Related Research Articles

The Goths were Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe.

Jordanes, also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history (Romana) and the other on the Goths (Getica). The latter, along with Isidore of Seville's Historia Gothorum, is one of only two extant ancient works dealing with the early history of the Goths.

The Ostrogoths were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century, having crossed the Lower Danube. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under the influence of the Amal dynasty, the family of Theodoric the Great.

The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians, were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his Germania who called them the Rugii, and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some centuries later, they were considered one of the "Gothic" or "Scythian" peoples who were located in the Middle Danube region. Like several other Gothic peoples there, they possibly arrived in the area as allies of Attila until his death in 453. They settled in what is now Lower Austria after the defeat of the Huns at Nedao in 454.

The Gepids were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the Goths and Vandals.

De origine actibusque Getarum, commonly abbreviated Getica, written in Late Latin by Jordanes in or shortly after 551 AD, claims to be a summary of a voluminous account by Cassiodorus of the origin and history of the Gothic people, which is now lost. However, the extent to which Jordanes actually used the work of Cassiodorus is unknown. It is significant as the only remaining contemporaneous resource that gives an extended account of the origin and history of the Goths, although to what extent it should be considered history or origin mythology is a matter of dispute.

Rodulf was king of the Heruli kingdom on the Middle Danube in the period around 500, and possibly of Scandinavian origin. He died in a battle with the neighbouring Lombards which led to the splitting up of the Heruli. He is probably the same Heruli king that Theoderic the Great wrote to in two surviving letters, in one of which Theoderic "adopted" him with a gift of arms. Less certainly, he is also sometimes equated to a King Rodulf that Jordanes mentions as having come from Scandinavia to Italy, to join Theoderic.

The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones".
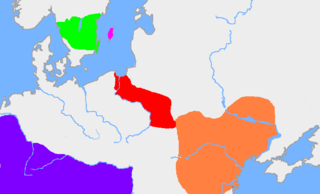
Oium was a name for Scythia, or a fertile part of it, roughly in modern Ukraine, where the Goths, under a legendary King Filimer, settled after leaving Gothiscandza, according to the Getica by Jordanes, written around 551.
The Amali – also called Amals, Amalings or Amalungs – were a leading dynasty of the Goths, a Germanic people who confronted the Roman Empire during the decline of the Western Roman Empire. They eventually became the royal house of the Ostrogoths and founded the Ostrogothic Kingdom.
The Gutones were a Germanic people who were reported by Roman era writers in the 1st and 2nd centuries to have lived in what is now Poland. The most accurate description of their location, by the geographer Ptolemy, placed them east of the Vistula river.
Peter John Heather is a British historian of late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Heather is Chair of the Medieval History Department and Professor of Medieval History at King's College London. He specialises in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the Goths, on which he for decades has been considered the world's leading authority.
Michael Kulikowski is an American historian. He is a professor of history and classics and the head of the history department at Pennsylvania State University. Kulikowski specializes in the history of the western Mediterranean world of late antiquity. He is sometimes associated with the Toronto School of History and was a student of Walter Goffart.

Balamber was ostensibly a chieftain of the Huns, mentioned by Jordanes in his Getica. Jordanes simply called him "king of the Huns" and writes the story of Balamber crushing the tribes of the Ostrogoths in the 370s; somewhere between 370 and more probably 376 AD.
The belagines were written laws which, according to Jordanes, were given to the Goths by Dicineus / Dekaineos, the Dacian-Getic legislator, Zalmoxian priest at the time of Burebista.

The Frankish Table of Nations is a brief early medieval genealogical text in Latin giving the supposed relationship between thirteen nations descended from three brothers. The nations are the Ostrogoths, Visigoths, Vandals, Gepids, Saxons, Burgundians, Thuringians, Lombards, Bavarians, Romans, Bretons, Franks and Alamanni.
Arne Søby Christensen is a Danish historian. He is an associate professor in history at the University of Copenhagen.
There were several origin stories of the Gothic peoples recorded by Latin and Greek authors in late antiquity, and these are relevant not only to the study of literature, but also by historians seeking evidence of real historical events involving the Goths and other peoples mentioned in these stories.

Haliurunas, haljarunae, Haliurunnas, haliurunnae, etc., were Gothic "witches" who appear once in Getica, a 6th century work on Gothic history. The account tells that the early Goth king Filimer found witches among his people when they had settled north of the Black Sea, and that he banished them to exile. They were impregnated by unclean spirits and engendered the Huns, and the account is a precursor of later Christian traditions where wise women were alleged to have sexual intercourse and even orgies with demons and the Devil.
Vadamerca or Valadamarca may have been a Gothic princess and Goth royal family member by birth, and consort of the Rex Hunnorum Balamber, possibly the first ruler of the Huns. The only extant source that mentions her or Balamber is Jordanes' Getica, and it is possible that both are unhistorical.
References
- ↑ Herwig Wolfram, Origo Gentis. in Reallexikon der Germanischen Altertumskunde , vol. 22 (2003)
- ↑ Plassmann 2006, p. 207.
- ↑ Plassmann 2006, p. 360.
- ↑ Arne Søby Christensen (2002). Cassiodorus, Jordanes and the History of the Goths: Studies in a Migration Myth. Museum Tusculanum Press. ISBN 978-87-7289-710-3.
- ↑ Goffart 1988.
- ↑ Plassmann 2006, p. 16.