Related Research Articles
The Missouria or Missouri are a Native American tribe that originated in the Great Lakes region of what is now the United States before European contact. The tribe belongs to the Chiwere division of the Siouan language family, together with the Iowa and Otoe.

Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States government for the relocation of Native Americans who held original Indian title to their land as an independent nation-state. The concept of an Indian territory was an outcome of the U.S. federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the U.S. government was one of assimilation.

Osage County is the largest county by area in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Created in 1907 when Oklahoma was admitted as a state, the county is named for and is home to the federally recognized Osage Nation. The county is coextensive with the Osage Nation Reservation, established by treaty in the 19th century when the Osage relocated there from Kansas. The county seat is in Pawhuska, one of the first three towns established in the county. The total population of the county as of 2020 was 45,818.

The Cherokee Outlet, or Cherokee Strip, was located in what is now the state of Oklahoma in the United States. It was a 60-mile-wide (97 km) parcel of land south of the Oklahoma–Kansas border between 96 and 100°W. The Cherokee Outlet was created in 1836. The United States forced the Cherokee Nation of Indians to cede to the United States all lands east of the Mississippi River in exchange for a reservation and an "outlet" in Indian Territory. At the time of its creation, the Cherokee Outlet was about 225 miles (360 km) long. The cities of Enid, Woodward, Ponca City, and Perry were later founded within the boundaries of what had been the Cherokee Outlet.
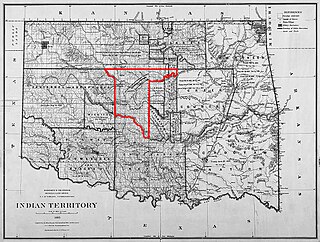
The Unassigned Lands in Oklahoma were in the center of the lands ceded to the United States by the Creek (Muskogee) and Seminole Indians following the Civil War and on which no other tribes had been settled. By 1883, it was bounded by the Cherokee Outlet on the north, several relocated Indian reservations on the east, the Chickasaw lands on the south, and the Cheyenne-Arapaho reserve on the west. The area amounted to 1,887,796.47 acres.

The Osage Nation, is a Midwestern American tribe of the Great Plains. The tribe developed in the Ohio and Mississippi river valleys around 700 B.C. along with other groups of its language family. They migrated west after the 17th century, settling near the confluence of the Missouri and Mississippi rivers, as a result of Iroquois expansion into the Ohio Country in the aftermath of the Beaver Wars.
The Treaty of Fort Wise of 1861 was a treaty entered into between the United States and six chiefs of the Southern Cheyenne and four of the Southern Arapaho Indian tribes. A significant proportion of Cheyennes opposed this treaty on the grounds that only a minority of Cheyenne chiefs had signed, and without the consent or approval of the rest of the tribe. Different responses to the treaty became a source of conflict between whites and Indians, leading to the Colorado War of 1864, including the Sand Creek Massacre.
John C. Sullivan was a surveyor who established the Indian Boundary Line and the Sullivan Line which were to form the boundary between Native Americans and white settlers in Indian Territory from Iowa to Texas.

The Treaty of Fort Clark was signed at Fort Osage on November 10, 1808, in which the Osage Nation ceded all the land east of the fort in Missouri and Arkansas north of the Arkansas River to the United States. The Fort Clark treaty and the Treaty of St. Louis in which the Sac (tribe) and Fox (tribe) ceded northeastern Missouri along with northern Illinois and southern Wisconsin were the first two major treaties in the newly acquired Louisiana Purchase. The affected tribes, upset with the terms, were to side with the British in the War of 1812. Following the settlement of that war, John C. Sullivan for the United States was to survey the ceded land in 1816 (adjusting it 23 miles westward to the mouth of the Kansas River to create the Indian Boundary Line west of which and south of which virtually all tribes were to be removed in the Indian Removal Act in 1830.
The timeline of Kansas details past events that happened in what is present day Kansas. Located on the eastern edge of the Great Plains, the U.S. state of Kansas was the home of sedentary agrarian and hunter-gatherer Native American societies, many of whom hunted American bison. The region first appears in western history in the 16th century at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, when Spanish conquistadors explored the unknown land now known as Kansas. It was later explored by French fur trappers who traded with the Native Americans. It became part of the United States in the Louisiana Purchase of 1803. In the 19th century, the first American explorers designated the area as the "Great American Desert."
A Half-Breed Tract was a segment of land designated in the western states by the United States government in the 19th century specifically for Métis of American Indian and European or European-American ancestry, at the time commonly known as half-breeds. The government set aside such tracts in several parts of the Midwestern prairie region, including in Iowa Territory, Nebraska Territory, Kansas Territory, Minnesota Territory, and Wisconsin Territory.
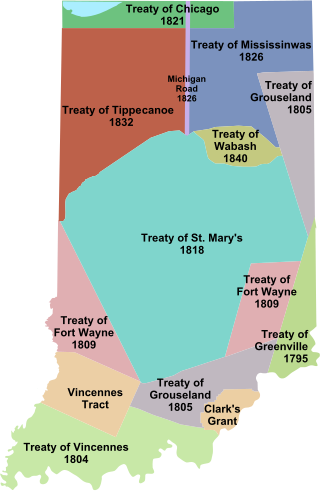
Indian removals in Indiana followed a series of the land cession treaties made between 1795 and 1846 that led to the removal of most of the native tribes from Indiana. Some of the removals occurred prior to 1830, but most took place between 1830 and 1846. The Lenape (Delaware), Piankashaw, Kickapoo, Wea, and Shawnee were removed in the 1820s and 1830s, but the Potawatomi and Miami removals in the 1830s and 1840s were more gradual and incomplete, and not all of Indiana's Native Americans voluntarily left the state. The most well-known resistance effort in Indiana was the forced removal of Chief Menominee and his Yellow River band of Potawatomi in what became known as the Potawatomi Trail of Death in 1838, in which 859 Potawatomi were removed to Kansas and at least forty died on the journey west. The Miami were the last to be removed from Indiana, but tribal leaders delayed the process until 1846. Many of the Miami were permitted to remain on land allotments guaranteed to them under the Treaty of St. Mary's (1818) and subsequent treaties.

