
Salta is a province of Argentina, located in the northwest of the country. Neighboring provinces are from the east clockwise Formosa, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Tucumán and Catamarca. It also surrounds Jujuy. To the north it borders Bolivia and Paraguay and to the west lies Chile.

Salta is the capital and largest city in the Argentine province of the same name. With a population of 618,375 according to the 2010 census, it is also the 7th most-populous city in Argentina. The city serves as the cultural and economic center of the Valle de Lerma Metropolitan Area, which is home to over 50.9% of the population of Salta Province and also includes the municipalities of La Caldera, Vaqueros, Campo Quijano, Rosario de Lerma, Cerrillos, La Merced and San Lorenzo. Salta is the seat of the Capital Department, the most populous department in the province.

The Argentine Northwest is a geographic and historical region of Argentina composed of the provinces of Catamarca, Jujuy, La Rioja, Salta, Santiago del Estero and Tucumán.
Cerrillos is a city in the province of Salta, Argentina. It has about 18,000 inhabitants as per the 2001 census [INDEC], and it is the head town of the Cerrillos Department. It is located just 15 km south of the city of Salta, capital of the province.

San José de Metán is a city in the south of the province of Salta, Argentina, 160 km from the provincial capital Salta, on National Routes 9 and 34. It has about 28,000 inhabitants as per the 2010 census [INDEC]. It is the head town of the Metán Department.

The Calchaquí Valley is an area in the northwestern region of Argentina which crosses the provinces of Catamarca, Tucumán, Jujuy and Salta. It is best known for its contrast of colors and its unique geography that ranges from the mountain desert to the subtropical forest.
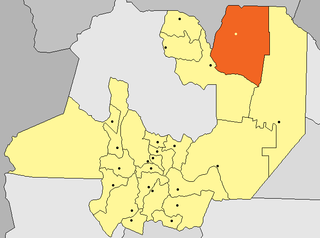
Salvador Mazza or Profesor Salvador Mazza is a city in northern Argentina, in Salta Province, 400 km (249 mi) north of the capital city of Salta, and 55 km (34 mi) from the city of Tartagal on National Route 34 in General José de San Martín Department, on the international border with Bolivia.
Chalicán is a town and municipality located in the southeast of Jujuy Province in Argentina. It is located between San Pedro de Jujuy and Fraile Pintado. The population of Chalicán mainly produces sugar cane and citrus fruits. Fishing also plays a large role in the economy of Chalicán.
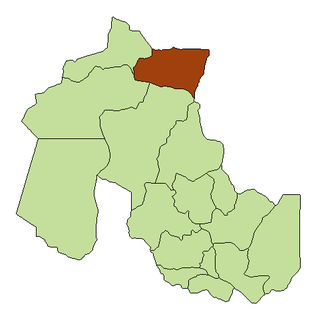
Barrios (Jujuy) is a rural municipality and village in Jujuy Province in Argentina.
Cochinoca is a rural municipality and village in Jujuy Province in Argentina.
Coranzuli is a rural municipality and village in Jujuy Province in Argentina.

Rinconada is a rural municipality and village in Jujuy Province in Argentina. It is located in the west of the province of Jujuy and is the head of the Rinconada Department.

Susques is a rural municipality and village in Jujuy Province in Argentina.

Colomé is a village and rural municipality in Salta Province in northwestern Argentina. It is located about 20 km from Molinos, Salta. This settlement was established by the last Spanish governor of Salta, Nicolás Severo de Isasmendi, in 1831. His daughter Ascención imported grapevines from France and planted them in the area at an average altitude of 2200 m, which is extremely high for viticulture. The climate is dry and arid, and temperature differences between day and night can be high. The winters are very cold.
La Poma is a village and rural municipality in Salta Province in northwestern Argentina.

Molinos is a village and rural municipality in Salta Province in northwestern Argentina.
Santa Rosa de los Pastos Grandes is a village and rural municipality in Salta Province in northwestern Argentina.

Negra Muerta is a caldera in Argentina. It is part of the volcanic centres of the Andean Volcanic Belt, which has formed a number of calderas in large ignimbrite producing eruptions. These calderas include Aguas Calientes, Cerro Panizos, Galan, Negra Muerta and La Pacana. Some of these volcanic centres appear to be associated with large fault zones that cross the Puna.

Nevado de Acay is a 5,950-metre-high (19,520 ft) mountain in Argentina. It is a volcanic intrusion that formed during the Miocene and was later exposed. The intrusion is formed by monzonite and is associated with a fault system that also connects to neighbouring volcanoes.
TulTul, Del Medio and Pocitos are three volcanoes in Argentina. Small Inka shrines have been found on their summits.













