| C36 | |
|---|---|
| ILO Convention | |
| Date of adoption | June 29, 1933 |
| Date in force | July 18, 1937 |
| This Convention has been "shelved". | |
| Classification | Old-age, Invalidity and Survivors Benefit |
| Subject | Social Security |
| Previous | Old-Age Insurance (Industry, etc.) Convention, 1933 (shelved) |
| Next | Invalidity Insurance (Industry, etc.) Convention, 1933 (shelved) |
Old-Age Insurance (Agriculture) Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
It was established in 1933:
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to compulsory old-age insurance,...
This concept contained in the convention were revised and included in ILO Convention C128, Invalidity, Old-Age and Survivors' Benefits Convention, 1967.
Prior to its shelving, the convention had been ratified by 10 states.[ citation needed ]

The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. This founding document, originally comprising seven articles, delineates the national frame of government. Its first three articles embody the doctrine of the separation of powers, whereby the federal government is divided into three branches: the legislative, consisting of the bicameral Congress ; the executive, consisting of the president and subordinate officers ; and the judicial, consisting of the Supreme Court and other federal courts. Article IV, Article V and Article VI embody concepts of federalism, describing the rights and responsibilities of state governments, the states in relationship to the federal government, and the shared process of constitutional amendment. Article VII establishes the procedure subsequently used by the 13 States to ratify it. It is regarded as the oldest written and codified national constitution in force.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The Convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.
The Convention for the Unification of certain rules relating to international carriage by air, commonly known as the Warsaw Convention, is an international convention which regulates liability for international carriage of persons, luggage, or goods performed by aircraft for reward.

The Twenty-first Amendment to the United States Constitution repealed the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which had mandated nationwide prohibition on alcohol. The Twenty-first Amendment was proposed by the 72nd Congress on February 20, 1933, and was ratified by the requisite number of states on December 5, 1933. It is unique among the 27 amendments of the U.S. Constitution for being the only one to repeal a prior amendment, as well as being the only amendment to have been ratified by state ratifying conventions.
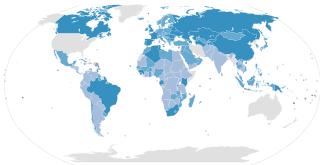
The ILO Convention concerning Minimum Age for Admission to Employment C138, is a convention adopted in 1973 by the International Labour Organization. It requires ratifying states to pursue a national policy designed to ensure the effective abolition of child labour and to raise progressively the minimum age for admission to employment or work. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions. Convention C138 replaces several similar ILO conventions in specific fields of labour.
State ratifying conventions are one of the two methods established by Article V of the United States Constitution for ratifying proposed constitutional amendments. The only amendment that has been ratified through this method thus far is the 21st Amendment.
Old-Age Insurance Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Invalidity Insurance Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Invalidity Insurance (Agriculture) Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Survivors' Insurance Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Survivors' Insurance (Agriculture) Convention, 1933 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Invalidity, Old-Age and Survivors' Benefits Convention, 1967 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Maintenance of Migrants' Pension Rights Convention, 1935 (shelved) is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Philippine constitutional plebiscite of 1973 ratified the 1973 Constitution of the Philippines.

John Treadwell was an American politician and the 21st Governor of Connecticut.
Work in Fishing Convention (2007) C 188, was adopted at the 96th International Labour Conference (ILC) of the International Labour Organization ILO in 2007. The objectives of the Convention is to ensure that fishers have decent conditions of work on board fishing vessels with regard to minimum requirements for work on board; conditions of service; accommodation and food; occupational safety and health protection; medical care and social security. It applies to all fishers and fishing vessels engaged in commercial fishing operations. It supersedes the old Conventions relating to fishermen.
The International Convention for the Suppression of the Traffic in Women and Children is a 1921 multilateral treaty of the League of Nations that addressed the problem of international trafficking of women and children.
The International Agreement for the suppression of the White Slave Traffic is a series of anti–human trafficking treaties, the first of which was first negotiated in Paris in 1904. It was one of the first multilateral treaties to address issues of slavery and human trafficking. The Slavery, Servitude, Forced Labour and Similar Institutions and Practices Convention of 1926 and the International Convention for the Suppression of the Traffic in Women of Full Age of 1933 are similar documents.
In Japan, a person with a disability is defined as: "a person whose daily life or life in society is substantially limited over the long term due to a physical disability or mental disability". Japan ratified the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) on 20 January 2014.