannabis to be used for medical purposes in the state. The initiative—backed by the American Civil Liberties Union, the Massachusetts Patient Advocacy Alliance, and the Committee for Compassionate Medicine—was filed with proponents turning in the required signatures to the Massachusetts Attorney General's office by the August 3, 2011 deadline. Those signatures were needed for the required ten qualified voters who submitted the original petition to put forward the full text of the law they want enacted. The initiative passed with support from 63% of state voters.

Florida Amendment 2, Use of Marijuana for Certain Medical Conditions, is an initiative that appeared on the November 4, 2014, ballot in the state of Florida as a citizen initiated state constitutional amendment.

Cannabis is strictly illegal in Wyoming. The state has some of the strictest cannabis laws in the United States. Cannabis itself is not allowed for medical purposes, but a 2015 law allows limited use of non-psychoactive Cannabidiol. An effort is ongoing to place two initiatives on the 2022 ballot, one to legalize medical cannabis, and the other to decriminalize personal use.

Cannabis in South Dakota is legal for medical use as of July 1, 2021, having been legalized by a ballot initiative on November 3, 2020. Prior to then, cannabis was fully illegal, with South Dakota being the only U.S. state which outlawed ingestion of controlled substances. Testing positive for cannabis can be a misdemeanor offense. South Dakota would have become the first state in US history to legalize recreational and medical cannabis simultaneously, but an amendment legalizing recreational marijuana that was approved in the same election was struck down as unconstitutional the following February. The challenge claimed the amendment violated Amendment Z, the "Single-Subject Rule". The decision was appealed to the South Dakota Supreme Court, which upheld the lower court's decision on November 24, 2021.

Cannabis in Oklahoma is illegal for recreational use, but legal for medical use with a state-issued license, while CBD oil derived from industrial hemp is legal without a license.
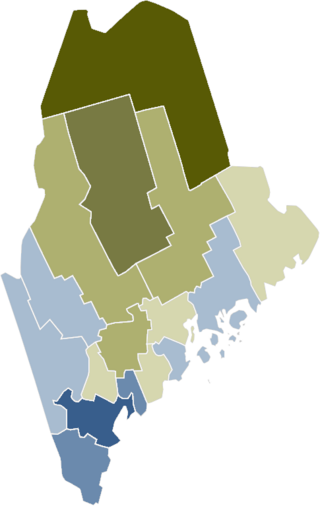
Maine Question 1, formally An Act to Legalize Marijuana, is a citizen-initiated referendum question that qualified for the Maine November 8, 2016 statewide ballot. It was qualified for the ballot after a Maine Superior Court judge ordered that petitions rejected by the Maine Secretary of State be reconsidered. The proposal sought to legalize the recreational use of marijuana in Maine for those over the age of 21, and institute a 10 percent tax on its sale. As the Maine Legislature and Governor Paul LePage declined to enact the proposal as written, it appeared on the ballot along with elections for President of the United States, Maine's two U.S. House seats, the Legislature, other statewide ballot questions, and various local elections.

The Adult Use of Marijuana Act (AUMA) was a 2016 voter initiative to legalize cannabis in California. The full name is the Control, Regulate and Tax Adult Use of Marijuana Act. The initiative passed with 57% voter approval and became law on November 9, 2016, leading to recreational cannabis sales in California by January 2018.

Cannabis in Arizona is legal for recreational use. A 2020 initiative to legalize recreational use passed with 60% of the vote. Possession and cultivation of recreational cannabis became legal on November 30, 2020, with the first state-licensed sales occurring on January 22, 2021.

Cannabis in Missouri is legal for recreational use. A ballot initiative to legalize recreational use passed by a 53–47 margin on November 8, 2022. Possession for adults 21 and over became legal on December 8, 2022, with the first licensed sales occurring on February 3, 2023.

Cannabis in Maryland is legal for medical use and illegal for recreational use, but as of January 1, 2023 thru June 30, 2023, decriminalization is temporarily expanded from possession of less than 1 oz to less than 1.5 oz, prior to full legalized recreational use of 1.5 oz or less on July 1st, 2023 due to the passage of the 2022 Maryland Question 4 referendum. In 2013, a state law was enacted to establish a state-regulated medical cannabis program. The program, known as the Natalie M. LaPrade Maryland Medical Cannabis Commission (MMCC) became operational on December 1, 2017.

John Kevin Stitt is an American businessman and politician serving as the 28th governor of Oklahoma since 2019. A member of the Republican Party, he was elected in 2018, defeating Democrat and former state Attorney General Drew Edmondson with 54.3% of the vote. Stitt was reelected to a second term in 2022, defeating Superintendent of Public Instruction Joy Hofmeister, a Republican turned Democrat, with 55.4% of the vote. A member of the Cherokee Nation, Stitt is the second governor of Native descent after former Oklahoma governor Johnston Murray.

South Dakota Initiated Measure 26 was a 2020 voter initiative to legalize medical cannabis in the U.S. state of South Dakota. The initiative was certified by the South Dakota Secretary of State for the 2020 ballot on December 19, 2019. The sponsor of the initiative was New Approach South Dakota, a volunteer group headed by Melissa Mentele. The group had unsuccessfully tried to get an initiative on the 2018 ballot. Polling in September 2020 indicated 70% voter support for the initiative.

