The Ontario West Shore Railway is a historic railway that operated in Ontario, Canada.
The company started construction on a railway line between Goderich and Kincardine in the early 1900s, but the line was never completed. The company's president was J. W. Moyes of Toronto, Ontario. [1] Moyes was neither wealthy nor a railroad man.
In 1902, Moyes incorporated the Huron, Bruce and Grey Electric Railway and proceeded to lobby local municipalities for capital. [2] He asked the town of Goderich for $50,000, the township of Ashfield for $50,000 and $25,000 each from Colbourne and West Wawanosh townships. [3]
The initial scheme was to build a railroad from Goderich to Dunlop. From Dunlop, the line was to split with one branch to Amberley and another to Dungannon. A third branch would be built from Saltford to Blyth. Freight and daily passenger service would operate on all lines. [4] [5]
Each municipality held a vote on the scheme. Goderich approved the $50,000 investment, [6] but the townships rejected the plan. [7] [8]
In 1906, after the company was renamed the Ontario West Shore Railway, the municipalities provided funding for a single line extending from Goderich to Kincardine. Goderich commits $150,000, Kincardine $50,000, and the townships commit money as well. [1]
In 1908, work on the track is started in Port Albert. [9] By the end of summer 1911, the railroad was completed from Goderich to Kintail. [10] At that point, one car of freight per day, mostly grain, was being loaded along the track. [11]
In January, 1912, the company defaulted on their bonds to the municipalities. [12] The line was never completed.
The Pennsylvania Railroad was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was so named because it was established in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania.

Wingham is a community located in the municipality of North Huron, Ontario, Canada, which is located in Huron County. Wingham became part of North Huron in 2001 when the Ontario government imposed amalgamation on the former township of East Wawanosh, the village of Blyth, and the town of Wingham.

The Canadian Northern Railway (CNoR) was a historic Canadian transcontinental railway. At its 1923 merger into the Canadian National Railway, the CNoR owned a main line between Quebec City and Vancouver via Ottawa, Winnipeg, and Edmonton.

The Philadelphia and Western Railroad was a high-speed, third rail-equipped, commuter-hauling interurban electric railroad operating in the western suburbs of the U.S. city of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. One of its lines is now SEPTA's Norristown High Speed Line; the other has been abandoned. Part of the abandoned line within Radnor Township is now the Radnor Trail, a multi-use path or rail trail.
Goderich is a town in the Canadian province of Ontario and is the county seat of Huron County. The town was founded by John Galt and William "Tiger" Dunlop of the Canada Company in 1827. First laid out in 1828, the town is named after Frederick John Robinson, 1st Viscount Goderich, who was prime minister of the United Kingdom at the time. It was incorporated as a town in 1850.

The Goderich–Exeter Railway is a short line freight railway that operates around 70 miles (110 km) of track in Southwestern Ontario, Canada. Created in 1992, it was the first short line railway in Canada to be purchased from a class I railway, in this case Canadian National Railway (CN). It took over operation of further CN trackage in 1998. As of 2004, the railway had 44 employees. Its headquarters are in Stratford, Ontario, and owned by short-line railroad holding company Genesee & Wyoming.
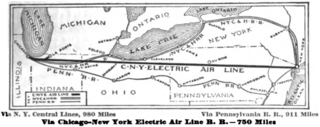
The Chicago – New York Electric Air Line Railroad (CNY) was a proposed high-speed electric air-line railroad between Chicago and New York City. At roughly 750 miles (1,210 km) it would have been over 150 miles (240 km) shorter than the two primary steam railroads on that route, the New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad. The promoters' vision proved wildly optimistic and, in the end, only a short interurban route in the vicinity of Gary, Indiana was built and operated. It was the most ambitious of several such proposals at the dawn of electric railroading, all of which ended in failure.