White Plume, also known as Nom-pa-wa-rah, Manshenscaw, and Monchousia, was a chief of the Kaw Indigenous American tribe. He signed a treaty in 1825 ceding millions of acres of Kaw land to the United States. Most present-day members of the Kaw Nation of Oklahoma trace their lineage back to him. He was the great-great-grandfather of Charles Curtis, 31st Vice President of the United States.

The Cherokee Commission, was a three-person bi-partisan body created by President Benjamin Harrison to operate under the direction of the Secretary of the Interior, as empowered by Section 14 of the Indian Appropriations Act of March 2, 1889. Section 15 of the same Act empowered the President to open land for settlement. The Commission's purpose was to legally acquire land occupied by the Cherokee Nation and other tribes in the Oklahoma Territory for non-indigenous homestead acreage.

An Organic Act is a generic name for a statute used by the United States Congress to describe a territory, in anticipation of being admitted to the Union as a state. Because of Oklahoma's unique history an explanation of the Oklahoma Organic Act needs a historic perspective. In general, the Oklahoma Organic Act may be viewed as one of a series of legislative acts, from the time of Reconstruction, enacted by Congress in preparation for the creation of a united State of Oklahoma. The Organic Act created Oklahoma Territory, and Indian Territory that were Organized incorporated territories of the United States out of the old "unorganized" Indian Territory. The Oklahoma Organic Act was one of several acts whose intent was the assimilation of the tribes in Oklahoma and Indian Territories through the elimination of tribes' communal ownership of property.
On the eve of the American Civil War in 1861, a significant number of Indigenous peoples of the Americas had been relocated from the Southeastern United States to Indian Territory, west of the Mississippi. The inhabitants of the eastern part of the Indian Territory, the Five Civilized Tribes, were suzerain nations with established tribal governments, well established cultures, and legal systems that allowed for slavery. Before European Contact these tribes were generally matriarchial societies, with agriculture being the primary economic pursuit. The bulk of the tribes lived in towns with planned streets, residential and public areas. The people were ruled by complex hereditary chiefdoms of varying size and complexity with high levels of military organization.

The Treaty of St. Louis of 1804 was a treaty concluded by William Henry Harrison on behalf of the United States of America and five Sauk and Meskwaki chiefs led by Quashquame.
The Treaty of St. Louis is the name of a series of treaties signed between the United States and various Native American tribes from 1804 through 1824. The fourteen treaties were all signed in the St. Louis, Missouri area.
The Treaty of St. Louis is the name of a series of treaties signed between the United States and various Native American tribes from 1804 through 1824. The fourteen treaties were all signed in the St. Louis, Missouri area.

Lovely's Purchase, also called Lovely's Donation, was part of the Missouri Territory and the Arkansaw Territory of the early nineteenth century. It was created in 1817, to give a haven to the Cherokee and other Native Americans who were being forced to leave the southeastern United States and moving west to Indian Territory through territory then inhabited by sometimes hostile White settlers and several other Indigenous nations, especially citizens of the Osage Nation. Following years of political maneuvering and sometimes conflicting treaties, the purchase was finally split between the Cherokee and White American settlers, with the larger section going solely to the Cherokee Nation.
References
- ↑ Oklahoma State University Library (Kappler Project: Indian Affairs: Laws and Treaties) - Treaty With The Osage, 1825 Archived 2006-09-02 at the Wayback Machine (Article I) The Great and Little Osage Tribes or Nations do, hereby cede and relinquish to the United States, all their right, title interest and claim, to lands lying within the State of Missouri and Territory of Arkansas, and to all lands lying West of the said State of Missouri and Territory of Arkansas, North and West of the Red River, South of the Kansas River, and East of a line to be drawn from the head sources of the Kansas, Southwardly through the Rock Saline, with such reservations, for such considerations, and upon such terms as are hereinafter specified, expressed, and provided for.