Related Research Articles

Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol is an open communication protocol designed for instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Based on XML, it enables the near-real-time exchange of structured data between two or more network entities. Designed to be extensible, the protocol offers a multitude of applications beyond traditional IM in the broader realm of message-oriented middleware, including signalling for VoIP, video, file transfer, gaming and other uses.
Enterprise information integration (EII) is the ability to support a unified view of data and information for an entire organization. In a data virtualization application of EII, a process of information integration, using data abstraction to provide a unified interface for viewing all the data within an organization, and a single set of structures and naming conventions to represent this data; the goal of EII is to get a large set of heterogeneous data sources to appear to a user or system as a single, homogeneous data source.
Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems.

MIFARE is a series of integrated circuit (IC) chips used in contactless smart cards and proximity cards.
Pirate decryption is the decryption, or decoding, of pay TV or pay radio signals without permission from the original broadcaster. The term "pirate" is used in the sense of copyright infringement. The MPAA and other groups which lobby in favour of intellectual property regulations have labelled such decryption as "signal theft" even though there is no direct tangible loss on the part of the original broadcaster, arguing that losing out on a potential chance to profit from a consumer's subscription fees counts as a loss of actual profit.
SmartRider is the contactless electronic ticketing system of the Public Transport Authority of Western Australia. The system uses RFID smartcard technology to process public transport fares across public bus, train, and ferry services.
Kolab is a free and open source groupware suite. It consists of the Kolab server and a wide variety of Kolab clients, including KDE PIM-Suite Kontact, Roundcube web frontend, Mozilla Thunderbird and Mozilla Lightning with SyncKolab extension and Microsoft Outlook with proprietary Kolab-Connector PlugIns.
UNICORE (UNiform Interface to COmputing REsources) is a grid computing technology for resources such as supercomputers or cluster systems and information stored in databases. UNICORE was developed in two projects funded by the German ministry for education and research (BMBF). In European-funded projects UNICORE evolved to a middleware system used at several supercomputer centers. UNICORE served as a basis in other research projects. The UNICORE technology is open source under BSD licence and available at SourceForge.
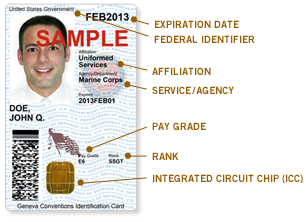
The common access card, also commonly referred to as the CAC, is the standard identification for active duty United States defense personnel. The card itself is a smart card about the size of a credit card. Defense personnel that use the CAC include the Selected Reserve and National Guard, United States Department of Defense (DoD) civilian employees, United States Coast Guard (USCG) civilian employees and eligible DoD and USCG contractor personnel. It is also the principal card used to enable physical access to buildings and controlled spaces, and it provides access to defense computer networks and systems. It also serves as an identification card under the Geneva Conventions. In combination with a personal identification number, a CAC satisfies the requirement for two-factor authentication: something the user knows combined with something the user has. The CAC also satisfies the requirements for digital signature and data encryption technologies: authentication, integrity and non-repudiation.
A card reader is a data input device that reads data from a card-shaped storage medium and provides the data to a computer. Card readers can acquire data from a card via a number of methods, including: optical scanning of printed text or barcodes or holes on punched cards, electrical signals from connections made or interrupted by a card's punched holes or embedded circuitry, or electronic devices that can read plastic cards embedded with either a magnetic strip, computer chip, RFID chip, or another storage medium.
A contactless smart card is a contactless credential whose dimensions are credit card size. Its embedded integrated circuits can store data and communicate with a terminal via NFC. Commonplace uses include transit tickets, bank cards and passports.
Calypso is an international electronic ticketing standard for microprocessor contactless smart cards, originally designed by a group of transit operators from 11 countries including Belgium, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Latvia, México, Portugal and others. It ensures multi-sources of compatible products, and allows for interoperability between several transport operators in the same area.

Palo is a memory resident multidimensional database server and typically used as a business intelligence tool for controlling and budgeting purposes with spreadsheet software acting as the user interface. Beyond the multidimensional data concept, Palo enables multiple users to share one centralised data storage.

NewGenLib is an integrated library management system developed by Verus Solutions Pvt Ltd. Domain expertise is provided by Kesavan Institute of Information and Knowledge Management in Hyderabad, India. NewGenLib version 1.0 was released in March 2005. On 9 January 2008, NewGenLib was declared free and open-source under GNU GPL. The latest version of NewGenLib is 3.1.1 released on 16 April 2015. Many libraries across the globe are using NewGenLib as their Primary integrated library management system as seen from the NewGenlib discussion forum.
CT Connect is a software product that allows computer applications to monitor and control telephone calls. This monitoring and control is called computer-telephone integration, or CTI. CT Connect implements CTI by providing server software that supports the CTI link protocols used by a range of telephone systems, and client software that provides an application programming interface (API) for telephony functions.

The Milan S Lines constitute the commuter rail system serving the metropolitan area of Milan, Italy. The system comprises 12 lines serving 124 stations, for a total length of 403 km. There are 415 trains per day with a daily ridership of about 230,000.

The TFI Leap Card is a contactless smart card for automated fare collection overseen by Transport for Ireland (TFI). It was introduced in the Greater Dublin area in 2011 for Luas, DART, Iarnród Éireann and Dublin Bus, but acceptance has significantly expanded, and it is now accepted in cities nationwide and on some longer distance commuter routes. Initially, Leap Cards offered only a pre-paid electronic wallet system for single-trip fares; since May 2014, it has also been possible to load it with weekly, monthly and annual subscriptions. In September 2017, there were over 2.5 million Leap Card users according to the National Transport Authority. The Leap Card is the result of many years' work by the Railway Procurement Agency and the National Transport Authority as part of the rollout of an integrated ticketing scheme for public transport in Dublin city. Fares are generally discounted compared to cash prices, and integrated ticketing is offered in the Dublin area via a flat fare system across all modes of transport. The minimum top-up for the card is currently €5, and it can be topped up via iPhone/Android App, at LUAS or DART ticketing machines, and in convenience stores offering Payzone services.
The Neveazzurra (Blue-snow) is a winter sports area in the Italian Alps, in Verbanio Cusio Ossola province (Piedmont). 150 kilometers of trails, 50 lifts from 1,000 to 3,000 meters and the opportunity to practice a wide variety of winter sports: alpine skiing, cross country skiing, off-piste skiing, downhill skiing, snow park, ice skating and ice climbing, free -Ride and heli-skiing.

Proxmark3 is a multi-purpose hardware tool for radio-frequency identification (RFID) security analysis, research and development. It supports both high frequency and low frequency proximity cards and allows users to read, emulate, fuzz, and brute force the majority of RFID protocols.
References
- ↑ OpenPass site
- ↑ (in Italian) The methodology OpenPass was formalized in the documents of the “Skipass Lombardia ” project:
- ↑ (in Italian) The Skipass Lombardia project Archived 2014-07-23 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ (in French) The Nordic Pass Rhône Alpes project Archived 2014-04-01 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ (in Italian) The SkiArea VCO project