The Norfolk Southern Railway was the final name of a railroad that ran from Norfolk, Virginia, southwest and west to Charlotte, North Carolina. It was acquired by the Southern Railway in 1974, which merged with the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1982 to form the current Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Argentine Central Railway was a 3 ft narrow gauge railroad in the United States built from the Colorado and Southern Railway at Silver Plume, Colorado, to Waldorf, Colorado, and onward to the summit of Mount McClellan. Construction began on August 1, 1905, and the line was opened to Waldorf a year later on August 1, 1906, a distance of about 6 miles. It was financed and organised by Edward J. Wilcox, owner of 65 mining properties in the Argentine region that were consolidated into the Waldorf Mining and Milling Company in 1902. His headquarters at Waldorf was accessible only by pack mule for much of the year.
King's Highway 21, commonly referred to as Highway 21, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario that begins at Highway 402 midway between Sarnia and London and ends at Highway 6, Highway 10 and Highway 26 in Owen Sound. The roadway is referred to as the Bluewater Highway because it remains very close to the eastern shoreline of Lake Huron.
The Guelph Junction Railway is a shortline railway owned by the City of Guelph, Ontario, and serves the city's northwest industrial park.
The London and Lake Erie Railway and Transportation Company is a defunct Interurban railway that operated in Ontario, Canada from 1902 to 1918. Originally chartered as the South Western Traction Company, the line was renamed the London and Lake Erie Railway in 1909. Throughout its short life, the line was always referred to locally as "The Traction Line".
The Algoma Eastern Railway was a railway in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. Originally known as the Manitoulin and North Shore Railway (M&NS) with a charter dating back to 1888, the full mainline was opened to traffic in 1913, serving the area along the north shore of Lake Huron between Sudbury and Little Current on Manitoulin Island. It and its sister railway, the Algoma Central, were originally owned by the Lake Superior Corporation, a conglomerate centred on Sault Ste. Marie which was founded by the American industrialist Francis Clergue. Despite ambitious plans to expand across Lake Huron to the Bruce Peninsula using a railcar ferry, the company failed to develop further and was acquired by the Canadian Pacific Railway in 1930. With freight traffic low during the Great Depression, Canadian Pacific soon abandoned much of the Algoma Eastern mainline in favour of its own Algoma Branch. Remaining sections of the Algoma Eastern line were turned into spurs, with the longest surviving section operated as a branch line known as the Little Current Subdivision.

Kincardine is a community and former town, located in the municipality of Kincardine on the shores of Lake Huron in Bruce County in the province of Ontario, Canada. The namesake town is located at the mouth of the Penetangore River, and was founded in 1848 by the name of Penetangore. The current municipality was created in 1999 by the amalgamation of the Town of Kincardine, the Township of Kincardine, and the Township of Bruce. The former town is Ward 1 within the current municipal boundaries.

The Staten Island Railway (SIR) is the only rapid transit line in the New York City borough of Staten Island and is operated by the Staten Island Rapid Transit Operating Authority, a unit of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority. The railway is considered a standard railroad line, but only the western portion of the North Shore Branch, which is disconnected from the rest of the SIR, is used by freight and is connected to the national railway system.
The London, Huron and Bruce Railway (LH&BR) was a short line railway in Ontario, Canada. It started in London, Ontario, running northward for 70 miles (110 km) to the small town of Wingham. It originally planned to continue north to Southampton or Kincardine, but instead joined the Wellington, Grey and Bruce Railway (WG&BR) at Wingham. The route was primarily used for farm shipments, and was nicknamed the "Butter and Egg Special", while passengers complaining about the rough ride constructed the backronym "Let 'er Hit and Bounce".
The Chicago Lake Shore and South Bend Railway is the earliest predecessor of the Chicago South Shore and South Bend Railroad formed in 1901.
The Wellington, Grey and Bruce Railway (WG&BR) is a historical railway in Ontario, Canada. It ran roughly northwest from Guelph to the port town Southampton on Lake Huron, a distance of 101 miles (163 km). It also had a 66 miles (106 km) long branch splitting off at Palmerston and running roughly westward to Kincardine, another port town. A branch running south from Southampton was built during the construction of the Bruce Nuclear Generating Station in the 1970s.

The Lake Erie and Northern Railway was an interurban electric railway which operated in the Grand River Valley in Ontario, Canada. The railway owned and operated a north–south mainline which ran from Galt in the north to Port Dover on the shore of Lake Erie in the south. Along the way, it ran through rural areas of Waterloo County, Brant County, and Norfolk County, as well as the city of Brantford, where it had an interchange with the Brantford and Hamilton Electric Railway. Construction on the mainline began in 1913. The railway began operations in 1916 as a subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), which had purchased the line before construction had finished. In 1931, it was consolidated with the Grand River Railway under a single CPR subsidiary, the Canadian Pacific Electric Lines (CPEL), which managed both interurban railways, though they continued to exist as legally separate entities. Passenger service was discontinued in 1955 but electric freight operations continued until 1961, when the LE&N's electric locomotives were replaced by diesel CPR locomotives and the line was de-electrified. In the same year, service on the mainline from Simcoe to Port Dover was discontinued, but the remainder continued to operate as a branchline which as early as 1975 was known as the CP Simcoe Subdivision. The remainder of the line was officially abandoned in the early 1990s, ending almost seventy-five years of operation.