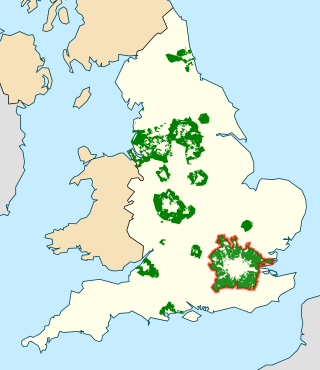
In British town planning, the green belt is a policy for controlling urban growth. The term, coined by Octavia Hill in 1875, refers to a ring of countryside where urbanisation will be resisted for the foreseeable future, maintaining an area where agriculture, forestry and outdoor leisure can be expected to prevail. The fundamental aim of green belt policy is to prevent urban sprawl by keeping land permanently open, and consequently the most important attribute of green belts is their openness.

In the United Kingdom a listed building is a structure of particular architectural and/or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, Cadw in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000, although the statutory term in Ireland is "protected structure".

The Government of Jersey is the executive body of the States of Jersey and is the central government of the Bailiwick of Jersey. The government is led by the Chief Minister, who nominates all the remaining ministers, all elected by the States Assembly.
Town and country planning in the United Kingdom is the part of English land law which concerns land use planning. Its goal is to ensure sustainable economic development and a better environment. Each country of the United Kingdom has its own planning system that is responsible for town and country planning, which outside of England is devolved to the Northern Ireland Assembly, the Scottish Parliament and the Senedd.

A town centre is the commercial or geographical centre or core area of a town. Town centres are traditionally associated with shopping or retail. They are also the centre of communications with major public transport hubs such as train or bus stations. Public buildings including town halls, museums and libraries are often found in town centres.
Regional spatial strategies (RSS) provided regional level planning frameworks for the regions of England outside London. They were introduced in 2004. Their revocation was announced by the new Conservative/Liberal Democrat government on 6 July 2010.
In the United Kingdom, Planning Policy Guidance Notes (PPG) were statements of the Government's national policy and principles towards certain aspects of the town planning framework.
Planning Policy Statements (PPS) were UK government statements of national policy and principles towards certain aspects of the town planning framework. In recent years they only applied to England. However, they still exist within the Northern Irish System.

Environmental Protection Department (EPD) is a department of Hong Kong Government concerning the issues of environmental protection in Hong Kong.The EPD is responsible for developing policies covering environmental protection, nature conservation; enforcing environmental legislation; monitoring environmental quality; providing collection, transfer, treatment and disposal facilities for many types of waste; advising on the environmental implications of town planning and new policies; handling pollution complaints and incidents; and raising awareness and support in the community for environmental initiatives.

A local development framework is the spatial planning strategy introduced in England and Wales by the Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act 2004 and given detail in Planning Policy Statements 12. In most parts of the two countries, maintaining the framework is the responsibility of English district councils and Welsh principal area councils.
Development Management, formerly known as planning control, or development control, is the element of the United Kingdom's system of town and country planning through which local government or the Secretary of State, regulates land use and new building, i.e. development. It relies on a "plan-led system" whereby development plans are produced, involving various stages of public consultation prior to being adopted. Subsequently, development that requires planning permission, which is granted or refused with reference to the development plan as the starting point, then other material considerations are taken into account. The term "development management" is often abbreviated to DM.
Planning Policy Statement 9: Biodiversity and Geological Conservation commonly abbreviated as PPS9, was a document produced by the British Government to advise Local planning authorities on planning policies for the protection of biodiversity and geological conservation through the planning system. This Planning Policy Statement was introduced in August 2005 and replaced Revised PPG 9: Nature conservation. PPS9 was reinforced and updated by Office of the Deputy Prime Minister (ODPM) Circular 06/2005: Biodiversity and Geological Conservation - Statutory Obligations and Their Impact Within the Planning System, also published by the British Government on 15 August 2005.

The Planning Act 2008 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom intended to speed up the process for approving major new infrastructure projects such as airports, roads, harbours, energy facilities such as nuclear power and waste facilities. Along with the Climate Change Bill and the Energy Bill this bill was considered by the Brown administration to be one of the "three legislative pillars of the Government's strategy to secure long-term prosperity and quality of life for all". The Infrastructure Planning Commission has since been abolished and replaced with the Planning Inspectorate as of 31 March 2012.

Nationally significant infrastructure projects (NSIP) are major infrastructure developments in England and Wales that bypass normal local planning requirements. These include proposals for power plants, large renewable energy projects, new airports and airport extensions, and major road projects. The NSIP nomenclature began to be used in 2008, and since April 2012 these projects have been managed by the Planning Inspectorate.

The Metropolitan Green Belt is a statutory green belt around London, England. It comprises parts of Greater London, Berkshire, Buckinghamshire, Essex, Hertfordshire, Kent and Surrey, parts of two of the three districts of Bedfordshire and a small area in Copthorne, Sussex. As of 2017/18, Government statistics show the planning designation covered 513,860 hectares of land.

The National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF) is a land-use planning policy in the United Kingdom. It was originally published by the UK's Department of Communities and Local Government in March 2012, consolidating over two dozen previously issued documents called Planning Policy Statements (PPS) and Planning Policy Guidance Notes (PPG) for use in England. It has since been revised in 2018, 2019 and 2021.
Khodar Bazar is a census town within the jurisdiction of the Baruipur police station in the Baruipur CD block in the Baruipur subdivision of the South 24 Parganas district in the Indian State of West Bengal.
Barkalikapur is a census town within the jurisdiction of the Bishnupur police station in the Bishnupur II CD block in the Alipore Sadar subdivision of the South 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal.
Bamna is a census town within the jurisdiction of the Usthi police station in the Magrahat I CD block in the Diamond Harbour subdivision of the South 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal.
Durganagar is a census town within the jurisdiction of the Diamond Harbour police station in the Diamond Harbour I CD block in the Diamond Harbour subdivision of the South 24 Parganas district in the Indian state of West Bengal.









