Related Research Articles

A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body such as from lung, breast, thyroid, kidney and prostate. There may be a lump, pain, or neurological signs from pressure. A bone tumor might present with a pathologic fracture. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, anemia and nausea. Sometimes there are no symptoms and the tumour is found when investigating another problem.

Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics, is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders.
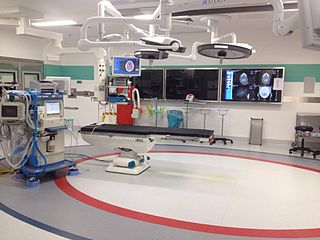
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical subspecialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement, and angioplasty of narrowed structures.

Interventional cardiology is a branch of cardiology that deals specifically with the catheter based treatment of structural heart diseases. Andreas Gruentzig is considered the father of interventional cardiology after the development of angioplasty by interventional radiologist Charles Dotter.
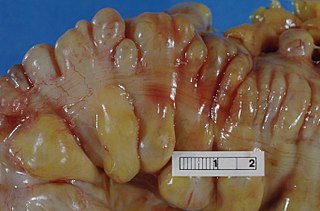
Diverticulitis, specifically colonic diverticulitis, is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by inflammation of abnormal pouches—diverticula—which can develop in the wall of the large intestine. Symptoms typically include lower abdominal pain of sudden onset, but the onset may also occur over a few days. There may also be nausea; and diarrhea or constipation. Fever or blood in the stool suggests a complication. Repeated attacks may occur.
Spinal tumors are neoplasms located in either the vertebral column or the spinal cord. There are three main types of spinal tumors classified based on their location: extradural and intradural. Extradural tumors are located outside the dura mater lining and are most commonly metastatic. Intradural tumors are located inside the dura mater lining and are further subdivided into intramedullary and extramedullary tumors. Intradural-intramedullary tumors are located within the dura and spinal cord parenchyma, while intradural-extramedullary tumors are located within the dura but outside the spinal cord parenchyma. The most common presenting symptom of spinal tumors is nocturnal back pain. Other common symptoms include muscle weakness, sensory loss, and difficulty walking. Loss of bowel and bladder control may occur during the later stages of the disease.

A pancreaticoduodenectomy, also known as a Whipple procedure, is a major surgical operation most often performed to remove cancerous tumours from the head of the pancreas. It is also used for the treatment of pancreatic or duodenal trauma, or chronic pancreatitis. Due to the shared blood supply of organs in the proximal gastrointestinal system, surgical removal of the head of the pancreas also necessitates removal of the duodenum, proximal jejunum, gallbladder, and, occasionally, part of the stomach.

Spinal fusion, also called spondylodesis or spondylosyndesis, is a neurosurgical or orthopedic surgical technique that joins two or more vertebrae. This procedure can be performed at any level in the spine and prevents any movement between the fused vertebrae. There are many types of spinal fusion and each technique involves using bone grafting—either from the patient (autograft), donor (allograft), or artificial bone substitutes—to help the bones heal together. Additional hardware is often used to hold the bones in place while the graft fuses the two vertebrae together. The placement of hardware can be guided by fluoroscopy, navigation systems, or robotics.

Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor or other dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium frequency alternating current. RFA is generally conducted in the outpatient setting, using either local anesthetics or conscious sedation anesthesia. When it is delivered via catheter, it is called radiofrequency catheter ablation.
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person.
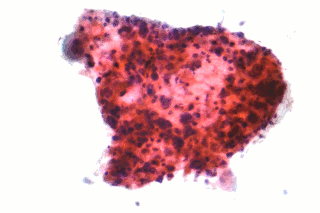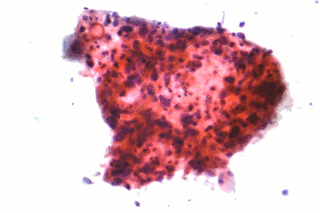
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively and postoperatively.

Cryoablation is a process that uses extreme cold to destroy tissue. Cryoablation is performed using hollow needles (cryoprobes) through which cooled, thermally conductive, fluids are circulated. Cryoprobes are positioned adjacent to the target in such a way that the freezing process will destroy the diseased tissue. Once the probes are in place, the attached cryogenic freezing unit removes heat from ("cools") the tip of the probe and by extension from the surrounding tissues.