Montana I-190, the Montana Marijuana Legalization and Tax Initiative was a cannabis legalization initiative that appeared on the November 3, 2020 Montana general election ballot. Passing with 56% approval, the initiative legalized recreational marijuana in the state effective January 1, 2021. Along with Arizona, New Jersey and South Dakota, Montana was one of four states that legalized cannabis via ballot measures in the November 2020 election.

Arizona Proposition 207 was a voter initiative that appeared on the November 3, 2020, Arizona general election ballot to legalize cannabis for recreational use. Passing with 60% of the vote, the initiative legalized the possession of up to an ounce of cannabis, licensed sales at dispensaries, and personal cultivation of up to six plants. Along with Montana, New Jersey and South Dakota, Arizona is one of four states that legalized recreational marijuana via ballot measures in 2020.
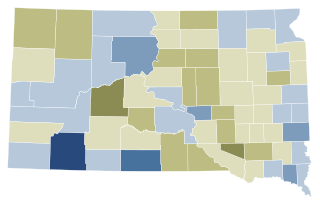
South Dakota Constitutional Amendment A, the Marijuana Legalization Initiative, was a cannabis legalization initiative that appeared on the November 3, 2020 South Dakota general election ballot. Passing with 54% of the vote, the measure would have legalized recreational marijuana in South Dakota effective July 1, 2021. Additionally, Amendment A required the South Dakota State Legislature to establish a medical marijuana program and legal hemp sales by April 1, 2022.
The Regulate Cannabis Like Alcohol initiative is a ballot initiative for legalization of cannabis in the U.S. state of Ohio. It was introduced in 2021, originally for the 2022 general ballot, then moved potentially to 2023 following a lawsuit.

2022 Missouri legalization initiative was a voter initiative on the November 2022 ballot. It was approved by voters, legalizing cannabis in the U.S. state of Missouri.
References
- ↑ "Outline of the Oklahoma Initiative and Referendum Petition Process". sos.ok.gov. Oklahoma Secretary of State. Retrieved 27 December 2021.
- 1 2 Carmen Forman. "Second petition filed to legalize recreational cannabis in Oklahoma". Oklahoman.
- ↑ "Group To Present Signatures To Secretary Of State To Get Recreational Marijuana State Question On November Ballot". Oklahoma City: News 9 Now. July 5, 2022.
- ↑ "SQ-820 To Be On Ballot After Getting Over 100,000 Signatures". Oklahoma City: KWTV-DT. August 22, 2022.
- ↑ Matt Patterson (August 25, 2022). "SQ 820 group asks state Supreme Court to put marijuana vote on November ballot". nondoc.com. Sustainable Journalism Foundation.
- ↑ Colleen Wilson. "'The frustration is real': SQ 820 delay debated in Oklahoma Supreme Court". KOKH.
"I don't think we would even be in this position of having to 'put the cart before the horse', if the state wasn't insistent on an August 26th deadline that doesn't exist anywhere in law," Ryan Kiesel, senior consultant for the SQ 820 campaign said after the hearing. 'You can't find it in administrative rule, you can't find it in statute, and certainly not the constitution." The SQ 820 campaign contends the Oklahoma Constitution specifies that initiative petitions be placed on the next 'upcoming' ballot. They argued the August 26th deadline set by the state election board is arbitrary and unnecessary.
- ↑ Clydesdale, Natalie; Raache, Hicham (August 30, 2022). "Oklahoma Supreme Court opts to temporarily not rule on request to put SQ 820 on ballot". Oklahoma City: KFOR-TV.
- ↑ Sean Murphy (August 30, 2022). "Oklahoma Supreme Court agrees to consider marijuana question". Associated Press.
- ↑ King, Kari; Camper, Nick (September 21, 2022). "Oklahomans won't vote on recreational marijuana this November". KFOR.
'There is still a possibility of rehearing in two of the protests' said the court
- ↑ Carmen Forman (September 21, 2022). "Oklahoma recreational cannabis question won't make November ballot". The Oklahoman.
- ↑ Sean Murphy (October 18, 2022). "Oklahoma governor sets March election for marijuana question". Associated Press – via The Hill.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Denwalt, Dale (February 3, 2023). "Former Oklahoma Gov. Frank Keating to lead campaign against recreational marijuana". The Oklahoman . Retrieved 4 February 2023.
- ↑ Patterson, Matt (20 October 2022). "Debate: Stitt, Hofmeister tussle over state performance, McGirt and abortion". Nondoc. Retrieved 22 October 2022.
Stitt said during the debate he opposes the state question and would personally vote against it. "No, I'm not supporting that. It is still illegal federally. We should not have a checkerboard of jurisdictions across the state, so I'm not supporting recreational marijuana," Stitt said.
- ↑ Pain, Mason (January 25, 2023). "To legalize or not to legalize? That is State Question 820". Oklahoma Gazette . Retrieved 30 January 2023.