Related Research Articles
A backplane is a group of electrical connectors in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors, forming a computer bus. It is used as a backbone to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete computer system. Backplanes commonly use a printed circuit board, but wire-wrapped backplanes have also been used in minicomputers and high-reliability applications.

PCI Express, officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard drives, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism, and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization.

A single-board computer (SBC) is a complete computer built on a single circuit board, with microprocessor(s), memory, input/output (I/O) and other features required of a functional computer. Single-board computers are commonly made as demonstration or development systems, for educational systems, or for use as embedded computer controllers. Many types of home computers or portable computers integrate all their functions onto a single printed circuit board.

CompactPCI is a computer bus interconnect for industrial computers, combining a Eurocard-type connector and PCI signaling and protocols. Boards are standardized to 3U or 6U sizes, and are typically interconnected via a passive backplane. The connector pin assignments are standardized by the PICMG US and PICMG Europe organizations. The connectors and the electrical rules allow for eight boards in a PCI segment. Multiple bus segments are allowed with bridges.

A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, while still having all the functional components to be considered a computer. Unlike a rack-mount server, a blade server fits inside a blade enclosure, which can hold multiple blade servers, providing services such as power, cooling, networking, various interconnects and management. Together, blades and the blade enclosure form a blade system, which may itself be rack-mounted. Different blade providers have differing principles regarding what to include in the blade itself, and in the blade system as a whole.
PC/104 is a family of embedded computer standards which define both form factors and computer buses by the PC/104 Consortium. PC/104 is intended for specialized environments where a small, rugged computer system is required. The standard is modular, and allows consumers to stack together boards from a variety of COTS manufacturers to produce a customized embedded system.
The PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group (PICMG) is a consortium of over 150 companies. Founded in 1994, the group was originally formed to adapt PCI technology for use in high-performance telecommunications, military, and industrial computing applications, but its work has now grown to include newer technologies. PICMG is distinct from the similarly named and adjacently-focused PCI Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG).
Advanced Mezzanine Cards are printed circuit boards (PCBs) that follow a specification of the PCI Industrial Computers Manufacturers Group (PICMG), with more than 100 companies participating.
ETX, standing for Embedded Technology eXtended, is an integrated and compact 95 × 125 mm (3.7 × 4.9 in) computer-on-module (COM) form factor, which can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component. Each ETX COM integrates core CPU and memory functionality, the common I/O of a PC/AT, USB, audio, graphics, and Ethernet. All I/O signals as well as a full implementation of ISA and PCI buses are mapped to four high-density, low-profile connectors on the bottom side of the module.
COM Express, a computer-on-module (COM) form factor, is a highly integrated and compact PC that can be used in a design application much like an integrated circuit component. Each COM Express Module COM integrates core CPU and memory functionality, the common I/O of a PC/AT, USB, audio, graphics (PEG), and Ethernet. All I/O signals are mapped to two high density, low profile connectors on the bottom side of the module. COM Express employs a mezzanine-based approach. The COM modules plug into a baseboard that is typically customized to the application. Over time, the COM Express mezzanine modules can be upgraded to newer, backwards-compatible versions. COM Express is commonly used in Industrial, Military/Aerospace, Gaming, Medical, Transportation, IoT, and General Computing embedded applications.
In computing, the form factor is the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case. Small form factors have been developed and implemented.

VPX technology was presented at Bus&Board (VITA) in 2004. VPX, also known as VITA 46, is an ANSI standard that provides VMEbus-based systems with support for switched fabrics over a new high speed connector. Defined by the VITA working group, it has been designed specifically with defense applications in mind, with an enhanced module standard that enables applications and platforms with superior performance. VPX retains VME's existing 6U and 3U Eurocard form factors, supporting existing PCI Mezzanine Card (PMC) and XMC mezzanines, and maintaining the maximum possible compatibility with VMEbus.

