
An ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid in which at least one –OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an –O– alkyl (alkoxy) group, as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils.

gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid or γ-Hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), also known as 4-hydroxybutanoic acid, is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter and a psychoactive drug. It is a precursor to GABA, glutamate, and glycine in certain brain areas. It acts on the GHB receptor and is a weak agonist at the GABAB receptor. GHB has been used in the medical setting as a general anesthetic and as a treatment for cataplexy, narcolepsy, and alcoholism. It is also used illegally as an intoxicant, as an athletic-performance enhancer, as a date-rape drug, and as a recreational drug.

Acetoacetic acid is the organic compound with the formula CH3COCH2COOH. It is the simplest beta-keto acid, and like other members of this class, it is unstable. The methyl and ethyl esters, which are quite stable, are produced on a large scale industrially as precursors to dyes. Acetoacetic acid is a weak acid.

A Morpholino, also known as a Morpholino oligomer and as a phosphorodiamidate Morpholino oligomer (PMO), is a type of oligomer molecule used in molecular biology to modify gene expression. Its molecular structure contains DNA bases attached to a backbone of methylenemorpholine rings linked through phosphorodiamidate groups. Morpholinos block access of other molecules to small specific sequences of the base-pairing surfaces of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Morpholinos are used as research tools for reverse genetics by knocking down gene function.
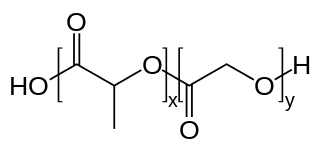
PLGA, PLG, or poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) is a copolymer which is used in a host of Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved therapeutic devices, owing to its biodegradability and biocompatibility. PLGA is synthesized by means of ring-opening co-polymerization of two different monomers, the cyclic dimers (1,4-dioxane-2,5-diones) of glycolic acid and lactic acid. Polymers can be synthesized as either random or block copolymers thereby imparting additional polymer properties. Common catalysts used in the preparation of this polymer include tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate, tin(II) alkoxides, or aluminum isopropoxide. During polymerization, successive monomeric units are linked together in PLGA by ester linkages, thus yielding a linear, aliphatic polyester as a product.
Capric acid, also known as decanoic acid or decylic acid, is a saturated fatty acid. Its formula is CH3(CH2)8COOH. Salts and esters of decanoic acid are called caprates or decanoates. The term capric acid is derived from the Latin "caper / capra" (goat) because the sweaty, unpleasant smell of the compound is reminiscent of goats.
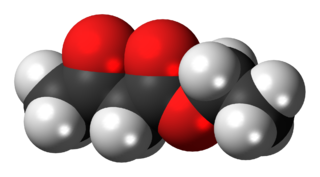
The organic compound ethyl acetoacetate (EAA) is the ethyl ester of acetoacetic acid. It is a colorless liquid. It is widely used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a wide variety of compounds. It is used as a flavoring for food.

β-Hydroxybutyric acid, also known as 3-hydroxybutyric acid, is an organic compound and a beta hydroxy acid with the chemical formula CH3CH(OH)CH2CO2H; its conjugate base is β-hydroxybutyrate, also known as 3-hydroxybutyrate. β-Hydroxybutyric acid is a chiral compound with two enantiomers: D-β-hydroxybutyric acid and L-β-hydroxybutyric acid. Its oxidized and polymeric derivatives occur widely in nature. In humans, D-β-hydroxybutyric acid is one of two primary endogenous agonists of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 (HCA2), a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR).

Polyphosphazenes include a wide range of hybrid inorganic-organic polymers with a number of different skeletal architectures with the backbone P-N-P-N-P-N-. In nearly all of these materials two organic side groups are attached to each phosphorus center. Linear polymers have the formula (N=PR1R2)n, where R1 and R2 are organic (see graphic). Other architectures are cyclolinear and cyclomatrix polymers in which small phosphazene rings are connected together by organic chain units. Other architectures are available, such as block copolymer, star, dendritic, or comb-type structures. More than 700 different polyphosphazenes are known, with different side groups (R) and different molecular architectures. Many of these polymers were first synthesized and studied in the research group of Harry R. Allcock.
Carbamic acid, which might also be called aminoformic acid or aminocarboxylic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula H2NCOOH. It can be obtained by the reaction of ammonia NH3 and carbon dioxide CO2 at very low temperatures, which also yields an equal amount of ammonium carbamate. The compound is stable only up to about 250 K (−23 °C); at higher temperatures it decomposes into those two gases. The solid apparently consists of dimers, with the two molecules connected by hydrogen bonds between the two carboxyl groups –COOH.
In enzymology, 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a hydroxybutyrate-dimer hydrolase (EC 3.1.1.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase is an enzyme used in the degradation processes of a natural polyester Poly(3-hydroxyburate). This enzyme has growing commercialization interests due to it implications in biodegradable plastic decomposition.

Aflatoxin B1 aldehyde reductase member 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR7A2 gene.

D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BDH1 gene.

The γ-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) receptor (GHBR), originally identified as GPR172A, is an excitatory G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds the neurotransmitter and psychoactive drug γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). As solute carrier family 52 member 2 (SLC52A2), it is also a transporter for riboflavin.

Sultopride (trade names Barnetil, Barnotil, Topral) is an atypical antipsychotic of the benzamide chemical class used in Europe, Japan, and Hong Kong for the treatment of schizophrenia. It was launched by Sanofi-Aventis in 1976. Sultopride acts as a selective D2 and D3 receptor antagonist. It has also been shown to have clinically relevant affinity for the GHB receptor as well, a property it shares in common with amisulpride and sulpiride.

CGP-35348 is a compound used in scientific research which acts as an antagonist at GABAB receptors.
Exogenous ketones are a class of ketone bodies that are ingested using nutritional supplements. This class of ketone bodies refers to the three water-soluble ketones. These ketone bodies are produced by interactions between macronutrient availability such as low glucose and high free fatty acids or hormone signaling such as low insulin and high glucagon/cortisol. Under physiological conditions, ketone concentrations can increase due to starvation, ketogenic diets, or prolonged exercise, leading to ketosis. However, with the introduction of exogenous ketone supplements, it is possible to provide a user with an instant supply of ketones even if the body is not within a state of ketosis before ingestion.

β-Butyrolactone is the intramolecular carboxylic acid ester (lactone) of the optically active 3-hydroxybutanoic acid. It is produced during chemical synthesis as a racemate. β-Butyrolactone is suitable as a monomer for the production of the biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoate poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB). Polymerisation of racemic (RS)-β-butyrolactone provides (RS)-polyhydroxybutyric acid, which, however, is inferior in essential properties to the (R)-poly-3-hydroxybutyrate originating from natural sources.













