Related Research Articles

A dental implant is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biological process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or zirconia form an intimate bond to the bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic/crown.
Osseointegration is the direct structural and functional connection between living bone and the surface of a load-bearing artificial implant. A more recent definition defines osseointegration as "functional ankylosis ", where new bone is laid down directly on the implant surface and the implant exhibits mechanical stability. Osseointegration has enhanced the science of medical bone and joint replacement techniques as well as dental implants and improving prosthetics for amputees.
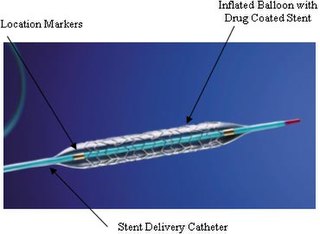
An implant is a medical device manufactured to replace a missing biological structure, support a damaged biological structure, or enhance an existing biological structure. For example, an implant may be a rod, used to strengthen weak bones. Medical implants are human-made devices, in contrast to a transplant, which is a transplanted biomedical tissue. The surface of implants that contact the body might be made of a biomedical material such as titanium, silicone, or apatite depending on what is the most functional. In some cases implants contain electronics, e.g. artificial pacemaker and cochlear implants. Some implants are bioactive, such as subcutaneous drug delivery devices in the form of implantable pills or drug-eluting stents.

Joint replacement is a procedure of orthopedic surgery known also as arthroplasty, in which an arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with an orthopedic prosthesis. Joint replacement is considered as a treatment when severe joint pain or dysfunction is not alleviated by less-invasive therapies. Joint replacement surgery is often indicated from various joint diseases, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.

Hip resurfacing has been developed as a surgical alternative to total hip replacement (THR). The procedure consists of placing a cap, which is hollow and shaped like a mushroom, over the head of the femur while a matching metal cup is placed in the acetabulum, replacing the articulating surfaces of the person's hip joint and removing very little bone compared to a THR. When the person moves the hip, the movement of the joint induces synovial fluid to flow between the hard metal bearing surfaces lubricating them when the components are placed in the correct position. The surgeon's level of experience with hip resurfacing is most important; therefore, the selection of the right surgeon is crucial for a successful outcome. Health-related quality of life measures are markedly improved and the person's satisfaction is favorable after hip resurfacing arthroplasty.

Per-Ingvar Brånemark was a Swedish physician and research professor, acknowledged as the "father of modern dental implantology". The Brånemark Osseointegration Center (BOC), named after its founder, was founded in 1989 in Gothenburg, Sweden.

Bioceramics and bioglasses are ceramic materials that are biocompatible. Bioceramics are an important subset of biomaterials. Bioceramics range in biocompatibility from the ceramic oxides, which are inert in the body, to the other extreme of resorbable materials, which are eventually replaced by the body after they have assisted repair. Bioceramics are used in many types of medical procedures. Bioceramics are typically used as rigid materials in surgical implants, though some bioceramics are flexible. The ceramic materials used are not the same as porcelain type ceramic materials. Rather, bioceramics are closely related to either the body's own materials or are extremely durable metal oxides.
Resonance frequency analysis (RFA) is a method used to determine stability in dental implants. The stability is presented as an implant stability quotient (ISQ) value. The higher the ISQ value the higher the stability.
Metallosis is the medical condition involving deposition and build-up of metal debris in the soft tissues of the body.

Tomas Albrektsson is a Swedish physician who trained under Per-Ingvar Brånemark and is noteworthy for having contributed significantly to the field of implant dentistry.

Titanium was first introduced into surgeries in the 1950s after having been used in dentistry for a decade prior. It is now the metal of choice for prosthetics, internal fixation, inner body devices, and instrumentation. Titanium is used from head to toe in biomedical implants. One can find titanium in neurosurgery, bone conduction hearing aids, false eye implants, spinal fusion cages, pacemakers, toe implants, and shoulder/elbow/hip/knee replacements along with many more. The main reason why titanium is often used in the body is due to titanium's biocompatibility and, with surface modifications, bioactive surface. The surface characteristics that affect biocompatibility are surface texture, steric hindrance, binding sites, and hydrophobicity (wetting). These characteristics are optimized to create an ideal cellular response. Some medical implants, as well as parts of surgical instruments are coated with titanium nitride (TiN).
Nikos Athanasou is a short story writer and novelist and musculoskeletal pathologist and scientist. He was born in Perth and grew up in Sydney where he studied medicine. He moved to England and is currently Professor of Musculoskeletal Pathology at Oxford University and a Fellow of Wadham College.
Implant failure refers to the failure of any medical implant to meet the claims of its manufacturer or the health care provider involved in its installation. Implant failure can have any number of causes. The rates of failure vary for different implants.
Cochlear Bone Anchored Solutions is a company based in Gothenburg, Sweden that manufactures and distributes bone conduction hearing solutions under the trademark Baha. The company was founded in 1999 under the name Entific Medical Systems. When Cochlear bought the company in 2005, the name was changed to Cochlear Bone Anchored Solutions. The acronym "BAHA" was trademarked into Baha, as it is not considered a hearing aid by insurance companies.
Bicon Dental Implants is a privately owned company located in Boston, MA. The company specializes in short dental implants that use a locking taper or cold welding connection to secure the abutment to the implant. Bicon is notable and worthy of mention for the following three reasons: First, Bicon implants are extremely short in length. The size of Bicon implants allow them to be placed in regions that are crowded with natural teeth and/or implants, or in regions that would otherwise require bone grafting. Second, the implants do not have the screw-form design typical of other available implants. Third, the abutments are connected to the implant via a locking taper. This is notable from both a medical and engineering standpoint as no other implant company offers an implant with a biological seal at the implant/abutment interface; almost all other implants possess an internal screw to connect their abutments.
Munjed Al Muderis is an Australian adjunct clinical professor in orthopaedic surgery, author and human rights activist. He has done pioneering work on prosthetics, especially on titanium devices.
Zygoma implants are different from conventional dental implants in that they anchor in to the zygomatic bone rather than the maxilla. They may be used when maxillary bone quality or quantity is inadequate for the placement of regular dental implants. Inadequate maxillary bone volume may be due to bone resorption as well as to pneumatization of the maxillary sinus or to a combination of both. The minimal bone height for a standard implant placement in the posterior region of the upper jaw should be about 10 mm to ensure acceptable implant survival. When there is inadequate bone available, bone grafting procedures and sinus lift procedures may be carried out to increase the volume of bone. Bone grafting procedures in the jaws have the disadvantage of prolonged treatment time, restriction of denture wear, morbidity of the donor surgical site and graft rejection.

