Related Research Articles
The Movement for the Survival of the Ogoni People (MOSOP), is a social movement organization representing the indigenous Ogoni people of Rivers State, Nigeria. The Ogoni contend that Shell Petroleum Development Company (SPDC), along with other petroleum multinationals and the Nigerian government, have destroyed their environment, polluted their rivers, and provided no benefits in return for enormous oil revenues extracted from their lands.
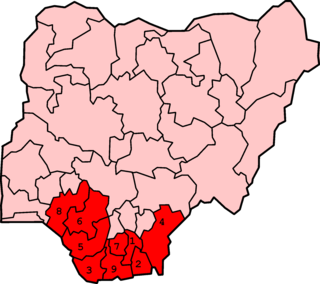
The Niger Delta is the delta of the Niger River sitting directly on the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean in Nigeria. It is located within nine coastal southern Nigerian states, which include: all six states from the South South geopolitical zone, one state (Ondo) from South West geopolitical zone and two states from South East geopolitical zone.

The Nun River, also known as Rio Nun, is a river in Bayelsa State, Nigeria. The river is formed when the Niger River splits into two at Toru-Abubou, near Agbere Town in Sagbama Local Government Area of Bayelsa State, forming the Nun and the Forcados rivers.

Bonny is a traditional, coastal town and a Local Government Area in Rivers State in southern Nigeria, on the Bight of Bonny. It is also the capital of the Kingdom of Bonny

Bonny Light oil was found at Oloibiri in the Niger delta region of Nigeria in 1956 for its commercial use. Due to its features of generating high profit, it is highly demanded by refiners. Bonny light oil has an API of 32.9, classified as light oil. It is regarded as more valuable than the other oils with lower API as more high-value products are produced in the refinement. However, in Nigeria, problems due to oil spillage caused by vandalism, affects both human and the ecosystem in detrimental ways. Some experiments on animals and soil are done to figure out those impacts on organisms.

Nigeria is the second largest oil and gas producer in Africa. Crude oil from the Niger Delta basin comes in two types: light, and comparatively heavy – the lighter has around 36 of API gravity while the heavier has 20–25 of API gravity. Both types are paraffinic and low in sulphur. Nigeria's economy and budget have been largely supported from income and revenues generated from the petroleum industry since 1960. Statistics as at February 2021 shows that the Nigerian oil sector contributes to about 9% of the entire GDP of the nation. Nigeria is a major exporter of crude oil and petroleum products to the United States of America. In 2010, Nigeria exported over one million barrels per day to the United States, representing 9% of the U.S. total crude oil and petroleum products imports and over 40% of Nigeria exports.

Shell Nigeria is the common name for Shell plc's Nigerian operations carried out through four subsidiaries—primarily Shell Petroleum Development Company of Nigeria Limited (SPDC). Royal Dutch Shell's joint ventures account for more than 21% of Nigeria's total petroleum production.

The current conflict in the Niger Delta first arose in the early 1990s over tensions between foreign oil corporations and a number of the Niger Delta's minority ethnic groups who feel they are being exploited, particularly the Ogoni and the Ijaw. Ethnic and political unrest continued throughout the 1990s despite the return to democracy and the election of the Obasanjo government in 1999. Struggle for oil wealth and environmental harm over its impacts has fueled violence between ethnic groups, causing the militarization of nearly the entire region by ethnic militia groups, Nigerian military and police forces, notably the Nigerian Mobile Police. The violence has contributed to Nigeria's ongoing energy supply crisis by discouraging foreign investment in new power generation plants in the region.
Environmental issues in the Niger Delta are caused by its petroleum industry. The delta covers 20,000 km2 (7,700 sq mi) within wetlands of 70,000 km2 (27,000 sq mi) formed primarily by sediment deposition. Home to 20 million people and 40 different ethnic groups, this floodplain makes up 7.5% of Nigeria's total land mass. It is the largest wetland and maintains the third-largest drainage basin in Africa. The Delta's environment can be broken down into four ecological zones: coastal barrier islands, mangrove swamp forests, freshwater swamps, and lowland rainforests. Fishing and farming are the main sources of livelihoods for majority of her residents.
The Bonga Field is an oilfield in Nigeria. It was located in License block OPL 212 off the Nigerian coast, which was renamed OML 118 in February 2000. The field covers approximately 60 km2 in an average water depth of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). The field was discovered in 1996, with government approval for its development given in 2002. The field began first production in November 2005. The field is worked via an FPSO vessel. The field produces both petroleum and natural gas; the petroleum is offloaded to tankers while the gas is piped back to Nigeria where it is exported via an LNG plant. The field contains approximately 6,000 mm barrels of oil.

