Related Research Articles

Al-Aqsa Mosque, properly Jāmiʿ al-Aqṣā, also known as the Qibli Mosque or Qibli Chapel, is a congregational mosque or prayer hall in the Old City of Jerusalem. In some sources the building is also named al-Masjid al-Aqṣā, but this name and its English translation "Al Aqsa Mosque" itself, is disputed as it can instead apply to the whole compound in which the building sits. The wider compound is also known as the Haram al-Sharif, the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound, and the Temple Mount.

Meknes is one of the four Imperial cities of Morocco, located in northern central Morocco and the sixth largest city by population in the kingdom. Founded in the 11th century by the Almoravids as a military settlement, Meknes became the capital of Morocco under the reign of Sultan Moulay Ismaïl (1672–1727), son of the founder of the Alaouite dynasty. Moulay Ismaïl created a massive imperial palace complex and endowed the city with extensive fortifications and monumental gates. The city recorded a population of 632,079 in the 2014 Moroccan census. It is the seat of Meknès Prefecture and an important economic pole in the region of Fès-Meknès.

Sudano-Sahelian architecture refers to a range of similar indigenous architectural styles common to the African peoples of the Sahel and Sudanian grassland (geographical) regions of West Africa, south of the Sahara, but north of the fertile forest regions of the coast.
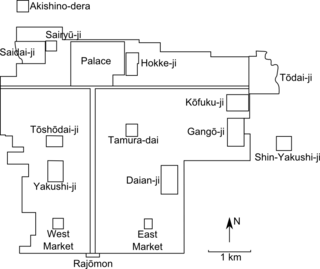
Heijō Palace was the imperial residence in the Japanese capital city Heijō-kyō, during most of the Nara period. The palace, which served as the imperial residence and the administrative centre of for most of the Nara period from 710 to 794 AD, was located at the north-central location of the city in accordance with the Chinese models used for the design of the capital.

The North Region makes up 66,090 km² of the northern half of The Republic of Cameroon. Neighbouring territories include the Far North Region to the north, the Adamawa Region to the south, Nigeria to the west, Chad to the east, and Central African Republic to the southeast. The city of Garoua is both the political and industrial capital. Garoua is Cameroon's third largest port, despite the fact that the Bénoué River upon which it relies is only navigable for short periods of the year.

Brú na Bóinne or Boyne valley tombs, is an area in County Meath, Ireland, located in a bend of the River Boyne. It contains one of the world's most important prehistoric landscapes dating from the Neolithic period, including the large Megalithic passage graves of Knowth, Newgrange and Dowth as well as some 90 additional monuments. The archaeological culture associated with these sites is called the "Boyne culture".

Like other aspects of the culture of Africa, the architecture of Africa is exceptionally diverse. Throughout the history of Africa, Africans have developed their own local architectural traditions. In some cases, broader regional styles can be identified, such as the Sudano-Sahelian architecture of West Africa. A common theme in traditional African architecture is the use of fractal scaling: small parts of the structure tend to look similar to larger parts, such as a circular village made of circular houses.

The Citadel of Cairo or Citadel of Saladin is a medieval Islamic-era fortification in Cairo, Egypt, built by Salah ad-Din (Saladin) and further developed by subsequent Egyptian rulers. It was the seat of government in Egypt and the residence of its rulers for nearly 700 years from the 13th to the 19th centuries. Its location on a promontory of the Mokattam hills near the center of Cairo commands a strategic position overlooking the city and dominating its skyline. When it was constructed it was among the most impressive and ambitious military fortification projects of its time. It is now a preserved historic site, including mosques and museums.

The Royal Alcázars of Seville, historically known as al-Qasr al-Muriq and commonly known as the Alcázar of Seville, is a royal palace in Seville, Spain, built for the Christian king Peter of Castile. It was built by Castilian Christians on the site of an Abbadid Muslim alcazar, or residential fortress. The fortress was destroyed after the Christian conquest of Seville in 1248.