The Small Form Factor Special Interest Group or SFF-SIG is an international non-profit standards body focused on modular computer hardware technologies used in embedded and small form factor computers and controllers. Members are mainly computer board and component manufacturers.
ESMexpress is a very compact computer-on-module (COM) standard. It is a complete processor module that currently supports several low-power Intel and PowerPC platforms. Apart from a CPU component, every module also includes memory and a range of serial communication interfaces such as PCI Express, Gigabit Ethernet, USB, SATA, SDVO, LVDS and HD audio. These interfaces are defined in the form factor's specification, and signals are assigned to two 120-pin connectors. This fixed pin mapping ensures that different ESMexpress modules can be exchanged more easily. Consequently, ESMexpress typically does not have an onboard FPGA. The idea behind this is to implement very specialized functions in an FPGA on the COM's carrier board to ease upgrades of the system CPU through exchange of the ESMexpress module.
CompactPCI Serial is an industrial standard for modular computer systems. It is based on the established PICMG 2.0 CompactPCI standard, which uses the parallel PCI bus for communication among a system's card components. In contrast to this, CompactPCI Serial uses only serial point-to-point connections. CompactPCI Serial was officially adopted by the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group PICMG as PICMG CPCI-S.0 CompactPCI Serial in March 2011. Its mechanical concept is based on the proven standards of IEEE 1101-1-1998 and IEEE 1101-10-1996. CompactPCI Serial includes different connectors that permit very high data rates. The new technology standard succeeding parallel CompactPCI comprises another specification called PICMG 2.30 CompactPCI PlusIO. This is why CompactPCI Serial and CompactPCI PlusIO as a whole were also called CompactPCI Plus. PICMG's first working title of CompactPCI Serial was CPLUS.0. CompactPCI Serial backplanes and chassis are developed by Schroff, Elmа, and Pixus Technologies companies, as for the CompactPCI Serial board level electronics – they are developed by MEN Mikro Elektronik, Fastwel, EKF, Emerson Embedded Computing, ADLINK, and Kontron.
Hybricon Corporation is a provider of systems packaging solutions serving the Military, Aerospace, Homeland Security, Medical and high-end Industrial markets and develops embedded computing systems and solutions for war fighter critical missions using OpenVPX, VPX, VXS, VMEbus, VME64X, CompactPCI, Rugged MicroTCA, and custom bus structures.
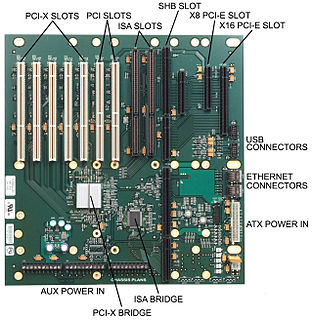
PICMG 1.0 is a PICMG specification that defines a CPU form factor and corresponding backplane connectors for PCI-ISA passive backplanes. This standard moves components typically located on the motherboard to a single plug-in card. PICMG 1.0 CPU Cards look much like standard ISA cards with extra gold finger connections for the ISA bus and the root PCI bus. The "motherboard" is replaced with a simple "passive backplane" that has only PCI and ISA connectors attached to it. These backplane connections include a dedicated system slot of the PICMG 1.0 CPU and various connections for standard ISA and PCI peripheral cards. This backplane is simple and robust, with a very low likelihood of failure, given its passive nature. This allows a much lower Mean Time to Repair than classic computer motherboard approaches, as electronics associated with CPUs can be replaced without having to remove peripheral devices.
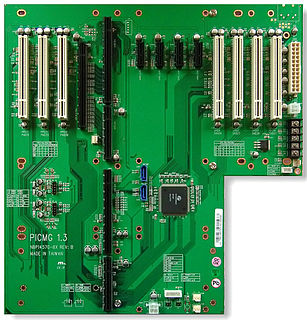
PICMG 1.3 is a PICMG specification which is commonly referred to as SHB Express. SHB Express is a modernization of PICMG 1.0 single board computer specification. SHB Express, or System Host Board – Express, uses the same physical form factor as PICMG 1.0 boards. The board-to-backplane interfaces are PCI Express instead of PCI and ISA, although the use of PCI remains as an option.
PICMG 2.5 is a specification by PICMG that standardizes the utilization of CompactPCI user definable pins for the computer telephony functions of standard TDM bus, telephony rear IO, 48 VDC and ringing distribution in a 6U chassis environment.
References
- ↑ "PICMG 1.2, EMBEDDED PCI-X SPECIFICATION". PICMG. Archived from the original on 2009-01-20. Retrieved 2009-11-11.
- ↑ "Embedded PCI-X (ePCI-X) for Standard Form Factor PCI". PICMG. Archived from the original on 2014-07-14.; "Embedded PCI-X (ePCI-X) for Standard Form Factor PCI". PICMG. Archived from the original on 2007-01-09.