Sweet Crude is a documentary film about Nigeria's oil-rich Niger Delta directed by Sandy Cioffi. The film premiered in April 2009 at the Full Frame Documentary Film Festival and has since screened at 30 film festivals around the world and has won numerous awards.
The Warri Crisis was a series of conflicts in Delta State, Nigeria between 1997 and 2003 between the Itsekiri, the Ijaw, and the Urhobo ethnic groups. Over 200,000 people were displaced by the Warri conflict between 1999 and 2006. Over 700,000 people were displaced during this period by violence in Delta State overall.
The Engenni people live in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria. They are considered to be Edoid based on linguistic grounds. They live in close proximity with Ijaw people. They primarily live in Ahoada west local government area of Rivers state, Nigeria. Although they consider themselves to be Engenni, the Engenni speak an Edoid language. Alagoa (2003) said: “---The penetration of the Niger-Delta by Edoid groups extends to the Epie-Atissa and Engenni of the central and Eastern Niger-Delta----The Epie, along with the Ogbia and other groups of the central and eastern Niger-Delta, are historically united with the Ijaw.” The other groups of the central and eastern Niger-Delta which Professor Ebiegberi Alagoa said that were historically united with the Ijaw, include the Engenni, as shown from his narrative above. The Engenni have close relations with neighbouring Ijaw tribes such as the Zarama and Epie-Atissa.
Oloibiri Oilfield is an onshore oilfield located in Oloibiri in Ogbia LGA of Bayelsa State, Nigeria, and was the first to be discovered in that country. It is located about 45 miles (72 km) east of Port Harcourt in the Niger Delta. Oloibiri field is about 13.75 square kilometres (5.31 sq mi) and lies in a swamp within OML 29

In 2018, Nigeria's primary energy consumption was about 155 Mtoe. Most of the energy comes from traditional biomass and waste, which accounted for 73.5% of total primary consumption in 2018. The rest is from fossil fuels (26.4%) and hydropower.
On May 1, 2010, a ruptured ExxonMobil pipeline in the state of Akwa Ibom, Nigeria, spilled more than a million gallons into the delta and contributed to the major environmental issues in the Niger Delta. The spill had occurred at an Exxon platform some 20–25 miles (32–40 km) offshore which feeds the Qua Iboe oil export terminal. Exxon Mobil declared force majeure on Qua Iboe oil shipments due to the pipeline damage. The leakage in the Qua Iboe oil field discharged about 232 barrels of crude into the Atlantic Ocean contaminating the waters and coastal settlements in the predominantly fishing communities along Akwa Ibom and Cross River.

OML 29 is also known as Oil Mining Licence 29. Oil Mining Licence OML is one of the two types of licences issued to oil producers in Nigeria "with validity periods ranging from 5 to 20 years respectively." OML29 is a large block located in the southeastern Niger Delta containing 11 oil and gas fields. OML29 stretches over an area of 983 square kilometres. It includes the Nembe Oil Field, Santa Barbara Oil Field and Okoroba Oil Fields. It also include related facilities like the Nembe Creek Trunk Line NCTL. A 100 kilometres long pipeline with a capacity of 600 thousand barrels per day.
The Niger Delta Avengers (NDA) is a militant group in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria. The group publicly announced their existence in March 2016.

Oloibiri is a 2016 Nigerian action thriller film directed by Curtis Graham, produced by Rogers Ofime and starring Olu Jacobs and Richard Mofe Damijo. The film tells a story on how government agencies, along with oil companies exploited the newly discovered oil in the historic town of Oloibiri. The film had its premier on 21 October 2016 at the Shell Nigeria hall, Muson center, Onikan. Former head of state, General Yakubu Gowon, former Secretary general, Commonwealth, Emeka Anyaoku were present at the event. Speaking to Channels TV after watching the film, former Minister for Information, Professor Jerry Gana described the film as having a "clear and powerful message" on the sufferings of people in the Niger Delta. He also encouraged other filmmakers to make more of such films. Richard Mofe Damijo, who played the role of a disgruntled indigene, who became a militant, "Gunpowder" in the oil rich town described his role as a "modern day Robinhood". He also stated that he hopes government and international organizations will come to the aid of people in Niger Delta.

Chevron Nigeria Limited is a subsidiary of Chevron Corporation and it is one of the largest oil producers in Nigeria. It was previously operating in Nigeria under the business name of Gulf Oil Company until merger activities changed its name to Chevron Nigeria. After another merger by the parent company with Texaco, the Nigerian oil and gas assets of Texaco Overseas Petroleum Company of Nigeria were merged into Chevron.
References
- ↑ Dr Raji, Yusuf (2013). "SHELL D ARCY EXPLORATION & THE DISCOVERY OF OIL" (PDF). Business and Management Review. 2.
- 60 Years After Nigeria's Crude. Vanguard Nigeria. Retrieved on October 10, 2016.
- Oloibiri: Where It All Began. Leadership Newspaper. Retrieved on October 10, 2016.