
Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, computer programming, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. The subsequent process of analyzing and interpreting data is referred to as computational biology.

A phylogenetic tree, phylogeny or evolutionary tree is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time. In other words, it is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. In evolutionary biology, all life on Earth is theoretically part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry. Phylogenetics is the study of phylogenetic trees. The main challenge is to find a phylogenetic tree representing optimal evolutionary ancestry between a set of species or taxa. Computational phylogenetics focuses on the algorithms involved in finding optimal phylogenetic tree in the phylogenetic landscape.
In bioinformatics, sequence clustering algorithms attempt to group biological sequences that are somehow related. The sequences can be either of genomic, "transcriptomic" (ESTs) or protein origin. For proteins, homologous sequences are typically grouped into families. For EST data, clustering is important to group sequences originating from the same gene before the ESTs are assembled to reconstruct the original mRNA.

A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy.
In computational biology, gene prediction or gene finding refers to the process of identifying the regions of genomic DNA that encode genes. This includes protein-coding genes as well as RNA genes, but may also include prediction of other functional elements such as regulatory regions. Gene finding is one of the first and most important steps in understanding the genome of a species once it has been sequenced.

Comparative genomics is a field of biological research in which the genomic features of different organisms are compared. The genomic features may include the DNA sequence, genes, gene order, regulatory sequences, and other genomic structural landmarks. In this branch of genomics, whole or large parts of genomes resulting from genome projects are compared to study basic biological similarities and differences as well as evolutionary relationships between organisms. The major principle of comparative genomics is that common features of two organisms will often be encoded within the DNA that is evolutionarily conserved between them. Therefore, comparative genomic approaches start with making some form of alignment of genome sequences and looking for orthologous sequences in the aligned genomes and checking to what extent those sequences are conserved. Based on these, genome and molecular evolution are inferred and this may in turn be put in the context of, for example, phenotypic evolution or population genetics.
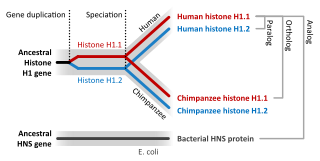
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal gene transfer event (xenologs).
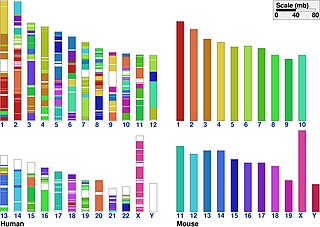
In genetics, the term synteny refers to two related concepts:
Phylogenomics is the intersection of the fields of evolution and genomics. The term has been used in multiple ways to refer to analysis that involves genome data and evolutionary reconstructions. It is a group of techniques within the larger fields of phylogenetics and genomics. Phylogenomics draws information by comparing entire genomes, or at least large portions of genomes. Phylogenetics compares and analyzes the sequences of single genes, or a small number of genes, as well as many other types of data. Four major areas fall under phylogenomics:
Computational phylogenetics, phylogeny inference, or phylogenetic inference focuses on computational and optimization algorithms, heuristics, and approaches involved in phylogenetic analyses. The goal is to find a phylogenetic tree representing optimal evolutionary ancestry between a set of genes, species, or taxa. Maximum likelihood, parsimony, Bayesian, and minimum evolution are typical optimality criteria used to assess how well a phylogenetic tree topology describes the sequence data. Nearest Neighbour Interchange (NNI), Subtree Prune and Regraft (SPR), and Tree Bisection and Reconnection (TBR), known as tree rearrangements, are deterministic algorithms to search for optimal or the best phylogenetic tree. The space and the landscape of searching for the optimal phylogenetic tree is known as phylogeny search space.
Caenorhabditis briggsae is a small nematode, closely related to Caenorhabditis elegans. The differences between the two species are subtle. The male tail in C. briggsae has a slightly different morphology from C. elegans. Other differences include changes in vulval precursor competence and the placement of the excretory duct opening. C. briggsae is frequently used to study the differences between it and the more intimately understood C. elegans, especially at the DNA and protein sequence level. Several mutant strains of C. briggsae have also been isolated that facilitate genetic analysis of this organism. C. briggsae, like C. elegans, is a hermaphrodite. The genome sequence for C. briggsae was determined in 2003.
Genomic phylostratigraphy is a novel genetic statistical method developed in order to date the origin of specific genes by looking at its homologs across species. It was first developed by Ruđer Bošković Institute in Zagreb, Croatia. The system links genes to their founder gene, allowing us to then determine their age. This could help us better understand many evolutionary processes such as patterns of gene birth throughout evolution, or the relationship between the age of a transcriptome throughout embryonic development. Bioinformatic tools like GenEra have been developed to calculate relative gene ages based on genomic phylostratigraphy.

