
Pak Tongjin (also Tong-jin) was the South Korean minister of foreign affairs in the 1970s. Much of his efforts involved building trade routes between the Soviet Union and non-Soviet countries through South Korea. [1]

Pak Tongjin (also Tong-jin) was the South Korean minister of foreign affairs in the 1970s. Much of his efforts involved building trade routes between the Soviet Union and non-Soviet countries through South Korea. [1]

The history of South Korea begins with the Japanese surrender on 2 September 1945. At that time, South Korea and North Korea were divided, despite being the same people and on the same peninsula. In 1950, the Korean War broke out. North Korea overran South Korea until US-led UN forces intervened. At the end of the war in 1953, the border between South and North remained largely similar. Tensions between the two sides continued. South Korea alternated between dictatorship and liberal democracy. It underwent substantial economic development.

Roh Tae-woo was a South Korean army general and politician who served as the sixth president of South Korea from 1988 to 1993. He was the first democratically elected president of South Korea.

The division of Koreade facto began on 2 September 1945, when Japan signed the surrender document, thus ending the Pacific Theater of World War II. It was officially divided with the establishment of the two Koreas in 1948. During World War II, the Allied leaders had already been considering the question of Korea's future following Japan's eventual surrender in the war. The leaders reached an understanding that Korea would be liberated from Japan but would be placed under an international trusteeship until the Koreans would be deemed ready for self-rule. In the last days of the war, the United States proposed dividing the Korean peninsula into two occupation zones with the 38th parallel as the dividing line. The Soviets accepted their proposal and agreed to divide Korea, which led to the declaration of General Order No. 1.

The Gwangju Uprising, also known in South Korea as May 18, was a series of student-led demonstrations that took place in Gwangju, South Korea, in May 1980, against the coup of Chun Doo-hwan. The uprising was violently suppressed by the South Korean military with the approval and logistical support of the United States under the Carter administration, which feared the uprising might spread to other cities and tempt North Korea to interfere.

Wars of national liberation, also called wars of independence or wars of liberation, are conflicts fought by nations to gain independence. The term is used in conjunction with wars against foreign powers to establish separate sovereign states for the rebelling nationality. From a different point of view, such wars are called insurgencies or rebellions. Guerrilla warfare or asymmetric warfare is often utilized by groups labeled as national liberation movements, often with support from other states. The term "wars of national liberation" is most commonly used for those fought during the decolonization movement. Since these were primarily in the third world, against Western powers and their economic influence, and a major aspect of the Cold War, the phrase has often been applied selectively to criticize the foreign power involved.
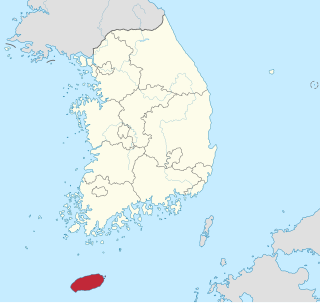
The Jeju uprising, known in South Korea as the Jeju April 3 incident, was an uprising on Jeju Island from April 1948 to May 1949. A year prior to its start, residents of Jeju had begun protesting elections scheduled by the United Nations Temporary Commission on Korea (UNTCOK) to be held in the United States-occupied half of Korea, which they believed would entrench the division of the country. A general strike was later organized by the Workers' Party of South Korea (WPSK) from February to March 1948. The WPSK launched an insurgency in April 1948, attacking police and Northwest Youth League members stationed on Jeju who had been mobilized to suppress the protests by force. The First Republic of Korea under President Syngman Rhee escalated the suppression of the uprising from August 1948, declaring martial law in November and beginning an "eradication campaign" against rebel forces in the rural areas of Jeju in March 1949, defeating them within two months. This resulting campaign has lead to the event being called the Jeju massacre. Many rebel veterans and suspected sympathizers were later killed upon the outbreak of the Korean War in June 1950, and the existence of the Jeju uprising was officially censored and repressed in South Korea for several decades.
Minjung (Korean: 민중) is a Korean word that combines the two hanja characters min (民) and jung (衆). Min is from inmin, which may be translated as "the people", and jung is from daejung, which may be translated as "the public". Thus, minjung can be translated to mean "the masses" or "the people."

