Related Research Articles

A transmission tower, also known as an electricity pylon or simply a pylon in British English and as a hydro tower in Canadian English, is a tall structure, usually a steel lattice tower, used to support an overhead power line.
The HVDC Volgograd–Donbass is a 475 kilometres (295 mi) long bipolar ±400 kV high voltage direct current powerline used for transmitting electric power from Volga Hydroelectric Station at Volgograd in Russia to Donbas in eastern Ukraine and vice versa.
The Mettlen–Lavorgo powerline, also called the Lukmanier powerline, is the 400 kV three-phase alternating current high voltage electric power transmission line over the Lukmanier Pass in Switzerland, from Mettlen substation, next Inwil, about 7-kilometre (4.3 mi) south of Hochdorf, to Lavorgo substation, next Lavorgo, about 5-kilometre (3.1 mi) south of Faido. Trees falling on the line in 2003 caused a major blackout in Italy.

The Pylons of Messina are two free-standing steel towers, the Sicilian one in Torre Faro and the Calabrian one in Villa San Giovanni. They were used from 1955 to 1994 to carry a 220 kilovolt power line across the Strait of Messina, between the Scilla substation in Calabria on the Italian mainland at 38°14′42″N15°40′59″E and the Messina-Santo substation in Sicily at 38°15′57″N15°39′04″E.

The Pylons of Cádiz, also known as the Towers of Cádiz, are two 158 m (518 ft)-tall pylons supporting a double-circuit 132 kV three-phase AC powerline over the bay of Cádiz, Spain, running from Puerto Real Substation to the substation of the former Cádiz Thermal Power Station, situated on the peninsula upon which the city of Cádiz stands.

An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to transmit electrical energy across large distances. It consists of one or more uninsulated electrical cables suspended by towers or poles.

The Suez Canal overhead powerline crossing is a major electrical power line built across the Suez Canal in 1998, located near Suez, Egypt. It is designed for two 500 kV circuits.
Bosporus overhead line crossings refers to the three transmission line crossings of the Bosporus, the strait in Istanbul, Turkey.

Bayswater Power Station is a bituminous (black) coal-powered thermal power station with four 660 megawatts (890,000 hp) Tokyo Shibaura Electric (Japan) steam driven turbo alternators for a combined capacity of 2,640 megawatts (3,540,000 hp). Commissioned between 1985 and 1986, the station is located 16 kilometres (10 mi) from Muswellbrook, and 28 km (17 mi) from Singleton in the Hunter Region of New South Wales, Australia.
The Yangtze River power line crossings are overhead power lines that cross the Yangtze River in China. There are at least three power line crossings on the Yangtze River at Jiangyin, Nanjing, and Wuhu. The towers of the crossing in Jiangyin are among the highest in the world.

The 400 kV Thames Crossing is an overhead power line crossing of the River Thames, between Botany Marshes in Swanscombe, Kent, and West Thurrock, Essex, England. Its towers are the tallest electricity pylons in the UK.
Enerhodar Dnipro Powerline Crossing consists of two overhead power lines that cross the Kakhovka Reservoir on the Dnipro river. They cross from Enerhodar and its two power stations on the south side to near Marhanets on the north side.
Belvedere Power Station was an oil-fired 480 MW power station on the river Thames at Belvedere, south-east London. It was commissioned in 1960 and operated for 26 years. It was decommissioned in 1986 and was subsequently demolished in 1993–94. The site has been redeveloped as industrial warehouses, although the fuelling jetty is extant.

In Poland, there are 6 powerline crossings of the Vistula river and one powerline crossing of the Odra river using pylons taller than 100 metres.

Hydro-Québec's electricity transmission system is an international electric power transmission system centred in Quebec, Canada. The system pioneered the use of very high voltage 735-kilovolt (kV) alternating current (AC) power lines that link the population centres of Montreal and Quebec City to distant hydroelectric power stations like the Daniel-Johnson Dam and the James Bay Project in northwestern Quebec and the Churchill Falls Generating Station in Labrador.

Yoshina Station is a railway station in Takehara, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan.

The Chūshi Powerline Crossing is a part of the Chūshi mainline, a 220 kV powerline in Japan. It has two circuits running over the Inland Sea from Takehara. It was built in 1962 and consists of two towers, each 226 metres tall, one situated in Takehara, Honshū at 34°19′55.8″N132°59′3.3″E, the other on the island of Ōkunoshima at 34°18′42.8″N132°59′32.2″E. These towers are the tallest electricity pylons in Japan and carry six conductors arranged in three levels. The span between the two towers has a length of 2,357 metres and has a minimum clearance of 42 metres. The conductors have a cross section of 170 mm2, a diameter 35.2 mm and are designed for a maximum current of 645 A.
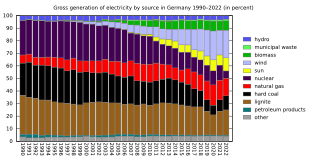
Germany's electrical grid is part of the Synchronous grid of Continental Europe. In 2020, due to COVID-19 conditions and strong winds, Germany produced 484 TW⋅
The Zhoushan Island Overhead Powerline Tie is a 220 kV three-phase AC interconnection of the power grid of Zhoushan Island with that of the Chinese mainland. It runs over several islands and consists of several long distance spans, the longest with a length of 2.7 kilometres (1.7 mi) south of Damao Island. This span uses two 370-metre-tall (1,210 ft) pylons, which were the highest electricity pylons in the world, until 500kV line to Zhoushan from mainland was completed. The north tower on Damao Island was completed in 2009, and the south tower on Liangmao Island was completed in 2010. These pylons resemble those of the Messina Strait, but are steel-tube lattice structures.
References
- 1 2 Kamiyama, Hideki; Hiratsuka, Satoshi; Fukuda, Nozomu; Kojima, Toru; Aotani, Shoji; Asayama, Osamu; Hanada, Koichi; Miyashita, Masanao (November 25, 1998). "Development of a High-Strength Conductor, Accessories and Stringing Method for an Over-Water Crossing of the Osaki Thermal Power Line". Furukawa Review (18) – via Furukawa Electric Group.