Environmental geology, like hydrogeology, is an applied science concerned with the practical application of the principles of geology in the solving of environmental problems created by man. It is a multidisciplinary field that is closely related to engineering geology and, to a lesser extent, to environmental geography. Each of these fields involves the study of the interaction of humans with the geologic environment, including the biosphere, the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, and to some extent the atmosphere. In other words, environmental geology is the application of geological information to solve conflicts, minimizing possible adverse environmental degradation, or maximizing possible advantageous conditions resulting from the use of natural and modified environment. With an increasing world population and industrialization, the natural environment and resources are under high strain which puts them at the forefront of world issues. Environmental geology is on the rise with these issues as solutions are found by utilizing it.

Mining in the engineering discipline is the extraction of minerals from underneath, open pit, above or on the ground. Mining engineering is associated with many other disciplines, such as mineral processing, exploration, excavation, geology, and metallurgy, geotechnical engineering and surveying. A mining engineer may manage any phase of mining operations, from exploration and discovery of the mineral resources, through feasibility study, mine design, development of plans, production and operations to mine closure.

Engineering geology is the application of geology to engineering study for the purpose of assuring that the geological factors regarding the location, design, construction, operation and maintenance of engineering works are recognized and accounted for. Engineering geologists provide geological and geotechnical recommendations, analysis, and design associated with human development and various types of structures. The realm of the engineering geologist is essentially in the area of earth-structure interactions, or investigation of how the earth or earth processes impact human made structures and human activities.

The California Geological Survey, previously known as the California Division of Mines and Geology, is the California state geologic agency.

Geoscience Australia is an agency of the Australian Government. It carries out geoscientific research. The agency is the government's technical adviser on all aspects of geoscience, and custodian of the geographic and geological data and knowledge of the nation.

The Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act of 1977 (SMCRA) is the primary federal law that regulates the environmental effects of coal mining in the United States.
The Utah Geological Survey is based in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. It also has an office in Cedar City, Utah.
The California Department of Conservation is a department within the government of California, belonging to the California Natural Resources Agency. With a team of scientists, engineers, environmental experts, and other specialists, the Department of Conservation administers a variety of programs vital to California's public safety, environment and economy. The department's mission is to manage California's working lands. It regulates oil, natural gas and geothermal wells; studies and maps earthquakes and other geologic phenomena; maps and classifies areas containing mineral deposits; ensures reclamation of land used for mining; and administers agricultural and open-space land conservation programs. A division within the department dedicated to encouraging beverage container recycling has been moved into the newly created Department of Resources Recovery and Recycling (CalRecycle). Despite the similar name, the Department of Conservation should not be confused with the California Conservation Corps, another department within the Natural Resources Agency, which provides work experience for young adults. The Department of Conservation often collaborates with its federal equivalents, such as the U.S. Geological Survey.

Pebble Mine is the common name of a proposed copper-gold-molybdenum mining project in the Bristol Bay region of Southwest Alaska, near Lake Iliamna and Lake Clark. Discovered in 1987, optioned by Northern Dynasty Minerals in 2001, explored in 2002, drilled from 2002-2013 with discovery in 2005. Preparing for the permitting process began and administrative review lasted over 13 years.
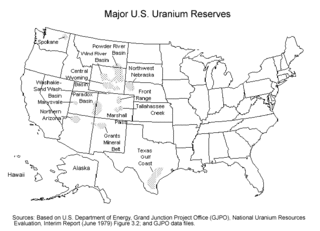
Uranium mining in the United States produced 173,875 pounds (78.9 tonnes) of U3O8 in 2019, 88% lower than the 2018 production of 1,447,945 pounds (656.8 tonnes) of U3O8 and the lowest US annual production since 1948. The 2019 production represents 0.3% of the anticipated uranium fuel requirements of the US's nuclear power reactors for the year.
The Energy Resources Conservation Board (ERCB) was an independent, quasi-judicial agency of the Government of Alberta. It regulated the safe, responsible, and efficient development of Alberta's energy resources: oil, natural gas, oil sands, coal, and pipelines. Led by eight Board members, the ERCB's team of engineers, geologists, technicians, economists, and other professionals served Albertans from thirteen locations across the province.

