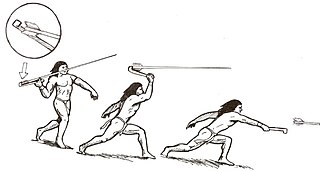
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever or atlatl is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a bearing surface which allows the user to store energy during the throw.

An oxbow lake is a U-shaped lake that forms when a wide meander of a river is cut off, creating a free-standing body of water. In south Texas, oxbows left by the Rio Grande are called resacas. In Australia, oxbow lakes are called billabongs. The word "oxbow" can also refer to a U-shaped bend in a river or stream, whether or not it is cut off from the main stream.

Clovis points are the characteristically fluted projectile points associated with the New World Clovis culture. They are present in dense concentrations across much of North America; in South America, they are largely restricted to the north of that continent. Clovis points date to the Early Paleoindian period, with all known points dating to the 600 years between roughly 13,500 to 12,800 calendar years ago. Clovis fluted points are named after the city of Clovis, New Mexico, where examples were first found in 1929 by Ridgely Whiteman.

The Ahrensburg culture or Ahrensburgian was a late Upper Paleolithic nomadic hunter culture in north-central Europe during the Younger Dryas, the last spell of cold at the end of the Weichsel glaciation resulting in deforestation and the formation of a tundra with bushy arctic white birch and rowan. The most important prey was the wild reindeer. The earliest definite finds of arrow and bow date to this culture, though these weapons might have been invented earlier. The Ahrensburgian was preceded by the Hamburg and Federmesser cultures and superseded by the Maglemosian and Swiderian cultures. Ahrensburgian finds were made in southern and western Scandinavia, the North German plain and western Poland. The Ahrensburgian area also included vast stretches of land now at the bottom of the North and Baltic Sea, since during the Younger Dryas the coastline took a much more northern course than today.
Oshara Tradition, the northern tradition of the Picosa culture, was a Southwestern Archaic Tradition centered in the area now called New Mexico and Colorado. Cynthia Irwin-Williams developed the sequence of Archaic culture for Oshara during her work in the Arroyo Cuervo area of northwestern New Mexico. Irwin contends that the Ancestral Puebloans developed, at least in part, from the Oshara.
The Comondú Complex is an archaeological pattern dating from the late prehistoric period in northern Baja California Sur and southern Baja California. It is associated with the historic Cochimí people of the peninsula.

The Swiderian culture is an Upper Palaeolithic/Mesolithic cultural complex, centred on the area of modern Poland. The type-site is Świdry Wielkie, in Otwock near the Swider River, a tributary to the Vistula River, in Masovia. The Swiderian is recognized as a distinctive culture that developed on the sand dunes left behind by the retreating glaciers. Rimantienė (1996) considered the relationship between Swiderian and Solutrean "outstanding, though also indirect", in contrast with the Bromme-Ahrensburg complex, for which she introduced the term "Baltic Magdalenian" for generalizing all other North European Late Paleolithic culture groups that have a common origin in Aurignacian.

The Eva site (40BN12) is a prehistoric Native American site in Benton County, Tennessee, in the Southeastern United States. Located along an ancient channel of the Tennessee River, the Eva site saw extensive periods of occupation during the Middle and Late Archaic period. The site's well-defined midden layers helped investigators identify three distinct Archaic cultures, the oldest of which was first identified at Eva and is still known as the "Eva culture" or the "Eva phase."
The Prehistory of West Virginia spans ancient times until the arrival of Europeans in the early 17th century. Hunters ventured into West Virginia's mountain valleys and made temporary camp villages since the Archaic period in the Americas. Many ancient human-made earthen mounds from various mound builder cultures survive, especially in the areas of Moundsville, South Charleston, and Romney. The artifacts uncovered in these areas give evidence of a village society with a tribal trade system culture that included limited cold worked copper. As of 2009, over 12,500 archaeological sites have been documented in West Virginia.
Prehistory of Colorado provides an overview of the activities that occurred prior to Colorado's recorded history. Colorado experienced cataclysmic geological events over billions of years, which shaped the land and resulted in diverse ecosystems. The ecosystems included several ice ages, tropical oceans, and a massive volcanic eruption. Then, ancient layers of earth rose to become the Rocky Mountains.

