Peer pressure is a direct or indirect influence on peers, i.e., members of social groups with similar interests, experiences, or social statuses. Members of a peer group are more likely to influence a person's beliefs, values, and behavior. A group or individual may be encouraged and want to follow their peers by changing their attitudes, values or behaviors to conform to those of the influencing group or individual. For the individual affected by peer pressure, this can have both a positive or negative effect on them.

"Just Say No" was an advertising campaign prevalent during the 1980s and early 1990s as a part of the U.S.-led war on drugs, aiming to discourage children from engaging in illegal recreational drug use by offering various ways of saying no. The slogan was created and championed by Nancy Reagan during her husband's presidency.

Drug Abuse Resistance Education, or D.A.R.E., is an education program that tries to prevent use of controlled drugs, membership in gangs, and violent behavior. It was founded in Los Angeles in 1983 as a joint initiative of then-LAPD chief Daryl Gates and the Los Angeles Unified School District as a demand-side drug control strategy of the American War on Drugs.
School violence includes violence between school students as well as attacks by students on school staff. It encompasses physical violence, including student-on-student fighting, corporal punishment; psychological violence such as verbal abuse, and sexual violence, including rape and sexual harassment. It includes many forms of bullying and carrying weapons to school. The one or more perpetrators typically have more physical, social, and/or psychological power than the victim. It is a widely accepted serious societal problem in recent decades in many countries, especially where weapons such as guns or knives are involved.
Alcohol education is the practice of disseminating information about the effects of alcohol on health, as well as society and the family unit. It was introduced into the public schools by temperance organizations such as the Woman's Christian Temperance Union in the late 19th century. Initially, alcohol education focused on how the consumption of alcoholic beverages affected society, as well as the family unit. In the 1930s, this came to also incorporate education pertaining to alcohol's effects on health. For example, even light and moderate alcohol consumption increases cancer risk in individuals. Organizations such as the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism in the United States were founded to promulgate alcohol education alongside those of the temperance movement, such as the American Council on Alcohol Problems.
Drug education is the planned provision of information, guidelines, resources, and skills relevant to living in a world where psychoactive substances are widely available and commonly used for a variety of both medical and non-medical purposes, some of which may lead to harms such as overdose, injury, infectious disease, or addiction.

The American juvenile justice system is the primary system used to handle minors who are convicted of criminal offenses. The system is composed of a federal and many separate state, territorial, and local jurisdictions, with states and the federal government sharing sovereign police power under the common authority of the United States Constitution. The juvenile justice system intervenes in delinquent behavior through police, court, and correctional involvement, with the goal of rehabilitation. Youth and their guardians can face a variety of consequences including probation, community service, youth court, youth incarceration and alternative schooling. The juvenile justice system, similar to the adult system, operates from a belief that intervening early in delinquent behavior will deter adolescents from engaging in criminal behavior as adults.
Phoenix House is a nonprofit drug and alcohol rehabilitation organization operating in ten states with 150 programs. Programs serve individuals, families, and communities affected by substance abuse and dependency.

KELY Support Group is a non-governmental bilingual organisation in Hong Kong which aims to provide support to youth between the ages of 14 and 24. Its programmes and services focus on prevention and intervention of alcoholism and other drug abuse, and are designed to tackle what the group regards as the common reasons for abuse such as boredom, peer pressure, lack of self-awareness, low self-esteem, poverty, unemployment and discrimination.
After-school activities, also known as after-school programs or after-school care, started in the early 1900s mainly just as supervision of students after the final school bell. Today, after-school programs do much more. There is a focus on helping students with school work but can be beneficial to students in other ways. An after-school program, today, will not limit its focus on academics but with a holistic sense of helping the student population. An after-school activity is any organized program that youth or adult learner voluntary can participate in outside of the traditional school day. Some programs are run by a primary or secondary school, while others are run by externally funded non-profit or commercial organizations. After-school youth programs can occur inside a school building or elsewhere in the community, for instance at a community center, church, library, or park. After-school activities are a cornerstone of concerted cultivation, which is a style of parenting that emphasizes children gaining leadership experience and social skills through participating in organized activities. Such children are believed by proponents to be more successful in later life, while others consider too many activities to indicate overparenting. While some research has shown that structured after-school programs can lead to better test scores, improved homework completion, and higher grades, further research has questioned the effectiveness of after-school programs at improving youth outcomes such as externalizing behavior and school attendance. Additionally, certain activities or programs have made strides in closing the achievement gap, or the gap in academic performance between white students and students of color as measured by standardized tests. Though the existence of after-school activities is relatively universal, different countries implement after-school activities differently, causing after-school activities to vary on a global scale.
The Drug Resistance Strategies Project (DRS), a program funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), teaches adolescents and pre-adolescents how to make decisions and resist alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs (ATOD).