A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, although backgrounds in physics, chemistry, biology, and other sciences are also useful. Field research is an important component of geology, although many subdisciplines incorporate laboratory and digitalized work. Geologists can be classified in a larger group of scientists, called geoscientists.

The Mines and Geo-sciences Bureau (MGB) is a government agency of the Philippines under the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR). The MGB is responsible for the conservation, management, development and use of the country's mineral resources, including those in reservations and public lands.

Geothermal exploration is the exploration of the subsurface in search of viable active geothermal regions with the goal of building a geothermal power plant, where hot fluids drive turbines to create electricity. Exploration methods include a broad range of disciplines including geology, geophysics, geochemistry and engineering.
Rosemont Copper is a proposed large open pit copper mine project by the Canadian mining corporation Hudbay Minerals. The project site is located within the Santa Rita Mountains and Coronado National Forest, in Pima County of southern Arizona. It has undergone a permitting review process under the direction of the United States Forest Service and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and has been delayed by legal judgements and suspension of its operating permit by the US Army Corps of Engineers.

The National Strategic and Critical Minerals Production Act of 2013 is a bill that was introduced into the United States House of Representatives during the 113th United States Congress. The bill would alter the rules and regulations surrounding getting permits/permission to undertake mining projects in the United States. The bill would also alter that legal framework associated with this type of mining.

The Federal Lands Jobs and Energy Security Act is a bill that would require the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) to establish certain fees for activities related to the development of oil and gas on federal lands. A portion of those amounts along with a portion of fees from renewable energy projects on federal lands would be available to the agency, subject to appropriation, to cover the costs of activities aimed at increasing energy development on federal lands. The bill also would exempt lawsuits related to energy production on federal lands from the Equal Access to Justice Act (EAJA). In addition, the legislation would require the BLM to offer for sale at least 25 percent of onshore federal lands nominated by firms for oil and gas leasing. It was introduced in the United States House of Representatives during the 113th United States Congress. President Barack Obama threatened to veto the bill on November 19, 2013.
The Wyoming Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) founded in 1973, is a Wyoming state agency to protect, conserve and enhance the environment of Wyoming "through a combination of monitoring, permitting, inspection, enforcement and restoration/remediation activities". It consists of 6 divisions and since 1992, the Environmental Quality Council (EQC), a separate operating agency of 7 governor-appointed members.
The Geological Survey and Mineral Exploration of Iran or in brief GSI is a government agency responsible for conducting geological and mineral surveys throughout the country, collecting the results of activities carried out in this field, establishing coordination, preparing and publishing geological maps of Iran. It is a subdivision of the Ministry of Industry, Mine and Trade, which was established in 1962 in cooperation with United Nations.

Geological engineering is a discipline of engineering concerned with the application of geological science and engineering principles to fields, such as civil engineering, mining, environmental engineering, and forestry, among others. The work of geological engineers often directs or supports the work of other engineering disciplines such as assessing the suitability of locations for civil engineering, environmental engineering, mining operations, and oil and gas projects by conducting geological, geoenvironmental, geophysical, and geotechnical studies. They are involved with impact studies for facilities and operations that affect surface and subsurface environments. The engineering design input and other recommendations made by geological engineers on these projects will often have a large impact on construction and operations. Geological engineers plan, design, and implement geotechnical, geological, geophysical, hydrogeological, and environmental data acquisition. This ranges from manual ground-based methods to deep drilling, to geochemical sampling, to advanced geophysical techniques and satellite surveying. Geological engineers are also concerned with the analysis of past and future ground behaviour, mapping at all scales, and ground characterization programs for specific engineering requirements. These analyses lead geological engineers to make recommendations and prepare reports which could have major effects on the foundations of construction, mining, and civil engineering projects. Some examples of projects include rock excavation, building foundation consolidation, pressure grouting, hydraulic channel erosion control, slope and fill stabilization, landslide risk assessment, groundwater monitoring, and assessment and remediation of contamination. In addition, geological engineers are included on design teams that develop solutions to surface hazards, groundwater remediation, underground and surface excavation projects, and resource management. Like mining engineers, geological engineers also conduct resource exploration campaigns, mine evaluation and feasibility assessments, and contribute to the ongoing efficiency, sustainability, and safety of active mining projects