The General Federation of Trade Unions of Korea is the sole legal trade union federation in North Korea. GFTUK was formed on November 30, 1945 as the General Federation of Trade Unions of North Korea. In January 1951, it was reorganized and adopted its current name. The chairman of the central committee of GFTUK is Pak In-chol.
Koryo-saram or Koryoin are ethnic Koreans of the former Soviet Union, who descend from Koreans that were living in the Russian Far East.

Hwang Sok-yong is a South Korean novelist.
In political science, the waves of democracy or waves of democratization are major surges of democracy that have occurred in history. Although the term appears at least as early as 1887, it was popularized by Samuel P. Huntington, a political scientist at Harvard University, in his article published in the Journal of Democracy and further expounded in his 1991 book, The Third Wave: Democratization in the Late Twentieth Century. Democratization waves have been linked to sudden shifts in the distribution of power among the great powers, which created openings and incentives to introduce sweeping domestic reforms.

Mongolia–North Korea relations are the historic and current bilateral relations between Mongolia and the Democratic People's Republic of Korea.
The Communist movement in Korea emerged as a political movement in the early 20th century. Although the movement had a minor role in pre-war politics, the division between the communist North Korea and the anti-communist South Korea came to dominate Korean political life in the post-World War II era. North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, continues to be a Jucheist state under the rule of the Workers' Party of Korea. In South Korea, the National Security Law has been used to criminalize advocacy of communism and groups suspected of alignment with North Korea. Due to the end of economic aid from the Soviet Union after its dissolution in 1991, the impractical ideological application of Stalinist policies in North Korea over years of economic slowdown in the 1980s, and the recession and famine during the 1990s, North Korea has replaced Marxism-Leninism with the Juche idea despite nominally upholding Communism. References to Communism were removed in the North Korean 1992 and 1998 constitutional revisions to make way for the personality cult of Kim's family dictatorship and the North Korean market economy reform. The Workers' Party of Korea under the leadership of Kim Jong Un later reconfirmed commitment to the establishment of a communist society, but orthodox Marxism has since been largely tabled in favor of "Socialism in our style". Officially, the DPRK still retains a command economy with complete state control of industry and agriculture. North Korea maintains collectivized farms and state-funded education and healthcare.

Kim Il Sung was a North Korean politician and military leader. He founded the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, commonly known as North Korea, which he led as Supreme Leader from its establishment in 1948 until his death in 1994. Afterwards, he was succeeded by his son Kim Jong Il and was declared Eternal President.

The Yeosu-Suncheon rebellion, also known as the Yeo-Sun incident, was a rebellion that began in October 1948 and mostly ended by November of the same year. However, pockets of resistance lasted through to 1957, almost 10 years later.

May 18th National Cemetery is a cemetery for those who participated in the Gwangju Uprising. Built by the government of South Korea in 1997, it is located in Gwangju. Every May, on the anniversary of the uprising, it is common for citizens to visit the cemetery to honor the dead.
Soviet democracy, also called council democracy, is a type of democracy in Marxism, in which the rule of a population is exercised by directly elected soviets. Soviets are directly responsible to their electors and bound by their instructions using a delegate model of representation. Such an imperative mandate is in contrast to a trustee model, in which elected delegates are exclusively responsible to their conscience. Delegates may accordingly be dismissed from their post at any time through recall elections. Soviet democracy forms the basis for the soviet republic system of government.
Yong Soon Min was a South Korean-born American artist, curator, and educator. She served as professor emeritus at the University of California, Irvine. Her artwork deals with issues including Korean-American identity, politics, personal narrative, and culture. Min was active in New York City and Los Angeles.
"March For the Beloved" is a Korean protest song that was composed in 1981 in honor of Democracy activist Yoon Sang-won and labor activist Park Ki-soon, who were killed during the Gwangju Uprising in 1980. The original author of the lyrics is Paik Ki-wan, and the composer is Kim Jong-ryul.