Substance abuse prevention, also known as drug abuse prevention, is a process that attempts to prevent the onset of substance use or limit the development of problems associated with using psychoactive substances. Prevention efforts may focus on the individual or their surroundings. A concept that is known as "environmental prevention" focuses on changing community conditions or policies so that the availability of substances is reduced as well as the demand. Individual Substance Abuse Prevention, also known as drug abuse prevention involves numerous different sessions depending on the individual to help cease or reduce the use of substances. The time period to help a specific individual can vary based upon many aspects of an individual. The type of Prevention efforts should be based upon the individual's necessities which can also vary. Substance use prevention efforts typically focus on minors and young adults – especially between 12–35 years of age. Substances typically targeted by preventive efforts include alcohol, tobacco, marijuana, inhalants, coke, methamphetamine, steroids, club drugs, and opioids. Community advocacy against substance use is imperative due to the significant increase in opioid overdoses in the United States alone. It has been estimated that about one hundred and thirty individuals continue to lose their lives daily due to opioid overdoses alone.
Project Graduation is a program offered by many high schools in the United States, in which organized, adult-supervised and alcohol-free activities are offered as part of a post-graduation party, as an alternative to student-run events involving alcoholic beverages or drugs. Events often last through the night and are held in hotels or community centers. Students are checked for illicit substances before entry and are carefully monitored.
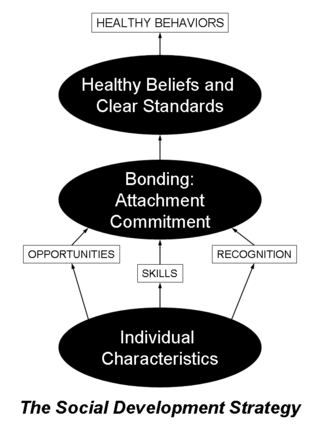
Communities That Care (CTC) is a program of the Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) in the office of the United States Government's Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). CTC is a coalition-based prevention operating system that uses a public health approach to prevent youth problem behaviors such as violence, delinquency, school drop out and substance abuse. Using strategic consultation, training, and research-based tools, CTC is designed to help community stakeholders and decision makers understand and apply information about risk and protective factors, and programs that are proven to make a difference in promoting healthy youth development, in order to most effectively address the specific issues facing their community's youth.

The United States incarcerates more of its youth than any other country in the world through the juvenile courts and the adult criminal justice system, which reflects the larger trends in incarceration practices in the United States. In 2010, approximately 70,800 juveniles were incarcerated in youth detention facilities alone. As of 2006, approximately 500,000 youth were brought to detention centers in a given year. This data does not reflect juveniles tried as adults. As of 2013, around 40% were incarcerated in privatized, for-profit facilities.
Big Brothers Big Sisters of Northern Nevada is a non-profit organization whose vision is "that all children achieve success in life." Their mission is "to provide children facing adversity with strong and enduring, professionally supported 1-to-1 relationships that change their lives for the better, forever."
National Families in Action was a non-profit organization that was founded in Atlanta, Georgia in 1977. Its mission is to help children succeed by empowering parents to create an academic and social environment where children thrive and are protected from substance abuse and other high-risk behaviors. In November 2021, marking 45 years, the organization announced it would cease operations in January 2022.
Students Against Destructive Decisions (SADD), formerly Students Against Driving Drunk, is an organization whose aim is to prevent accidents from students taking potentially destructive decisions.
The elaboration principle is when "non-group" members form relationships with an "in-group" member and later are incorporated into the existing "in-group."
J. David Hawkins is an American sociologist, academic, and author. He is Emeritus Endowed Professor of Prevention and founding director of the Social Development Research Group in the School of Social Work at the University of Washington. His research focuses on the prevention of behavior problems in children and adolescents. He developed the Communities That Care prevention system with Richard F. Catalano.






