Castile is a territory of imprecise limits located in Spain. Its extension is often ascribed to the sum of the regions of Old Castile and New Castile, as they were formally defined in the 1833 territorial division of Spain. Those two regions cover the following modern autonomous communities: the eastern part of Castile and León, Castile-La Mancha, and Community of Madrid as well as Cantabria and La Rioja. However, it has been pointed out that in practice the modern limits of Castile are imprecise, and that this name has been used mainly as a reference for the image of Spain as a nation.

Castile and León is an autonomous community in north-western Spain.

The Province of Burgos is a province of northern Spain, in the northeastern part of the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is bordered by the provinces of Palencia, Cantabria, Vizcaya, Álava, La Rioja, Soria, Segovia, and Valladolid. Its capital is the city of Burgos.

La Rioja is an autonomous community and province in Spain, in the north of the Iberian Peninsula. Its capital is Logroño. Other cities and towns in the province include Calahorra, Arnedo, Alfaro, Haro, Santo Domingo de la Calzada, and Nájera. It has an estimated population of 315,675 inhabitants, making it the least populated region of Spain.
The Divisiones Regionales de Fútbol in the Community of Castile and León:

The Region of León, Leonese region or Leonese Country is a historic territory defined by the 1833 Spanish administrative organisation. The Leonese region encompassed the provinces of Salamanca, Zamora, and León, now part of the modern Spanish autonomous community of Castile and León. As is the case with other historical regions, and continuing with centuries of history, the inhabitants of the Leonese region are still called Leonese. Even today, according with official autonomous government, the historical territorial adjective is used in addition with the modern annexed territory, the rest of Old Castile, being "Castilians and Leonese".
The Consejo Superior de los Colegios de Arquitectos de España (CSCAE), is the higher council of Architects Associations in Spain, and is the only established professional body of Spanish architects, located in the Paseo de la Castellana, Madrid. The current president is Jordi Ludevid i Anglada.
The Unidad Regionalista de Castilla y León or Regionalist Unity of Castile and León (URCL) is a "regionalist, democratic, modern and innovative political party that, focusing on the principles of freedom, justice and solidarity, assumes the uncompromising defense of the legitimate interests of Castile and León."

This is the results breakdown of the Congress of Deputies election held in Spain on 28 October 1982. The following tables show detailed results in each of the country's 17 autonomous communities and in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, as well as a summary of constituency results.

This is the results breakdown of the Congress of Deputies election held in Spain on 9 March 2008. The following tables show detailed results in each of the country's 17 autonomous communities and in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, as well as a summary of constituency results.

Yesca is a Castilian nationalist and anticapitalist youth organization in Castile. It's recognized by Castilian Left as its youth referent. Yesca defends the right of self-determination of Castile, a nation that would be integrated by the current Spanish autonomies of Castilla y León, Castilla-La Mancha, Madrid, Cantabria, La Rioja and the area of Requena-Utiel in the Valencian Country.

This is the results breakdown of the Congress of Deputies election held in Spain on 22 June 1986. The following tables show detailed results in each of the country's 17 autonomous communities and in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, as well as a summary of constituency results.

This is the results breakdown of the Congress of Deputies election held in Spain on 6 June 1993. The following tables show detailed results in each of the country's 17 autonomous communities and in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, as well as a summary of constituency results.

This is the results breakdown of the Congress of Deputies election held in Spain on 12 March 2000. The following tables show detailed results in each of the country's 17 autonomous communities and in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, as well as a summary of constituency results.
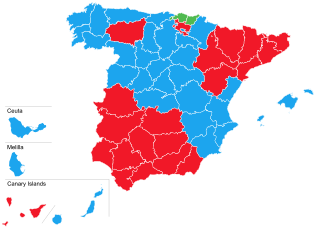
This is the results breakdown of the Congress of Deputies election held in Spain on 14 March 2004. The following tables show detailed results in each of the country's 17 autonomous communities and in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, as well as a summary of constituency results.

This is the results breakdown of the Congress of Deputies election held in Spain on 1 March 1979. The following tables show detailed results in each of the country's 17 autonomous communities and in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, as well as a summary of constituency results.
The Office of the Public Prosecutor was created in the Autonomous communities of Spain by Royal Decree 1754/2007 of December 28.
This is the results breakdown of the local elections held in Castile and León on 22 May 2011. The following tables show detailed results in the autonomous community's most populous municipalities, sorted alphabetically.













