Ordbog over det danske Sprog (Danish : Dictionary of the Danish language) or ODS is a comprehensive dictionary of the Danish language, describing its usage from c. 1700 to 1955 in great detail.
The ODS was published in 28 volumes between 1919 and 1956 by the Society for Danish Language and Literature (Det Danske Sprog- og Litteraturselskab). [1] Five supplementary volumes were published between 1992 and 2005.
The project was begun by Danish linguist Verner Dahlerup. Since 1915, the project was led by linguist Lis Jacobsen.
A digitized version of the ODS has been maintained by the Society for Danish Language and Literature since November 2005. This organization also maintains a sister dictionary Den Danske Ordbog covering Danish language use since 1950. In addition, the society maintains Holbergordbogen, named for the 18th-century playwright Ludvig Holberg, covering language use between 1700 and 1750 and a digital version of Moths Ordbog a Danish-Latin dictionary from around 1700.
Ordbog over det danske Sprog covers approximately 225,000 entries. [2]

Danish is a North Germanic language spoken by about six million people, principally in Denmark, Greenland, the Faroe Islands and in the region of Southern Schleswig in northern Germany, where it has minority language status. Also, minor Danish-speaking communities are found in Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina. Due to immigration from Denmark, about 10% of the population of Greenland speak Danish as their first language.
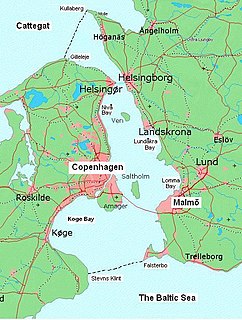
Øresund or Öresund, commonly known in English as the Sound, is a strait which forms the Danish–Swedish border, separating Zealand (Denmark) from Scania (Sweden). The strait has a length of 118 kilometres (73 mi); its width varies from 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) to 28 kilometres (17 mi). It is 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) wide at its narrowest point between Helsingør in Denmark and Helsingborg in Sweden.
ODS may refer to:
Jan Mendoses was a European pirate or merchant who lived during the 17th century. It is possible that Jan Mendoses' real name was Juan [de] Mendoza. There is considerable doubt about his nationality, some sources claiming he was a Belgian named Mandaus, others that he was Spanish. He may even have been a merchant heading for Russia, rather than the "notorious pirate" claimed by Danish sources.

Den Store Danske Encyklopædi is the most comprehensive contemporary Danish language encyclopedia. The 20 volumes of the encyclopedia were published successively between 1994 and 2001; a one-volume supplement was published in 2002 and two index volumes in 2003. The work comprises 115,000 articles, ranging in size from single-line cross references to the 130-page entry on Denmark. The articles were written by a staff of about 4,000 academic experts led by editor-in-chief Jørn Lund. Articles longer than a few dozen lines are signed by their authors. Many articles are illustrated.
Holger Marius Nielsen (1905–1993) was an official of the Danish Ministry of Education.

Dr. Jakob Jakobsen was a Faroese linguist and scholar. The first Faroe Islander to earn a doctoral degree, his thesis on the Norn language of Shetland was a major contribution to its historical preservation.

Félag was a joint financial venture between partners in Viking Age society.

Alf Torp was a Norwegian philologist and author. He is most known for his work with Indo-European and Nordic language history and meaning of ancient languages.

Jens Andreas Friis was a Norwegian philologist, lexicographer and author. He was a university professor and a prominent linguist in the languages spoken by the Sami people. He is widely recognized as the founder of the studies of the Sami languages. Today he is also commonly associated with his novel Lajla: A New Tale of Finmark, which became the basis for Laila, a 1929 silent film.
Hygge is a Danish and Norwegian word for a mood of coziness and comfortable conviviality with feelings of wellness and contentment. As a cultural category with its sets of associated practices hygge has more or less the same meanings in Danish and Norwegian. The emphasis on hygge as a core part of Danish culture is a recent phenomenon, dating to the late 20th century.
The Ranks and insignia of Royal Danish Army follows the NATO system of ranks and insignia, as does the rest of the Danish Defence. The ranks are based around German and French military terms.
Fredrik Otto Lindeman is a Norwegian linguist. He is professor emeritus in historical linguistics at University of Oslo.

Jakob Langebek was a Danish historian, linguist, lexicographer, and archivist.
Insular Danish are the traditional Danish dialects spoken on the islands of Zealand, Langeland, Funen, Falster, Lolland, and Møn. They are recorded in the Dictionary of Danish Insular Danish (Ømålsordbogen) which has been collected since the 1920s, and published in biannual volumes since 1992. There are significant differences between the different insular varieties, but they also share a number of features. A major difference is between Modern Danish and the traditional insular dialects are that some of them lack the stød but kept the tonal accent. Also, they kept three noun genders.

Peder Pedersen Syv or in Latin Petrus Petri Septimius was a Danish philologist, folklorist and priest, known for his collections of Danish proverbs and folksongs, and his contributions to the development of Danish as a written language.
The Etymological Dictionary of the German Language is a reference book for the history of the German language, and was one of the first books of its kind ever written. Originally written in 1883 by Friedrich Kluge, it is still actively maintained and considered a standard work among the German etymological dictionaries. The most recent publication was released in 2011 in print, eBook and as an Android app.
Elisabeth (Lis) Jacobsen, née Rubin, was a Danish philologist, archaeologist and writer. She is remembered first and foremost for her research and publications on the history of the Danish language but she was also an expert runologist who published a comprehensive analysis of all known runic inscriptions in Denmark. From 1911, Jacobsen played a major role in all fields of research related to the Danish language.
Niels Aage Anton Nielsen was a Danish professor of Nordic languages at Aarhus University. He was also a leader in the Danish resistance movement.