The Fasil Ghebbi is a fortress located in Gondar, Amhara Region, Ethiopia. It was founded in the 17th century by Emperor Fasilides and was the home of Ethiopian emperors. Its unique architecture shows diverse influences including Hindu, Arab, and Baroque characteristics. Because of its historical importance and architecture, the fortress was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979. Ghebbi is an Amharic word for a compound or enclosure.

Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is located in Panchmahal district in Gujarat, India. It is located around the historical city of Champaner, a city which was founded by Vanraj Chavda, the most prominent king of the Chavda Dynasty, in the eighth century. He named it after the name of his friend and general Champa, also known later as Champaraj. The heritage site is studded with forts with bastions starting from the hills of Pavagadh, and extending into the city of Champaner. The park's landscape includes archaeological, historic and living cultural heritage monuments such as chalcolithic sites, a hill fortress of an early Hindu capital, and remains of the 16th-century capital of the state of Gujarat. There are palaces, entrance gates and arches, mosques, tombs and temples, residential complexes, agricultural structures and water installations such as stepwells and tanks, dating from the eighth to the 14th centuries. The Kalika Mata Temple, located on top of the 800 metres (2,600 ft) high Pavagadh Hill, is an important Hindu shrine in the region, attracting large numbers of pilgrims throughout the year.

Sukur or Sukur Cultural Landscape is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located on a hill above the village of Sukur in the Adamawa State of Nigeria. It is situated in the Mandara Mountains, close to the border with Cameroon. Its UNESCO inscription is based on the cultural heritage, material culture, and the naturally-terraced fields. Sukur is Africa's first cultural landscape to receive World Heritage List inscription.

The Caferağa Medrese or Cafer Ağa Madrasa is a former medrese, located in Istanbul, Turkey, next to the Hagia Sophia. It was built in 1559 by Mimar Sinan on the orders of Cafer Ağa, during the reign of Sultan Süleyman the Magnificent (1520-1566).

The City of the Dead, or Cairo Necropolis, also referred to as theQarafa, is a series of vast Islamic-era necropolises and cemeteries in Cairo, Egypt. They extend to the north and to the south of the Cairo Citadel, below the Mokattam Hills and outside the historic city walls, covering an area roughly 4 miles (6.4 km) long. They are included in the UNESCO World Heritage Site of "Historic Cairo".

The Agdal Gardens are a large area of historic gardens and orchards in Marrakesh, Morocco. The gardens are located to the south of the city's historic Kasbah and its royal palace. Together with the medina of Marrakech and the Menara Gardens, the Agdal Gardens were listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site in 1985. The gardens contain several historic water reservoirs as well as several historic palaces and pavilions, including the Dar el-Hana and the Dar al-Bayda.

Qasr Mushatta is the ruin of an Umayyad winter palace, probably commissioned by Caliph Al-Walid II during his brief reign (743-744). The ruins are located approximately 30 km south of Amman, Jordan, north of Queen Alia International Airport, and are part of a string of castles, palaces and caravanserais known collectively in Jordan and the wider Southern Levant region as the Desert Castles. Though much of the ruins can still be found in situ, the most striking feature of the palace, its facade, has been removed and is on display at the Pergamon Museum in Berlin. The complex was never completed.
Tibati is a town and commune in the Adamawa Region, Cameroon. The town and region are ruled by a local monarch, the Lamido.

Warangal Fort is located in Warangal District, Telangana, India. It was the capital city of Kakatiya dynasty and Musunuri Nayakas. It appears to have existed since at least the 12th century when it was the capital of the Kakatiyas. The fort has four ornamental gates, known as Kakatiya Kala Thoranam, that originally formed the entrances to a now ruined great Shiva temple. The Kakatiyan arch has been adopted and officially incorporated into the emblem of Telangana after the bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh. The fort is included in the "tentative list" of UNESCO World Heritage Site and was submitted by the Permanent Delegation of India to UNESCO on 10/09/2010.
Rey Bouba is a city in North Region, Cameroon.
References
Le Lamidat de Rey-Bouba - UNESCO World Heritage Centre Accessed on 2009-02-23.