The Paiján culture was an archaeological culture that emerged on the northern coast of Peru between 13,000 and 10,000 cal BP. It was first described by Peruvian archaeologist Rafael Larco Hoyle in the 1940s from the Pampa de los Fósiles site. Later research, mainly by French archaeologist Claude Chauchat, identified dozens of open air sites, which include camps, workshops and quarries.
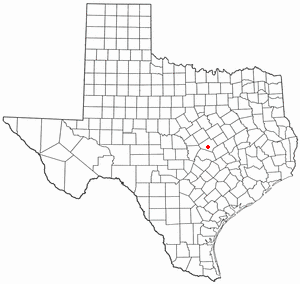
Buttermilk Creek Complex refers to the remains of a paleolithic settlement along the shores of Buttermilk Creek in present-day Salado, Texas dated to approximately 15,500 years old. If confirmed, the site represents evidence of human settlement in the Americas that pre-dates the Clovis culture.

Golondrina points are lanceolate spear or dart projectile points, of medium size, dated to the transitional Paleo-Indian Period, between 9000–7000 BP. Golondrina points were attached on split-stem hafts and may have served to bring down medium-sized animals such as deer, as well as functioning as butchering knives. Distribution is widespread throughout most of Texas, and points have also been discovered in Arkansas and Mexico. The concentration of Golondrina specimens is highest across the South Texas Plains, where the point is the most prevalent of Paleo-Indian types and defines a distinctive cultural pattern for the region. The Golondrina point is so named for its flared basal corners ("ears"), which resemble a swallow's split tail. Classification of Golondrina can be difficult because of its similarity to other types, particularly the Plainview point, to which it was originally thought to be related.

In the classification of Archaeological cultures of North America, the term Plainview points refer to Paleoindian projectile points dated between 10,000–9,000 Before Present. The point was named in 1947 after the discovery of a large cache of unfluted, lanceolate spear tips with concave bases that were found in a Bison antiquus kill site along the Running Water Draw river, near the town of Plainview in Texas, United States. The point is found primarily throughout the South Plains, however, this range may sometimes be misidentified, as "Plainview" was previously used as a general term to describe unfluted lanceolate points throughout the entirety of the Plains, as well as the eastern Upper Mississippi Valley.

The Jurgens Site is a Paleo-Indian site located near Greeley in Weld County, Colorado. While the site was used primarily to hunt and butcher bison antiquus, there is evidence that the Paleo-Indians also gathered plants and seeds for food about 7,000 to 7,500 BC.
Apex complex is a cultural tradition of the Middle Archaic period. Apex complex artifacts, dated from about 3000 to 500 BC, first appeared in the Magic Mountain Site near Apex Creek in Colorado.
The Goshen point is a medium-sized, lanceolate-shaped, Paleo-Indian projectile point with a straight or concave base. It exhibits characteristic fine flaking.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the prehistoric people of Colorado, which covers the period of when Native Americans lived in Colorado prior to contact with the Domínguez–Escalante expedition in 1776. People's lifestyles included nomadic hunter-gathering, semi-permanent village dwelling, and residing in pueblos.

The La Garma cave complex is a parietal art-bearing paleoanthropological cave system in Cantabria, Spain. It is located just north of the village of Omoño, part of the municipality of Ribamontán al Monte. The cave complex is noted for one of the best preserved floors from the Paleolithic containing more than 4,000 fossils and more than 500 graphical units. It is part of the Cave of Altamira and Paleolithic Cave Art of Northern Spain World Heritage Site.
The Quad Site is a series of Paleoindian sites and localities in Limestone County near Decatur, Alabama. It was first reported by Frank Soday in 1954, and later findings were also documented by James Cambron, David Hulse and Joe Wright and Cambron and Hulse. The Quad Locale can seldom be viewed at current lake levels, even during normal winter pool, due to extensive erosion, but is considered one of the most important and well known Paleoindian sites in the Southeastern United States.











