Related Research Articles

An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection.

Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is acute if it resolves within six months, and chronic if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer.

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin. The virus persists in the liver, becoming chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach.

Incubation period is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical, or radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent. In a typical infectious disease, the incubation period signifies the period taken by the multiplying organism to reach a threshold necessary to produce symptoms in the host.

Hepatitis A is an infectious disease of the liver caused by Hepatovirus A (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is 2–6 weeks. When symptoms occur, they typically last 8 weeks and may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain. Around 10–15% of people experience a recurrence of symptoms during the 6 months after the initial infection. Acute liver failure may rarely occur, with this being more common in the elderly.

Hepatitis E is inflammation of the liver caused by infection with the hepatitis E virus (HEV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Hepatitis E has mainly a fecal-oral transmission route that is similar to hepatitis A, although the viruses are unrelated. In retrospect, the earliest known epidemic of hepatitis E occurred in 1955 in New Delhi, but the virus was not isolated until 1983 by Russian scientists investigating an outbreak in Afghanistan. HEV is a positive-sense, single-stranded, nonenveloped, RNA icosahedral virus and one of five known human hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.
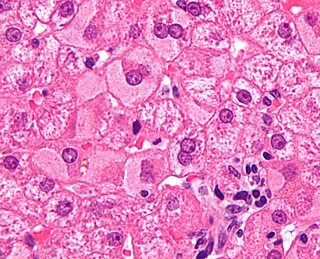
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute form as a recent infection with relatively rapid onset, or in chronic form, typically progressing from a long-lasting asymptomatic condition up to a decompensated hepatic disease and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).

Haemophilus influenzae is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacteria are mesophilic and grow best at temperatures between 35 and 37 °C.

A needlestick injury is the penetration of the skin by a hypodermic needle or other sharp object that has been in contact with blood, tissue or other body fluids before the exposure. Even though the acute physiological effects of a needlestick injury are generally negligible, these injuries can lead to transmission of blood-borne diseases, placing those exposed at increased risk of infection from disease-causing pathogens, such as the hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Among healthcare workers and laboratory personnel worldwide, more than 25 blood-borne virus infections have been reported to have been caused by needlestick injuries. In addition to needlestick injuries, transmission of these viruses can also occur as a result of contamination of the mucous membranes, such as those of the eyes, with blood or body fluids, but needlestick injuries make up more than 80% of all percutaneous exposure incidents in the United States. Various other occupations are also at increased risk of needlestick injury, including law enforcement, laborers, tattoo artists, food preparers, and agricultural workers.
Hepatitis B is endemic in China. Of the 350 million individuals worldwide infected with the hepatitis B virus (HBV), one-third reside in China. As of 2006 China has immunized 11.1 million children in its poorest provinces as part of several programs initiated by the Chinese government and as part of the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization (GAVI). However, the effects of these programs have yet to reach levels of immunization that would limit the spread of hepatitis B effectively.

Medical microbiology, the large subset of microbiology that is applied to medicine, is a branch of medical science concerned with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases. In addition, this field of science studies various clinical applications of microbes for the improvement of health. There are four kinds of microorganisms that cause infectious disease: bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses, and one type of infectious protein called prion.

Hepatitis B vaccine is a vaccine that prevents hepatitis B. The first dose is recommended within 24 hours of birth with either two or three more doses given after that. This includes those with poor immune function such as from HIV/AIDS and those born premature. It is also recommended that health-care workers be vaccinated. In healthy people, routine immunization results in more than 95% of people being protected.

Hepatitis A vaccine is a vaccine that prevents hepatitis A. It is effective in around 95% of cases and lasts for at least twenty years and possibly a person's entire life. If given, two doses are recommended beginning after the age of one. It is given by injection into a muscle. The first hepatitis A vaccine was approved in Europe in 1991, and the United States in 1995. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.

World Hepatitis Day, observed on July 28 every year, aims to raise global awareness of hepatitis — a group of infectious diseases known as hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E — and encourage prevention, diagnosis and treatment. Hepatitis affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide, causing acute and chronic disease and killing close to 1.34 million people every year. Hepatitis can cause inflammation of the liver both acutely and chronically, and can kill a person. In some countries hepatitis B is the most common cause of cirrhosis and may also cause liver cancer.

The California Department of Public Health (CDPH) is the state department responsible for public health in California. It is a subdivision of the California Health and Human Services Agency. It enforces some of the laws in the California Health and Safety Codes, notably the licensing of some types of healthcare facilities. One of its functions is to oversee vital records operations throughout the state.

In precolonial Ghana, infectious diseases were the main cause of morbidity and mortality. The modern history of health in Ghana was heavily influenced by international actors such as Christian missionaries, European colonists, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund. In addition, the democratic shift in Ghana spurred healthcare reforms in an attempt to address the presence of infectious and noncommunicable diseases eventually resulting in the formation of the National Health insurance Scheme in place today.
Ian David Gust AO, FRCPA, FRACP, MASM, FT is an Australian medical researcher, virologist, and former science administrator. Gust's area of work is in the development of drugs and vaccines against viral diseases and he is best known for the development of vaccines against the Hepatitis A virus. He currently serves as a non–executive company director and consultant.

The Alliance for Consumer Education (ACE) is a 501(c)(3), non-profit foundation based in Washington, D.C., dedicated to advancing community health and well-being.

Neonatal infections are infections of the neonate (newborn) acquired during prenatal development or within the first four weeks of life. Neonatal infections may be contracted by mother to child transmission, in the birth canal during childbirth, or after birth. Neonatal infections may present soon after delivery, or take several weeks to show symptoms. Some neonatal infections such as HIV, hepatitis B, and malaria do not become apparent until much later. Signs and symptoms of infection may include respiratory distress, temperature instability, irritability, poor feeding, failure to thrive, persistent crying and skin rashes.
References
- ↑ "April 2005 : Parents Possessing, Accessing and Communicating Knowledge about vaccines - Children's Hospital of Philadelphia". Archived from the original on 2009-07-25. Retrieved 2008-10-01. The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia on PKIDs
- ↑ "Needle Points - Organization Aims to Educate About Immunizations". Archived from the original on 2007-11-11. Retrieved 2008-10-01.
- ↑ https://www.charitynavigator.org/ein/911842030
- ↑ Green, William Finley; Hari Conjeevaram (2002). The First Year: Hepatitis B: An Essential Guide for the Newly Diagnosed . Marlowe & Company. ISBN 1-56924-533-9.
- ↑ "404 - this page does not exist". www.kidsgrowth.com. Archived from the original on 2010-02-05. Retrieved 2008-10-01.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help)