Optware is a free software package manager for embedded systems. Originally developed as a distribution mechanism for the Unslung Linux distribution for the Linksys NSLU2, Optware has been adopted by a variety of hobbyist communities and device developers. [1] [2]
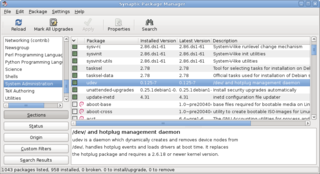
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer's operating system in a consistent manner.

An embedded system is a controller programmed and controlled by a real-time operating system (RTOS) with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system, often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. Embedded systems control many devices in common use today. Ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured are used in embedded systems.
Unslung is an open source firmware for the Linksys NSLU2. It is based on the stock Linksys firmware. Due to the device running Linux, and therefore licensed under, and subject to the terms of the GNU General Public License, Linksys released the source code.
Contents
Optware has been used on a number of platforms, including the webOS community working on the Palm Pre [3] and Pixi, the WL-500g, WL-HDD, WL-500gx, WL-500gP Asus routers, Plug computers (Pogoplug V1, V2, Pro, Biz, Dockstars, etc.), Asustor and Synology NAS devices. In late 2010, the first Optware for Android was released by the Novaports team for the Nook Color.
webOS, also known as LG webOS and previously known as Open webOS,HP webOS and Palm webOS, is a Linux kernel-based multitasking operating system for smart devices such as smart TVs and it has been used as a mobile operating system. Initially developed by Palm, Inc., HP made the platform open source, at which point it became Open webOS. The operating system was later sold to LG Electronics. In January 2014, Qualcomm announced that it had acquired technology patents from HP, which included all the webOS and Palm patents.

The Palm Pre, styled as palm prē, is a multitasking smartphone that was designed and marketed by Palm with a multi-touch screen and a sliding keyboard. The smartphone was the first to use Palm's Linux based mobile operating system, webOS. The Pre functions as a camera phone and a portable media player, and has location and navigation capabilities. The Pre also serves as a personal information manager, has a number of communication and collaboration applications, and has Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity built-in.

A plug computer is an external device, often configured for use in the home or office as a compact computer. It consists of a high-performance, low-power system-on-a-chip processor with several I/O ports and typically runs any of a number of Linux distributions. Most versions do not have provisions for connecting a display and are best suited as for running media server, back-up services, file sharing and remote access functions, thus acting as a bridge between in-home protocols such as Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) and Server Message Block (SMB) and cloud based services. There are, however, plug computer offerings that have analog VGA monitor and/or HDMI connectors, which, along with multiple USB ports, permit the use of a display, keyboard, and mouse, thus making them full-fledged, low-power alternatives to desktop and notebook computers.







