Related Research Articles

A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow.

Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation within the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750-420 terahertz, between the infrared and the ultraviolet.
In physics, attenuation or, in some contexts, extinction is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variable attenuation rates.

A tractor-beam is a device with the ability to attract one object to another from a distance. The concept originates in fiction: The term was coined by E. E. Smith in his novel Spacehounds of IPC (1931). Since the 1990s, technology and research has labored to make it a reality, and have had some success on a microscopic level. Less commonly, a similar beam that repels is called a pressor beam or repulsor-beam. Gravity impulse and gravity propulsion beams are traditionally areas of research from fringe physics that coincide with the concepts of tractor and repulsor-beams.

Cathodoluminescence is an optical and electromagnetic phenomenon in which electrons impacting on a luminescent material such as a phosphor, cause the emission of photons which may have wavelengths in the visible spectrum. A familiar example is the generation of light by an electron beam scanning the phosphor-coated inner surface of the screen of a television that uses a cathode ray tube. Cathodoluminescence is the inverse of the photoelectric effect, in which electron emission is induced by irradiation with photons.
Q-switching, sometimes known as giant pulse formation or Q-spoiling, is a technique by which a laser can be made to produce a pulsed output beam. The technique allows the production of light pulses with extremely high (gigawatt) peak power, much higher than would be produced by the same laser if it were operating in a continuous wave mode. Compared to modelocking, another technique for pulse generation with lasers, Q-switching leads to much lower pulse repetition rates, much higher pulse energies, and much longer pulse durations. The two techniques are sometimes applied together.
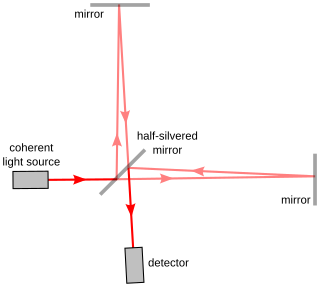
Interferometry is a technique which uses the interference of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy, quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms.
Optical tweezers are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move the microscopic and sub-microscopic objects like atoms, nanoparticles and droplets, in a manner similar to tweezers. If the object is held in air or vacuum without additional support, it can be called optical levitation.

The resolution of an optical imaging system – a microscope, telescope, or camera – can be limited by factors such as imperfections in the lenses or misalignment. However, there is a principal limit to the resolution of any optical system, due to the physics of diffraction. An optical system with resolution performance at the instrument's theoretical limit is said to be diffraction-limited.
The Faraday effect or Faraday rotation, sometimes referred to as the magneto-optic Faraday effect (MOFE), is a physical magneto-optical phenomenon. The Faraday effect causes a polarization rotation which is proportional to the projection of the magnetic field along the direction of the light propagation. Formally, it is a special case of gyroelectromagnetism obtained when the dielectric permittivity tensor is diagonal. This effect occurs in most optically transparent dielectric materials under the influence of magnetic fields.
Brillouin scattering, named after Léon Brillouin, refers to the interaction of light with the material waves in a medium. It is mediated by the refractive index dependence on the material properties of the medium; as described in optics, the index of refraction of a transparent material changes under deformation.

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost due to reflection. In complex systems such as cameras, binoculars, telescopes, and microscopes the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.
Masklesslithography (MPL) is a photomask-less photolithography-like technology used to project or focal-spot write the image pattern onto a chemical resist-coated substrate by means of UV radiation or electron beam.
Holographic data storage is a potential technology in the area of high-capacity data storage. While magnetic and optical data storage devices rely on individual bits being stored as distinct magnetic or optical changes on the surface of the recording medium, holographic data storage records information throughout the volume of the medium and is capable of recording multiple images in the same area utilizing light at different angles.
Phased-array optics is the technology of controlling the phase and amplitude of light waves transmitting, reflecting, or captured (received) by a two-dimensional surface using adjustable surface elements. An optical phased array (OPA) is the optical analog of a radio-wave phased array. By dynamically controlling the optical properties of a surface on a microscopic scale, it is possible to steer the direction of light beams, or the view direction of sensors, without any moving parts. Phased-array beam steering is used for optical switching and multiplexing in optoelectronic devices and for aiming laser beams on a macroscopic scale.
An optical rectenna is a rectenna that works with visible or infrared light. A rectenna is a circuit containing an antenna and a diode, which turns electromagnetic waves into direct current electricity. While rectennas have long been used for radio waves or microwaves, an optical rectenna would operate the same way but with infrared or visible light, turning it into electricity.

Lightpainting is an art form developed by artist Stephen Knapp and introduced in 2002. Lightpainting is not to be confused with light painting, the latter of which is a photographic process recording traces of light on film or digital media to create images that must be reproduced in printed or transparency form. Lightpainting uses white light projected in space through specially coated glass that breaks the light into bands of color, producing optically complex virtual 3D images that sit at the intersection of painting and sculpture. Lightpaintings can take the form of moveable wall-mounted panels but the most spectacular effects are achieved in large-scale architectural installations. Layers of metallic coating are applied to glass pieces to refract and reflect colors, which becomes the palette to be used as pure chroma or mixed into a wide spectrum of colors. Glass is cut into various sizes and shapes that determine planes of color and other elements that can be used much as in traditional painting or sculpture.
Optical lift is an optical analogue of aerodynamic lift, in which a cambered refractive object with differently shaped top and bottom surfaces experiences a stable transverse lift force when placed in a uniform stream of light.
The Optical Stretcher is a dual-beam optical trap that is used for trapping and deforming ("stretching") micrometer-sized soft matter particles, such as biological cells in suspension. The forces used for trapping and deforming objects arise from photon momentum transfer on the surface of the objects, making the Optical Stretcher - unlike atomic force microscopy or micropipette aspiration - a tool for contact-free rheology measurements.
In quantum computing, quantum memory is the quantum-mechanical version of ordinary computer memory. Whereas ordinary memory stores information as binary states, quantum memory stores a quantum state for later retrieval. These states hold useful computational information known as qubits. Unlike the classical memory of everyday computers, the states stored in quantum memory can be in a quantum superposition, giving much more practical flexibility in quantum algorithms than classical information storage.
References
- ↑ Top 100 Stories of 2009 #83: Like Magnets, Light Can Attract and Repel Itself, Discover magazine, from the January–February 2010 special issue; published online December 21, 2009