
Vitiligo is a long-term skin condition characterized by patches of the skin losing their pigment. The patches of skin affected become white and usually have sharp margins. The hair from the skin may also become white. The inside of the mouth and nose may also be involved. Typically both sides of the body are affected. Often the patches begin on areas of skin that are exposed to the sun. It is more noticeable in people with dark skin. Vitiligo may result in psychological stress and those affected may be stigmatized.
PUVA is an ultraviolet light therapy treatment for eczema, psoriasis, graft-versus-host disease, vitiligo, mycosis fungoides, large-plaque parapsoriasis and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma using the sensitizing effects of the drug psoralen. The psoralen is applied or taken orally to sensitize the skin, then the skin is exposed to UVA.

Methoxsalen is a drug used to treat psoriasis, eczema, vitiligo, and some cutaneous lymphomas in conjunction with exposing the skin to UVA light from lamps or sunlight. Methoxsalen modifies the way skin cells receive the UVA radiation, allegedly clearing up the disease. The dosage comes in 10 mg tablets, which are taken in the amount of 30 mg 75 minutes before a PUVA light treatment. Levels of individual patient PUVA exposure were originally determined using the Fitzpatrick scale. The scale was developed after patients demonstrated symptoms of phototoxicity after oral ingestion of Methoxsalen followed by PUVA therapy. Chemically, methoxsalen belongs to a class of organic natural molecules known as furanocoumarins. They consist of coumarin annulated with furan. It can also be injected and used topically.

The music of the Harry Potter film series was recorded and released in conjunction with the post-production and releases of each of the eight corresponding films. The scores were composed by John Williams, Patrick Doyle, Nicholas Hooper, and Alexandre Desplat. Musicians credited with writing source music include Jarvis Cocker, The Ordinary Boys and Nick Cave and the Bad Seeds. Jeremy Soule and James Hannigan wrote the music for the Harry Potter video games.
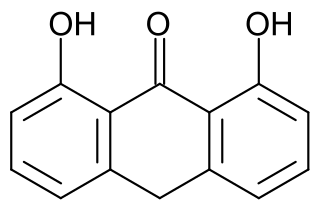
Dithranol (INN) or anthralin is a Hydroxyanthrone, anthracene derivative, medicine applied to the skin of people with psoriasis. It is available as creams, ointment or pastes in 0.1 to 2% strengths. The terms dithranol and anthralin are sometimes used synonymously.

A lentigo is a small pigmented spot on the skin with a clearly defined edge, surrounded by normal-appearing skin. It is a harmless (benign) hyperplasia of melanocytes which is linear in its spread. This means the hyperplasia of melanocytes is restricted to the cell layer directly above the basement membrane of the epidermis where melanocytes normally reside. This is in contrast to the "nests" of multi-layer melanocytes found in moles. Because of this characteristic feature, the adjective "lentiginous" is used to describe other skin lesions that similarly proliferate linearly within the basal cell layer.

Necrobiosis lipoidica is a necrotising skin condition that usually occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus but can also be associated with rheumatoid arthritis. In the former case it may be called necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum (NLD). NLD occurs in approximately 0.3% of the diabetic population, with the majority of sufferers being women.

The Fitzpatrick scale is a numerical classification schema for human skin color. It was developed in 1975 by Thomas B. Fitzpatrick as a way to estimate the response of different types of skin to ultraviolet (UV) light. It was initially developed on the basis of skin color to measure the correct dose of UVA for PUVA therapy, and when the initial testing based only on hair and eye colour resulted in too high UVA doses for some, it was altered to be based on the patient's reports of how their skin responds to the sun; it was also extended to a wider range of skin types. The Fitzpatrick scale remains a recognized tool for dermatological research into human skin pigmentation.
Lichen nitidus is a chronic inflammatory disease of unknown cause characterized by 1–2 mm, discrete and uniform, shiny, flat-topped, pale flesh-colored or reddish-brown papules that may appear as hypopigmented against dark skin. Occasionally, minimal scaling is present or can be induced by rubbing the surface of the papules. The disease usually affects children and young adults and is painless and usually nonpruritic, although protracted itching may occur in some cases. It is sometimes referred to by dermatologists as "mini lichen planus".

Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris is a chronic recurrent pustular dermatosis localized on the palms and soles only, characterized histologically by intraepidermal pustules filled with neutrophils. It can occur as part of the SAPHO syndrome.
Large plaque parapsoriasis are skin lesions that may be included in the modern scheme of cutaneous conditions described as parapsoriasis. These lesions, called plaques, may be irregularly round-shaped to oval and are 10 cm (4 in) or larger in diameter. They can be very thin plaques that are asymptomatic or mildly pruritic. Large-plaque parapsoriasis is a common associate of retiform parapsoriasis, can be accompanied by poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans, and can in rare occasions be a precursor to cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji is a rare disorder most commonly found in Japan, characterized by pruritic papules that spare the skinfolds, producing bands of uninvolved cutis, creating the so-called deck-chair sign. Frequently there is associated blood eosinophilia. Skin biopsies reveal a dense lymphohistiocytic infiltrate, eosinophils in the papillary dermis, and increased Langerhans cells. Systemic steroids are the treatment of choice and may result in long-term remissions.
Secondary cutaneous amyloidosis is a skin condition that occurs following PUVA therapy and in benign and malignant cutaneous neoplasms in which deopsits of amyloid may be found.
PUVA lentigines are a cutaneous condition caused by PUVA therapy.

Nevus depigmentosus is a loss of pigment in the skin which can be easily differentiated from vitiligo. Although age factor has not much involvement in the nevus depigmentosus but in about 19% of the cases these are noted at birth. Their size may however grow in proportion to growth of the body. The distribution is also fairly stable and are nonprogressive hypopigmented patches. The exact cause of nevus depigmentosus is still not clearly understood. A sporadic defect in the embryonic development has been suggested to be a causative factor. It has been described as "localised albinism", though this is incorrect. Those with nevus depigmentosus may be prone to sunburn due to the lack of pigment, and the patient should use good sun protection. Sunscreen should be applied to all exposed skin, since reduced tanning of normal skin will decrease the contrast with hypopigmented skin. Most patients with nevus depigmentosus do not pursue treatment for their lesion. There is no way to repigment the skin. If, however, the lesion is of cosmetic concern, camouflage makeup is effective. If the lesion is small one could also consider excision.
Itchy red bump disease is a cutaneous condition characterized by a red rash that may be treated with PUVA therapy.

Garlic allergy or allergic contact dermatitis to garlic is a common inflammatory skin condition caused by contact with garlic oil or dust. It mostly affects people who cut and handle fresh garlic, such as chefs, and presents on the tips of the thumb, index and middle fingers of the non-dominant hand. The affected fingertips show an asymmetrical pattern of fissure as well as thickening and shedding of the outer skin layers, which may progress to second- or third-degree burn of injured skin.

Angelicin is the parent compound in a family of naturally occurring organic compounds known as the angular furanocoumarins. Structurally, it can be considered as benzapyra-2-one fused with a furan moiety in the 7,8-position. Angelicin is commonly found in certain Apiaceae and Fabaceae plant species such as Bituminaria bituminosa. It has a skin permeability coefficient (LogKp) of -2.46. The maximum absorption is observed at 300 nm. The 1HNMR spectrum is available; the infrared and mass spectra of angelicin can be found in this database. The sublimation of angelicin occurs at 120 °C and the pressure of 0.13 Pa. Angelicin is a coumarine.











