In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, and most commonly, digital logic circuits.
A web service (WS) is either:
Flexible Image Transport System (FITS) is an open standard defining a digital file format useful for storage, transmission and processing of data: formatted as multi-dimensional arrays, or tables. FITS is the most commonly used digital file format in astronomy. The FITS standard was designed specifically for astronomical data, and includes provisions such as describing photometric and spatial calibration information, together with image origin metadata.

Hierarchical Data Format (HDF) is a set of file formats designed to store and organize large amounts of data. Originally developed at the U.S. National Center for Supercomputing Applications, it is supported by The HDF Group, a non-profit corporation whose mission is to ensure continued development of HDF5 technologies and the continued accessibility of data stored in HDF.
OPeNDAP is an acronym for "Open-source Project for a Network Data Access Protocol," an endeavor focused on enhancing the retrieval of remote, structured data through a Web-based architecture and a discipline-neutral Data Access Protocol (DAP). Widely used, especially in Earth science, the protocol is layered on HTTP, and its current specification is DAP4, though the previous DAP2 version remains broadly used. Developed and advanced by the non-profit OPeNDAP, Inc., DAP is intended to enable remote, selective data-retrieval as an easily invoked Web service. OPeNDAP, Inc. also develops and maintains zero-cost (reference) implementations of the DAP protocol in both server-side and client-side software.
COLLADA is an interchange file format for interactive 3D applications. It is managed by the nonprofit technology consortium, the Khronos Group, and has been adopted by ISO as a publicly available specification, ISO/PAS 17506.
A GIS software program is a computer program to support the use of a geographic information system, providing the ability to create, store, manage, query, analyze, and visualize geographic data, that is, data representing phenomena for which location is important. The GIS software industry encompasses a broad range of commercial and open-source products that provide some or all of these capabilities within various information technology architectures.
GRIB is a concise data format commonly used in meteorology to store historical and forecast weather data. It is standardized by the World Meteorological Organization's Commission for Basic Systems, known under number GRIB FM 92-IX, described in WMO Manual on Codes No.306. Currently there are three versions of GRIB. Version 0 was used to a limited extent by projects such as TOGA, and is no longer in operational use. The first edition is used operationally worldwide by most meteorological centers, for Numerical Weather Prediction output (NWP). A newer generation has been introduced, known as GRIB second edition, and data is slowly changing over to this format. Some of the second-generation GRIB is used for derived products distributed in the Eumetcast of Meteosat Second Generation. Another example is the NAM model.
JT is an openly-published ISO-standardized 3D CAD data exchange format used for product visualization, collaboration, digital mockups, and other purposes. It was developed by Siemens.

Tecplot is the name of a family of visualization & analysis software tools developed by American company Tecplot, Inc., which is headquartered in Bellevue, Washington. The firm was formerly operated as Amtec Engineering. In 2016, the firm was acquired by Vela Software, an operating group of Constellation Software, Inc. (TSX:CSU).
PLY is a computer file format known as the Polygon File Format or the Stanford Triangle Format. It was principally designed to store three-dimensional data from 3D scanners. The data storage format supports a relatively simple description of a single object as a list of nominally flat polygons. A variety of properties can be stored, including color and transparency, surface normals, texture coordinates and data confidence values. The format permits one to have different properties for the front and back of a polygon.
Specialized wind energy software applications aid in the development and operation of wind farms.
NetCDF is a set of software libraries and self-describing, machine-independent data formats that support the creation, access, and sharing of array-oriented scientific data. The project homepage is hosted by the Unidata program at the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR). They are also the chief source of netCDF software, standards development, updates, etc. The format is an open standard. NetCDF Classic and 64-bit Offset Format are an international standard of the Open Geospatial Consortium.

OpenDRIVE is an open format specification to describe a road network's logic. Its objective is to standardize the logical road description between different driving simulators.
The Functional Mock-up Interface defines a standardized interface to be used in computer simulations to develop complex cyber-physical systems.

INCA is a measurement, calibration and diagnostic software published by ETAS. With its large installation base in the auto industry, this development software is deployed during all phases of the development of electronic control units (ECUs) and ECU software programs for measuring, calibration, diagnostics and programming.

Google Fusion Tables was a web service provided by Google for data management. Fusion tables was used for gathering, visualising and sharing data tables. Data are stored in multiple tables that Internet users can view and download.
ecu.test is a software tool developed by tracetronic GmbH, based in Dresden, Germany, for test and validation of embedded systems. Since the first release of ecu.test in 2003, the software is used as standard tool in the development of automotive ECUs and increasingly in the development of heavy machinery as well as in factory automation. The development of the software started within a research project on systematic testing of control units and laid the foundation for the spin-off of tracetronic GmbH from TU Dresden. ecu.test aims at the specification, implementation, documentation, execution and assessment of test cases. Owing to various test automation methods, the tool ensures an efficient implementation of all necessary activities for the creation, execution and assessment of test cases.
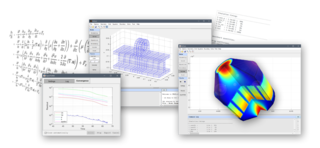
FEATool Multiphysics is a physics, finite element analysis (FEA), and partial differential equation (PDE) simulation toolbox. FEATool Multiphysics features the ability to model fully coupled heat transfer, fluid dynamics, chemical engineering, structural mechanics, fluid-structure interaction (FSI), electromagnetics, as well as user-defined and custom PDE problems in 1D, 2D (axisymmetry), or 3D, all within a graphical user interface (GUI) or optionally as script files. FEATool has been employed and used in academic research, teaching, and industrial engineering simulation contexts.