MicrobesOnline is a publicly and freely accessible website that hosts multiple comparative genomic tools for comparing microbial species at the genomic, transcriptomic and functional levels. MicrobesOnline was developed by the Virtual Institute for Microbial Stress and Survival, which is based at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in Berkeley, California. The site was launched in 2005, with regular updates until 2011.
SUPERFAMILY is a database and search platform of structural and functional annotation for all proteins and genomes. It classifies amino acid sequences into known structural domains, especially into SCOP superfamilies. Domains are functional, structural, and evolutionary units that form proteins. Domains of common Ancestry are grouped into superfamilies. The domains and domain superfamilies are defined and described in SCOP. Superfamilies are groups of proteins which have structural evidence to support a common evolutionary ancestor but may not have detectable sequence homology.

In molecular biology and genetics, DNA annotation or genome annotation is the process of describing the structure and function of the components of a genome, by analyzing and interpreting them in order to extract their biological significance and understand the biological processes in which they participate. Among other things, it identifies the locations of genes and all the coding regions in a genome and determines what those genes do.

OrthoDB presents a catalog of orthologous protein-coding genes across vertebrates, arthropods, fungi, plants, and bacteria. Orthology refers to the last common ancestor of the species under consideration, and thus OrthoDB explicitly delineates orthologs at each major radiation along the species phylogeny. The database of orthologs presents available protein descriptors, together with Gene Ontology and InterPro attributes, which serve to provide general descriptive annotations of the orthologous groups, and facilitate comprehensive orthology database querying. OrthoDB also provides computed evolutionary traits of orthologs, such as gene duplicability and loss profiles, divergence rates, sibling groups, and gene intron-exon architectures.
PhylomeDB is a public biological database for complete catalogs of gene phylogenies (phylomes). It allows users to interactively explore the evolutionary history of genes through the visualization of phylogenetic trees and multiple sequence alignments. Moreover, phylomeDB provides genome-wide orthology and paralogy predictions which are based on the analysis of the phylogenetic trees. The automated pipeline used to reconstruct trees aims at providing a high-quality phylogenetic analysis of different genomes, including Maximum Likelihood tree inference, alignment trimming and evolutionary model testing.
Microbial phylogenetics is the study of the manner in which various groups of microorganisms are genetically related. This helps to trace their evolution. To study these relationships biologists rely on comparative genomics, as physiology and comparative anatomy are not possible methods.
Horizontal or lateral gene transfer is the transmission of portions of genomic DNA between organisms through a process decoupled from vertical inheritance. In the presence of HGT events, different fragments of the genome are the result of different evolutionary histories. This can therefore complicate investigations of the evolutionary relatedness of lineages and species. Also, as HGT can bring into genomes radically different genotypes from distant lineages, or even new genes bearing new functions, it is a major source of phenotypic innovation and a mechanism of niche adaptation. For example, of particular relevance to human health is the lateral transfer of antibiotic resistance and pathogenicity determinants, leading to the emergence of pathogenic lineages.
In molecular phylogenetics, relationships among individuals are determined using character traits, such as DNA, RNA or protein, which may be obtained using a variety of sequencing technologies. High-throughput next-generation sequencing has become a popular technique in transcriptomics, which represent a snapshot of gene expression. In eukaryotes, making phylogenetic inferences using RNA is complicated by alternative splicing, which produces multiple transcripts from a single gene. As such, a variety of approaches may be used to improve phylogenetic inference using transcriptomic data obtained from RNA-Seq and processed using computational phylogenetics.









