Related Research Articles

Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body.
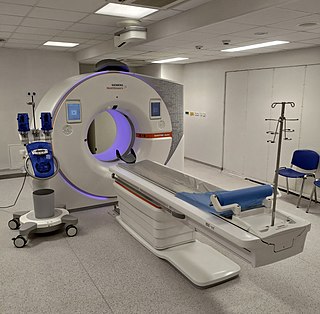
A computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.
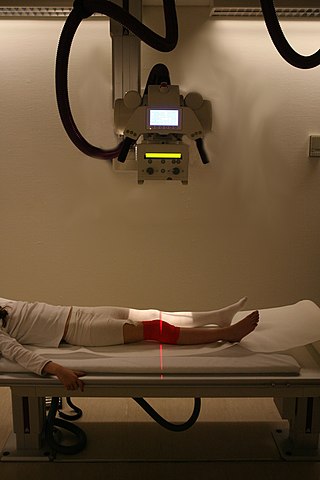
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security,. To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and it is projected towards the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation are absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a detector. The generation of flat two-dimensional images by this technique is called projectional radiography. In computed tomography, an X-ray source and its associated detectors rotate around the subject, which itself moves through the conical X-ray beam produced. Any given point within the subject is crossed from many directions by many different beams at different times. Information regarding the attenuation of these beams is collated and subjected to computation to generate two-dimensional images on three planes which can be further processed to produce a three-dimensional image.
Medical physics deals with the application of the concepts and methods of physics to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of human diseases with a specific goal of improving human health and well-being. Since 2008, medical physics has been included as a health profession according to International Standard Classification of Occupation of the International Labour Organization.

Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.

Single-photon emission computed tomography is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera, but is able to provide true 3D information. This information is typically presented as cross-sectional slices through the patient, but can be freely reformatted or manipulated as required.

Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography, plasma physics, materials science, cosmochemistry, astrophysics, quantum information, and other areas of science. The word tomography is derived from Ancient Greek τόμος tomos, "slice, section" and γράφω graphō, "to write" or, in this context as well, "to describe." A device used in tomography is called a tomograph, while the image produced is a tomogram.

Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann Radon. A notable example of applications is the reconstruction of computed tomography (CT) where cross-sectional images of patients are obtained in non-invasive manner. Recent developments have seen the Radon transform and its inverse used for tasks related to realistic object insertion required for testing and evaluating computed tomography use in airport security.
Iterative reconstruction refers to iterative algorithms used to reconstruct 2D and 3D images in certain imaging techniques. For example, in computed tomography an image must be reconstructed from projections of an object. Here, iterative reconstruction techniques are usually a better, but computationally more expensive alternative to the common filtered back projection (FBP) method, which directly calculates the image in a single reconstruction step. In recent research works, scientists have shown that extremely fast computations and massive parallelism is possible for iterative reconstruction, which makes iterative reconstruction practical for commercialization.

Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Increasingly it is also being used for quantitative research studies of brain disease and psychiatric illness. Neuroimaging is highly multidisciplinary involving neuroscience, computer science, psychology and statistics, and is not a medical specialty. Neuroimaging is sometimes confused with neuroradiology.
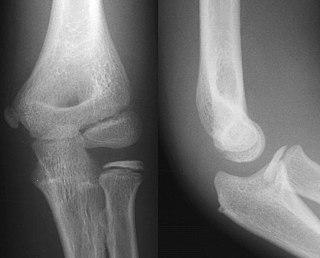
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by X-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images are often examined by radiologists. Both the procedure and any resultant images are often simply called 'X-ray'. Plain radiography or roentgenography generally refers to projectional radiography. Plain radiography can also refer to radiography without a radiocontrast agent or radiography that generates single static images, as contrasted to fluoroscopy, which are technically also projectional.
Image-guided radiation therapy is the process of frequent imaging, during a course of radiation treatment, used to direct the treatment, position the patient, and compare to the pre-therapy imaging from the treatment plan. Immediately prior to, or during, a treatment fraction, the patient is localized in the treatment room in the same position as planned from the reference imaging dataset. An example of IGRT would include comparison of a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) dataset, acquired on the treatment machine, with the computed tomography (CT) dataset from planning. IGRT would also include matching planar kilovoltage (kV) radiographs or megavoltage (MV) images with digital reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) from the planning CT.
In statistics, sieve estimators are a class of non-parametric estimators which use progressively more complex models to estimate an unknown high-dimensional function as more data becomes available, with the aim of asymptotically reducing error towards zero as the amount of data increases. This method is generally attributed to Ulf Grenander.

