Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes Mountains and the Pacific Ocean. With an area of 756,102 square kilometers (291,933 sq mi) and a population of 17.5 million as of 2017, Chile shares borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. The country also controls several Pacific islands, including Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island, and claims about 1,250,000 square kilometers (480,000 sq mi) of Antarctica as the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The capital and largest city of Chile is Santiago, and the national language is Spanish.

This is a list of the lists of islands in the world grouped by country, by continent, by body of water, and by other classifications. For rank-order lists, see the other lists of islands below.

South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern subregion of the Americas.

The geography of Chile is extremely diverse, as the country extends from a latitude of 17° South to Cape Horn at 56° and from the Pacific Ocean at its west to the Andes at its east. Chile is situated in southern South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean and a small part of the South Atlantic Ocean. Chile's territorial shape is considered among the world's most unusual; from north to south, the country extends 4,270 km (2,653 mi), and yet it only averages 177 km (110 mi) east to west. Chile reaches from the middle of South America's west coast straight down to the southern tip of the continent, where it curves slightly eastward. Diego Ramírez Islands and Cape Horn, the southernmost points in the Americas, where the Pacific and Atlantic oceans meet, are Chilean territory. Chile's northern neighbors are Peru and Bolivia, and its border with Argentina to the east, at 5,150 km (3,200 mi), is the world's third-longest. The total land size is 756,102 km2 (291,933 sq mi). The very long coastline of 6,435 km (3,999 mi) gives Chile the 11th largest exclusive economic zone of 3,648,532 km2 (1,408,706 sq mi).

The Ring of Fire is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes.

The Southern Hemisphere is the half (hemisphere) of Earth that is south of the Equator. It contains all or parts of five continents and four oceans, as well as New Zealand and most of the Pacific Islands in Oceania. Its surface is 80.9% water, compared with 60.7% water in the Northern Hemisphere, and it contains 32.7% of Earth's land.

The Desventuradas Islands is a group of four small oceanic islands located 850 kilometres (530 mi) off the coast of Chile, northwest of Santiago in the Pacific Ocean. They are considered part of Insular Chile.

The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of 3,687 km2 (1,424 sq mi). They lie about 120 kilometres north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between 430 and 900 km southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes.

The Asia–Pacific (APAC) is the region of the world adjoining the western Pacific Ocean. The region's precise boundaries vary depending on context, but countries and territories in Australasia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia are often included. In a wider context, Central Asia, North Asia, the Pacific Islands, South Asia, West Asia, and even Pacific-adjoining countries in the Americas can be included. For example, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) includes five countries in the New World. The term has become popular since the late 1980s in commerce, finance, and politics. Despite the heterogeneity of the regions' economies, most individual nations within the zone are emerging markets experiencing rapid growth. Sometimes, the notion of "Asia–Pacific excluding Japan" (APEJ) is considered useful.

Mataveri International Airport or Isla de Pascua Airport is at Hanga Roa on Rapa Nui /. The most remote airport in the world, it is 2,336 miles (3,759 km) from Santiago, Chile (SCL) which has scheduled flights to it on the Chilean carrier LATAM Chile. The runway starts just inland from the island's southeast coast at Mataveri, and nearly reaches the west coast, almost separating the mountain of Rano Kau from the rest of the island. The airport is the main point of entry for visitors to Easter Island. It has a transit lounge that was formerly used by passengers continuing to or returning from Papeete, Tahiti, which was serviced by LATAM until June 2020.

Falkland Islanders, also called Falklanders and nicknamed Kelpers, are the people of the British Overseas Territory of the Falkland Islands.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Chile:
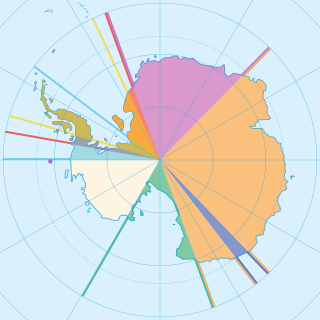
Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom – have made eight territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and study facilities within their respective claimed territories; however, a number of such facilities are located outside of the area claimed by their respective countries of operation, and countries without claims such as China, India, Italy, Japan, Pakistan, Russia, South Africa (SANAE), Poland, and the United States have constructed research facilities within the areas claimed by other countries. There are overlaps among the territories claimed by Argentina, Chile, and the United Kingdom.

Since the mid-1990s, tourism in Chile has become one of the main sources of income for the country, especially in its most extreme areas. In 2005, this sector grew by 13.6%, generating more than US$500 million, equivalent to 1.33% of the national GDP.
The South American Board of New Football Federations, also known by its acronym COSANFF is the administrative and controlling body for non-FIFA football federations in South America. It was also initially affiliated with the now defunct N.F.-Board.
The 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup qualification for the FIBA Americas region, began in November 2017 and concluded in February 2019. The process determined the seven teams that would participate at the 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cup.