An osteoid osteoma is a benign (non-cancerous) bone tumor that arises from osteoblasts and some components of osteoclasts. It was originally thought to be a smaller version of an osteoblastoma. Osteoid osteomas tend to be less than 1.5 cm in size. The tumor can be in any bone in the body but are most common in long bones, such as the femur and tibia. They account for 10 to 12 percent of all benign bone tumors. Osteoid osteomas may occur at any age, and are most common in patients between the ages of 4 and 25 years old. Males are affected approximately three times more commonly than females.
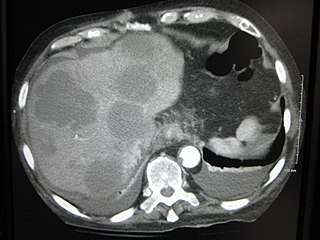
A liver metastasis is a malignant tumor in the liver that has spread from another organ affected by cancer. The liver is a common site for metastatic disease because of its rich, dual blood supply. Metastatic tumors in the liver are 20 times more common than primary tumors. In 50% of all cases the primary tumor is of the gastrointestinal tract, other common sites include the breast, ovaries, bronchus and kidney.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent cells found in multiple human adult tissues including bone marrow, synovial tissues, and adipose tissues. Since they are derived from the mesoderm, they have been shown to differentiate into bone, cartilage, muscle, and adipose tissue. MSCs from embryonic sources have shown promise scientifically while creating significant controversy. As a result, many researchers have focused on adult stem cells, or stem cells isolated from adult humans that can be transplanted into damaged tissue.

Bone metastases, or osseous metastatic disease, is a category of cancer metastases that results from primary tumor invasion to bone. Bone-originating primary tumors such as osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing's sarcoma are rare. Bone metastases can be classified as osteolytic, osteoblastic, or both. Unlike hematological malignancies that originate in the blood and form non-solid tumors, bone metastases generally arise from epithelial tumors and form a solid mass inside the bone. Bone metastases cause severe pain, characterized by a dull, constant ache with periodic spikes of incident pain.

Metastatic breast cancer, also referred to as metastases, advanced breast cancer, secondary tumors, secondaries or stage IV breast cancer, is a stage of breast cancer where the breast cancer cells have spread to distant sites beyond the axillary lymph nodes. There is no cure for metastatic breast cancer; There is no stage after IV.
John H. Healey is an American cancer surgeon, researcher, and expert in the surgical treatment of benign and malignant bone tumors and other musculoskeletal cancers. He serves as Chair of the Orthopaedic Service and Stephen P. McDermott Chair in Surgery at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC), as well as Professor of Surgery at Weill Cornell Medical College, in New York, NY.
DFINE, Inc. was an American medical device company with headquarters in San Jose, California. It was known for its development of minimally invasive therapeutic devices built upon a radiofrequency platform for the treatment of spinal diseases. The platform included two applications, the StabiliT Vertebral Augmentation System for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures and the STAR Tumor Ablation System for pain relief treatment of metastatic spinal tumors.
Interventional oncology is a subspecialty field of interventional radiology that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer and cancer-related problems using targeted minimally invasive procedures performed under image guidance. Interventional oncology has developed to a separate pillar of modern oncology and it employs X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help guide miniaturized instruments to allow targeted and precise treatment of solid tumours located in various organs of the human body, including but not limited to the liver, kidneys, lungs, and bones. Interventional oncology treatments are routinely carried out by interventional radiologists in appropriate settings and facilities.
References
- ↑ Collins English Dictionary 1998
- ↑ Arthroscopic Labral Repair with Osteoplasty of Femoral Neck and Acetabulum. Snibbe Orthopedics. Retrieved 11 October 2014.
- ↑ 'Miraculous' Effects, Pain Relief Of Osteoplasty Shown For Those Suffering From Metastatic Bone Disease. Science Daily (10 March 2009). Retrieved 11 October 2014.
- ↑ Anselmetti, Giovanni Carlo (June 2010). "Osteoplasty: Percutaneous Bone Cement Injection beyond the Spine". Seminars in Interventional Radiology. 27 (2): 199–208. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1253518. PMC 3036518 . PMID 21629409.
- ↑ Luca Pierannunzii, MD; Marco d'Imporzano, MD Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement: A Modified Resection Osteoplasty Technique Through an Anterior Approach. Healio Orthopedics (February 2007, Vol 30, Issue 2). Retrieved 11 October 2014.