
Onondaga County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 476,516. The county seat is Syracuse. The county is part of the Central New York region of the state.
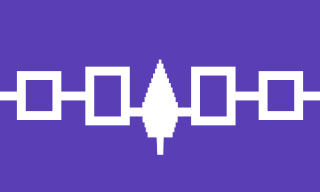
Among the Haudenosaunee the Great Law of Peace, also known as Gayanashagowa, is the oral constitution of the Iroquois Confederacy. The law was written on wampum belts, conceived by Dekanawidah, known as the Great Peacemaker, and his spokesman Hiawatha. The original five member nations ratified this constitution near modern-day Victor, New York, with the sixth nation being added in 1722.

The County of Brant is a single-tier municipality in the Canadian province of Ontario. Although it retains the word "county" in its name, the municipality is a single-tier municipal government and has no upper tier. The County of Brant has service offices in Burford, Paris, Oakland, Onondaga and St. George. The largest population centre is Paris.
Onondaga is an unincorporated community in the U.S. state of Michigan. The community is located within Onondaga Township in Ingham County. As an unincorporated community, Onondaga has no legally defined boundaries or population statistics of its own but does have its own post office with the 49264 ZIP Code. The Onondaga 49264 ZIP Code serves the majority of the township, as well as smaller areas in Hamlin Township to the west and Tompkins Township to the south.

The Onondaga people are one of the five original nations of the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) Confederacy in the Northeastern Woodlands. Their historical homelands are in and around present-day Onondaga County, New York, south of Lake Ontario.

Six Nations is demographically the largest First Nations reserve in Canada. As of the end of 2017, it has a total of 27,276 members, 12,848 of whom live on the reserve. These nations are the Mohawk, Cayuga, Onondaga, Oneida, Seneca and Tuscarora. Some Lenape live in the territory as well.
Six Nations may refer to:
First Nations in Ontario constitute many nations. Common First Nations ethnicities in the province include the Anishinaabe, Haudenosaunee, and the Cree. In southern portions of this province, there are reserves of the Mohawk, Cayuga, Onondaga, Oneida, Seneca and Tuscarora.
The Great Peacemaker, sometimes referred to as Deganawida or Tekanawí:ta was by tradition, along with Jigonhsasee and Hiawatha, the founder of the Haudenosaunee, commonly called the Iroquois Confederacy. This is a political and cultural union of six Iroquoian-speaking Native American tribes governing parts of the present-day state of New York, northern Pennsylvania, and the eastern portion of the provinces of Ontario, and Quebec Canada, recognized as sovereign by both the USA and Canada.
Ohsweken is a dispersed rural community located within the Six Nations of the Grand River, in the County of Brant, Ontario, Canada. Approximately 300 of the 2,700 homes on the reserve are in Ohsweken, and it is the site of the reserve governmental and administrative offices.

The Six Nations Rebels are a Canadian Junior "B" box lacrosse team from Hagersville, Ontario on the Six Nations of the Grand River Reserve. The Rebels play in the OLA Junior B Lacrosse League. The Rebels hold the record for most Junior B national championships in Founders Cup history with seven.

The Iroquois, also known as the Five Nations, and later as the Six Nations from 1722 onwards; alternatively referred to by the endonym Haudenosaunee are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of Native Americans and First Nations peoples in northeast North America. They were known by the French during the colonial years as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy, while the English simply called them the "Five Nations". The peoples of the Iroquois included the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca. After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, from which point it was known as the "Six Nations".

Six Nations Polytechnic (SNP) is a Haudenosaunee-governed Indigenous institute on Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation. SNP is an Indigenous Institute, the third pillar of post-secondary education in Ontario, as recognized by the Indigenous Institutes Act of 2017, The Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation are the Mohawk, Cayuga, Onondaga, Oneida, Seneca, and Tuscarora. The Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation reserve acreage at present covers some 46,000 acres (190 km2) near the city of Brantford, Ontario. Six Nations Polytechnic has two campuses, one located in Ohsweken and one located in Brantford.
Bearfoot Onondaga First Nation is an Onondaga First Nation in southern Ontario. It is a member of the Six Nations of the Grand River. Its reserves include the shared Glebe Farm 40B reserve in Brantford.
Glebe Farm 40B is a shared First Nations reserve within the city of Brantford. It is shared between the Bay of Quinte Mohawks, Bearfoot Onondaga, Delaware, Konadaha Seneca, Lower Cayuga, Lower Mohawk, Niharondasa Seneca, Oneida, Onondaga Clear Sky, Tuscarora, Upper Cayuga, Upper Mohawk & Walker Mohawk First Nations.

John Arthur Gibson (1850–1912) was a chief of the Seneca nation of the North American Iroquois confederation. Part Onondaga and part Seneca, he resided within the reserve of the Six Nations of the Grand River in Ontario, Canada. Knowledgeable about Iroquois (Haudosaunee) culture, he is best known for the versions he provided of the Iroquois oral constitution, the Great Law of Peace. He acted as an advisor to the Canadian Department of Indian Affairs in matters relating both to Iroquois and non-Iroquois indigenous people. He was a well-respected player of the traditional Iroquois sport of lacrosse until he was blinded during a game when he was 31.
Simeon Gibson was a member of the Cayuga tribe and the Onondaga Longhouse on the Six Nations Reserve. Gibson (Iroquois) worked closely with Iroquois researchers, including Horatio Hale, David Boyle, Mark Raymond Harrington, A.C. Parker, and John Napoleon Brinton (J.N.B.) Hewitt. Gibson worked with these researchers to interpret his father Chief Gibson’s two records of the Daganawi:dah legend.

John Buck, titled Skanawati among other variants, was a leader of the Onondaga who lived near Ontario's Grand River. He was the official keeper of the wampum records of the Iroquois, sometimes described as a firekeeper. He took on the role of wampum keeper in 1843. Buck was described in a contemporary account as "a capable ruler and an able and trustworthy negotiator". Kenyon and Kenyon identify him as a "follower of Handsome Lake".
Seth Newhouse was a leader of the Iroquois confederacy. He advocated for their self-government in the Grand River region of Ontario and worked to record and preserve traditions of the people. In 1885 he arranged a manuscript version of the Great Law of Peace, which has been analyzed since, particularly for its faithfulness to the original.