Daniel Y. Sullivan was an American dentist, prosthodontist, author, and teacher credited with helping to bring the practice of osseointegrated dental implants, or the fusion of bone and titanium inside the mouth, to the United States. He worked alongside Swedish pioneer Per-Ingvar Brånemark to insert the U.S.’s first osseointegrated dental implants in 1982. In later years, he taught the technique to thousands of dentists, served as president of two prestigious dental membership organizations, and co-wrote one of the first textbooks in the United States on the subject of esthetic dental implants.
The history of dental treatments dates back to thousands of years. The scope of this article is limited to the pre-1981 history.
A root-analog dental implant (RAI) – also known as a truly anatomic dental implant, or an anatomical/custom implant – is a medical device to replace one or more roots of a single tooth immediately after extraction. In contrast to common titanium screw type implants, these implants are custom-made to exactly match the extraction socket of the specific patient. Thus there is usually no need for surgery.
References
- ↑ Unger, AS. "Evaluation of a porous tantalum uncemented actetabular cup in revision total hip arthoplasty. Clinical and radiological results of 60 hips". J Arthroplasty, 2005, p 1002-1009
- ↑ Cohen R. "A porous tantalum trabedcular metal: basic science". Am J Orthrop, 2002, p. 216-217
- ↑ Bobyn JD. "UHMWPE: the good, bad, & ugly. Fixation and bearing surfaces for the next millennium". Orthop, 1999, p. 810-812
- ↑ Branemark PI. "Introduction to osseointegration". In Branemark PI, Zarb GA, and Albrektsson T. eds.: Tissue-Integrated Prosthese. Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry. Chicago, IL: Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc.: 1985, p. 11-76
- ↑ Branemark PI. "Introduction to osseointegration". In Branemark PI, Zarb GA, and Albrektsson T. eds.: Tissue-Integrated Prosthese. Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry. Chicago, IL: Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc.: 1985, p. 11-76
- ↑ Osseointegration Study, Journal of Oral Implantology, 2001—Burton E. Balkin et al.
- ↑ Unger, AS. "Evaluation of a porous tantalum uncemented actetabular cup in revision total hip arthoplasty. Clinical and radiological results of 60 hips". J Arthroplasty, 2005, p 1002-1009
- ↑ Cohen R. "A porous tantalum trabedcular metal: basic science". Am J Orthrop, 2002, p. 216-217
- ↑ Bobyn JD. "UHMWPE: the good, bad, & ugly. Fixation and bearing surfaces for the next millennium". Orthop, 1999, p. 810-812
- ↑ Tsao AK. "Biomechanical and clinical evaluations of a porous tantaluym implant for the treatment of early-stage osteonecrosis". J Bone Joint Surg, 2005, p.22-27
- ↑ Bobyn JD. "Clinical validation of a structural porous tantalum biomaterial for adult reconstruction". J Bone Joint Surg, 2004, p. 123-129
- ↑ E.T. den Braber, H.V. Jansen, M.J. de Boer, H.J.E. Croes, M. Elwenspoek, and J.A. Jansen, Scanning electron microscopic, transmission electron microscopic, and confocal laser scanning microscopic observation of fibroblasts cultured on microgrooved surfaces of bulk titanium substrata, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 1998, 425-433
- ↑ S. Raghavendra, M. C. Wood, T. D. Taylor. Early wound healing adjacent to endosseous dental implants: A review of the literature. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants., 2005, 425–31
- ↑ F. Rupp, L. Scheideler, N. Olshanska, M. de Wild, M. Wieland, J. Geis-Gerstorfer. Enhancing surface free energy and hydrophilicity through chemical modification of microstructured titanium implant surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2006, 323–33 4