
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), whose members are nicknamed "Wobblies", is an international labor union founded in Chicago in 1905. The nickname's origin is uncertain. Its ideology combines general unionism with industrial unionism, as it is a general union, subdivided between the various industries which employ its members. The philosophy and tactics of the IWW are described as "revolutionary industrial unionism", with ties to socialist, syndicalist, and anarchist labor movements.

Joe Hill, born Joel Emmanuel Hägglund and also known as Joseph Hillström, was a Swedish-American labor activist, songwriter, and member of the Industrial Workers of the World. A native Swedish speaker, he learned English during the early 1900s, while working various jobs from New York to San Francisco. Hill, an immigrant worker frequently facing unemployment and underemployment, became a popular songwriter and cartoonist for the union. His songs include "The Preacher and the Slave", "The Tramp", "There Is Power in a Union", "The Rebel Girl", and "Casey Jones—the Union Scab", which express the harsh and combative life of itinerant workers, and call for workers to organize their efforts to improve working conditions.

Carlo Tresca was an Italian-American newspaper editor, orator, and labor organizer and activist who was a leader of the Industrial Workers of the World during the 1910s. He is remembered as a leading public opponent of fascism, Stalinism, and Mafia infiltration of the trade unions for the purposes of labor racketeering and corruption.

The Western Federation of Miners (WFM) was a labor union that gained a reputation for militancy in the mines of the western United States and British Columbia. Its efforts to organize both hard rock miners and smelter workers brought it into sharp conflicts – and often pitched battles – with both employers and governmental authorities. One of the most dramatic of these struggles occurred in the Cripple Creek district of Colorado in 1903–1904; the conflicts were thus dubbed the Colorado Labor Wars. The WFM also played a key role in the founding of the Industrial Workers of the World in 1905 but left that organization several years later.

William Dudley "Big Bill" Haywood was an American labor organizer and founding member and leader of the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) and a member of the executive committee of the Socialist Party of America. During the first two decades of the 20th century, Haywood was involved in several important labor battles, including the Colorado Labor Wars, the Lawrence Textile Strike, and other textile strikes in Massachusetts and New Jersey.

Vincent Saint John (1876–1929) was an American labor leader and prominent Wobbly, among the most influential radical labor leaders of the 20th century.

Franklin Henry Little, commonly known as Frank Little, was an American labor leader who was murdered in Butte, Montana. No one was apprehended or prosecuted for Little's murder. He joined the Industrial Workers of the World in 1905, organizing miners, lumberjacks, and oil field workers. He was a member of the union's Executive Board when he was brutally murdered.

The Lawrence Textile Strike, also known as the Bread and Roses Strike, was a strike of immigrant workers in Lawrence, Massachusetts, in 1912 led by the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW). Prompted by a two-hour pay cut corresponding to a new law shortening the workweek for women, the strike spread rapidly through the town, growing to more than twenty thousand workers and involving nearly every mill in Lawrence. On January 1, 1912, the Massachusetts government enforced a law that cut mill workers' hours in a single work week from 56 hours, to 54 hours. Ten days later, they found out that pay had been reduced along with the cut in hours.

Joseph James "Smiling Joe" Ettor (1885–1948) was an Italian-American trade union organizer who, in the middle-1910s, was one of the leading public faces of the Industrial Workers of the World. Ettor is best remembered as a defendant in a controversial trial related to a killing in the seminal Lawrence Textile Strike of 1912, in which he was acquitted of charges of having been an accessory.

Arturo M. Giovannitti was an Italian-American union leader, socialist political activist, and poet. He is best remembered as one of the principal organizers of the 1912 Lawrence textile strike and as a defendant in a celebrated trial caused by that event.

Elizabeth Gurley Flynn was an American labor leader, activist, and feminist who played a leading role in the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW). Flynn was a founding member of the American Civil Liberties Union and a visible proponent of women's rights, birth control, and women's suffrage. She joined the Communist Party USA in 1936 and late in life, in 1961, became its chairwoman. She died during a visit to the Soviet Union, where she was accorded a state funeral with processions in Red Square attended by over 25,000 people.

Charles H. Moyer was an American labor leader and president of the Western Federation of Miners (WFM) from 1902 to 1926. He led the union through the Colorado Labor Wars, was accused of murdering an ex-governor of the state of Idaho, and was shot in the back during a bitter copper mine strike. He also was a leading force in founding the Industrial Workers of the World, although he later denounced the organization.
Joseph Francis Quinn (1857–1929) was the first Irish American to become a judge in Massachusetts for any significant period of time. He served on the bench of the Essex County Superior Court after being appointed by Governor Eugene Foss in 1911 until his death in 1929. He lived in Salem and was the son of an immigrant from the days of the Great Famine. He attended the University of Ottawa in Canada due to discrimination against the Irish in the U.S. at the time, graduating in 1881, and went on to be admitted to the bar in Massachusetts in 1884 after attending Boston University School of Law and apprenticing under a local attorney. After working for the local U.S. Attorney, Joseph Quinn started his own thriving practice.

Anna LoPizzo was an Italian immigrant striker killed during the Lawrence Textile Strike, considered one of the most significant struggles in U.S. labor history.

Fred H. Moore (1882–1933) was a socialist lawyer and the defense attorney of the controversial Sacco and Vanzetti case. He had collaborated in many labor and Industrial Workers of the World trials. He played a minor role in several celebrated I.W.W. trials, including the Los Angeles Times bombing case in 1911 and the Ettor–Giovannitti case, which arose from the 1912 Lawrence, Massachusetts, textile strike. Following the acquittal of Ettor and Giovannitti, Moore spent the next several years roaming the country defending I.W.W. organizers. He was involved in the Centralia massacre trial and the mass prosecution, on charges of sedition, of the I.W.W. in Chicago in 1918. Errors in a later trial, however, led Big Bill Haywood to demand Moore's resignation as I.W.W. attorney in 1920. Moore's career was revived by his being hired to head the defense team for Sacco and Vanzetti in the summer of 1920.
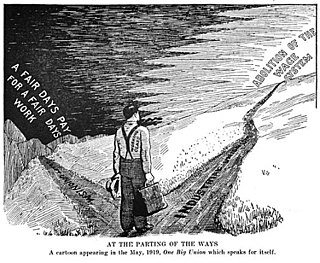
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) is a union of wage workers which was formed in Chicago in 1905 by militant unionists and their supporters due to anger over the conservatism, philosophy, and craft-based structure of the American Federation of Labor (AFL). Throughout the early part of the 20th century, the philosophy and tactics of the IWW were frequently in direct conflict with those of the AFL concerning the best ways to organize workers, and how to best improve the society in which they toiled. The AFL had one guiding principle—"pure and simple trade unionism", often summarized with the slogan "a fair day's pay for a fair day's work." The IWW embraced two guiding principles, fighting like the AFL for better wages, hours, and conditions, but also promoting an eventual, permanent solution to the problems of strikes, injunctions, bull pens, and union scabbing.
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) is a union of wage workers which was formed in Chicago in 1905. The IWW experienced a number of divisions and splits during its early history.

Arthur Patrick L. "Pat" Quinlan (1883–1948) was an Irish trade union organizer, journalist, and socialist political activist. Quinlan is best remembered for the part he played as an organizer for the Industrial Workers of the World in the 1913 Paterson silk strike — an event which led to his imprisonment for two years in the New Jersey State Penitentiary.
George Francis Vanderveer was an American lawyer who defended Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) members during the union's years of "deepest trouble."