Tomosynthesis, also digital tomosynthesis (DTS), is a method for performing high-resolution limited-angle tomography at radiation dose levels comparable with projectional radiography. It has been studied for a variety of clinical applications, including vascular imaging, dental imaging, orthopedic imaging, mammographic imaging, musculoskeletal imaging, and chest imaging.
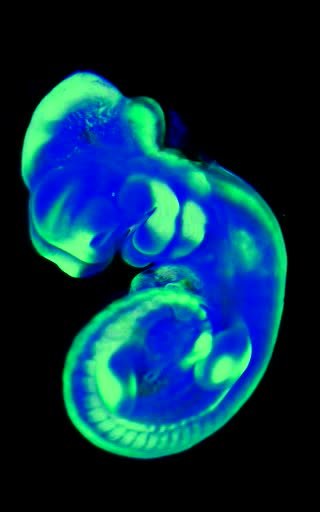
Optical projection tomography is a form of tomography involving optical microscopy. The OPT technique is sometimes referred to as optical computed tomography (optical-CT) and optical emission computed tomography (optical-ECT) in the literature, to address the fact that the technique bears similarity to X-ray computed tomography (CT) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).

The computed tomography imaging spectrometer (CTIS) is a snapshot imaging spectrometer which can produce in fine the three-dimensional hyperspectral datacube of a scene.
Preclinical or small-animal Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) is a radionuclide based molecular imaging modality for small laboratory animals. Although SPECT is a well-established imaging technique that is already for decades in use for clinical application, the limited resolution of clinical SPECT (~10 mm) stimulated the development of dedicated small animal SPECT systems with sub-mm resolution. Unlike in clinics, preclinical SPECT outperforms preclinical coincidence PET in terms of resolution and, at the same time, allows to perform fast dynamic imaging of animals.

X-ray computed tomography operates by using an X-ray generator that rotates around the object; X-ray detectors are positioned on the opposite side of the circle from the X-ray source.
Photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) is a form of X-ray computed tomography (CT) in which X-rays are detected using a photon-counting detector (PCD) which registers the interactions of individual photons. By keeping track of the deposited energy in each interaction, the detector pixels of a PCD each record an approximate energy spectrum, making it a spectral or energy-resolved CT technique. In contrast, more conventional CT scanners use energy-integrating detectors (EIDs), where the total energy deposited in a pixel during a fixed period of time is registered. These EIDs thus register only photon intensity, comparable to black-and-white photography, whereas PCDs register also spectral information, similar to color photography.
Spectral imaging is an umbrella term for energy-resolved X-ray imaging in medicine. The technique makes use of the energy dependence of X-ray attenuation to either increase the contrast-to-noise ratio, or to provide quantitative image data and reduce image artefacts by so-called material decomposition. Dual-energy imaging, i.e. imaging at two energy levels, is a special case of spectral imaging and is still the most widely used terminology, but the terms "spectral imaging" and "spectral CT" have been coined to acknowledge the fact that photon-counting detectors have the potential for measurements at a larger number of energy levels.
References
- Hudson, H.M., Larkin, R.S. (1994) "Accelerated image reconstruction using ordered subsets of projection data", IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging, 13 (4), 601–609 doi : 10.1109/42.363108