This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
This article is missing information about historic events related to the product since 2005 .(February 2016) |
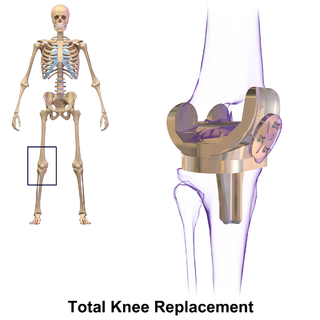
Oxinium is the brand name of a material used for replacement joints manufactured by the reconstructive orthopedic surgery division of medical devices company Smith & Nephew. It consists of a zirconium alloy metal substrate that transitions into a ceramic zirconium oxide outer surface.

Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics, also spelled orthopaedics, is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders.
Smith & Nephew plc is a British multinational medical equipment manufacturing company headquartered in London, United Kingdom. It is an international producer of advanced wound management products, arthroscopy products, trauma and clinical therapy products, and orthopaedic reconstruction products. Its products are sold in over 120 countries. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.

Zirconium is a chemical element with symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name zirconium is taken from the name of the mineral zircon, the most important source of zirconium. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that closely resembles hafnium and, to a lesser extent, titanium. Zirconium is mainly used as a refractory and opacifier, although small amounts are used as an alloying agent for its strong resistance to corrosion. Zirconium forms a variety of inorganic and organometallic compounds such as zirconium dioxide and zirconocene dichloride, respectively. Five isotopes occur naturally, three of which are stable. Zirconium compounds have no known biological role.
The ceramic surface is extremely abrasion resistant compared to traditional metal implant materials such as cobalt chromium. It also has a lower coefficient of friction against ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), the typical counterface material used in total joint replacements. These two factors likely contribute to the significantly lower UHMWPE wear rates observed in simulator testing. Reducing UHMWPE wear is thought to decrease the risk of implant failure due to osteolysis. All-ceramic materials can have a similar effect on reducing wear, but are brittle and difficult to manufacture. The metal substrate of Oxinium implants makes components easier to manufacture and gives them greater toughness (a combination of strength and ductility). In essence, this technology combines the abrasion resistance and low friction of a ceramic with the workability and toughness of a metal.[ citation needed ]

Vitallium is a trademark for an alloy of 65% cobalt, 30% chromium, 5% molybdenum, and other substances. The alloy is used in dentistry and artificial joints, because of its resistance to corrosion. It is also used for components of turbochargers because of its thermal resistance. Vitallium was developed by Albert W. Merrick for the Austenal Laboratories in 1932.
Osteolysis is an active resorption of bone matrix by osteoclasts and can be interpreted as the reverse of ossification. Although osteoclasts are active during the natural formation of healthy bone the term "osteolysis" specifically refers to a pathological process. Osteolysis often occurs in the proximity of a prosthesis that causes either an immunological response or changes in the bone's structural load. Osteolysis may also be caused by pathologies like bone tumors, cysts, or chronic inflammation.
This combination of properties led to Oxinium technology being the first ever implant-related technology to win the prestigious ASM International Engineering Materials Achievement Award (EMAA) in 2005.[ citation needed ]

ASM International, formerly known as the American Society for Metals, is a professional organization for materials scientists and engineers.
Current competitive reduced-wear options in total hip arthroplasty (THA) are ceramic-on-ceramic, metal-on-metal, and metal-on-cross-linked polyethylene. The only competitive reduced-wear option for total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is metal-on-cross-linked polyethylene.

Hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant, that is, a hip prosthesis. Hip replacement surgery can be performed as a total replacement or a hemi (half) replacement. Such joint replacement orthopaedic surgery is generally conducted to relieve arthritis pain or in some hip fractures. A total hip replacement consists of replacing both the acetabulum and the femoral head while hemiarthroplasty generally only replaces the femoral head. Hip replacement is currently one of the most common orthopaedic operations, though patient satisfaction short- and long-term varies widely. Approximately 58% of total hip replacements are estimated to last 25 years. The average cost of a total hip replacement in 2012 was $40,364 in the United States, and about $7,700 to $12,000 in most European countries.

A ceramic is a solid material comprising an inorganic compound of metal, non-metal or metalloid atoms primarily held in ionic and covalent bonds. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick.

A metal is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically malleable or ductile. A metal may be a chemical element such as iron, or an alloy such as stainless steel.
In September 2003, Smith & Nephew recalled its Macrotextured Oxinium Profix and Genesis II knee implants because of reports that 30 people receiving the implants without bone cement had to undergo a replacement surgery after they became loose. [1]