
The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out.

The Solent is a strait between the Isle of Wight and mainland Great Britain; the major historic ports of Southampton and Portsmouth lie inland of its shores. It is about 20 miles long and varies in width between 2+1⁄2 and 5 mi, although the Hurst Spit which projects 1+1⁄2 mi (2.4 km) into the Solent narrows the sea crossing between Hurst Castle and Colwell Bay to just over 1 mi (1.6 km).

The Broads is a network of mostly navigable rivers and lakes in the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. Although the terms "Norfolk Broads" and "Suffolk Broads" are correctly used to identify specific areas within the two counties respectively, the whole area is frequently referred to as the Norfolk Broads.

Great Yarmouth, often called Yarmouth, is a seaside town which gives its name to the wider Borough of Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, England; it straddles the River Yare and is located 20 miles (32 km) east of Norwich. Its fishing industry, mainly for herring, shrank after the mid-20th century and has all but ended. North Sea oil from the 1960s supplied an oil-rig industry that services offshore natural gas rigs; more recently, offshore wind power and other renewable energy industries have ensued.

Gorleston-on-Sea, historically and colloquially known as Gorleston, is a seaside town in the borough of Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, England. It lies to the south of Great Yarmouth, on the opposite side of the mouth of the River Yare. Historically in Suffolk, it was a port town at the time of the Domesday Book. It was incorporated into Great Yarmouth in 1836. Gorleston's port became a centre of fishing for herring along with salt pans used for the production of salt to preserve the fish. In Edwardian times the fishing industry rapidly declined and the town's role changed to that of a seaside resort.

Creswell Crags is an enclosed limestone gorge on the border between Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire, England, near the villages of Creswell and Whitwell. The cliffs in the ravine contain several caves that were occupied during the last ice age, between around 43,000 and 10,000 years ago. Its caves contain the northernmost cave art in Europe. The evidence of occupation found in the rich series of sediments that accumulated over many thousands of years is regarded as internationally unique in demonstrating how prehistoric people managed to live at the extreme northernmost limits of their territory during the Late Pleistocene period.

A spit or sandspit is a deposition bar or beach landform off coasts or lake shores. It develops in places where re-entrance occurs, such as at a cove's headlands, by the process of longshore drift by longshore currents. The drift occurs due to waves meeting the beach at an oblique angle, moving sediment down the beach in a zigzag pattern. This is complemented by longshore currents, which further transport sediment through the water alongside the beach. These currents are caused by the same waves that cause the drift.

Several species of humans have intermittently occupied Great Britain for almost a million years. The earliest evidence of human occupation around 900,000 years ago is at Happisburgh on the Norfolk coast, with stone tools and footprints probably made by Homo antecessor. The oldest human fossils, around 500,000 years old, are of Homo heidelbergensis at Boxgrove in Sussex. Until this time Britain had been permanently connected to the Continent by a chalk ridge between South East England and northern France called the Weald-Artois Anticline, but during the Anglian Glaciation around 425,000 years ago a megaflood broke through the ridge, and Britain became an island when sea levels rose during the following Hoxnian interglacial.

The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent 26,000 and 20,000 years ago. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing a major expansion of deserts, along with a large drop in sea levels.

The three Storegga Slides are amongst the largest known submarine landslides. They occurred at the edge of Norway's continental shelf in the Norwegian Sea, approximately 6225–6170 BCE. The collapse involved an estimated 290 km (180 mi) length of coastal shelf, with a total volume of 3,500 km3 (840 cu mi) of debris, which caused a paleotsunami in the North Atlantic Ocean.
The Older Dryas was a stadial (cold) period between the Bølling and Allerød interstadials, about 14,000 years Before Present, towards the end of the Pleistocene. Its date range is not well defined, with estimates varying by 400 years, but its duration is agreed to have been around two centuries.

The South Asian Stone Age covers the Palaeolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic periods in the Indian subcontinent. Evidence for the most ancient Homo sapiens in South Asia has been found in the cave sites of Cudappah of India, Batadombalena and Belilena in Sri Lanka. In Mehrgarh, in what is today western Pakistan, the Neolithic began c. 7000 BCE and lasted until 3300 BCE and the beginnings of the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Age. In South India, the Mesolithic lasted until 3000 BCE, and the Neolithic until c. 1000 BCE, followed by a Megalithic transitional period mostly skipping the Bronze Age. The Iron Age in India began roughly simultaneously in North and South India, around c. 1200 to 1000 BCE.
The prehistory of the County of Norfolk, England is broken into specific time periods, these being Palaeolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic.

Doggerland was an area of land in Northern Europe, now submerged beneath the North Sea, that connected Britain to continental Europe. It was repeatedly exposed at various times during the Pleistocene epoch due to the lowering of sea levels during glacial periods. It was last flooded by rising sea levels around 6500–6200 BCE. The flooded land is known as the Dogger Littoral. Geological surveys have suggested that it stretched from what is now the east coast of Great Britain to what is now the Netherlands, the western coast of Germany and the Danish peninsula of Jutland. It was probably a rich habitat with human habitation in the Mesolithic period, although rising sea levels gradually reduced it to low-lying islands before its final submergence, possibly following a tsunami caused by the Storegga Slide. Doggerland was named after the Dogger Bank, which in turn was named after 17th-century Dutch fishing boats called doggers.

The Schöningen spears are a set of ten wooden weapons from the Palaeolithic Age that were excavated between 1994 and 1999 from the 'Spear Horizon' in the open-cast lignite mine in Schöningen, Helmstedt district, Germany. The spears are the oldest hunting weapons discovered and were found together with animal bones and stone and bone tools. Being used by the oldest known group of hunters, they provided never before uncovered proof that early human ancestors were much closer to modern humans in both complex social structure and technical ability than thought before. The excavations took place under the management of Hartmut Thieme of the Lower Saxony State Service for Cultural Heritage (NLD).

The Neanderthals in Gibraltar were among the first to be discovered by modern scientists and have been among the most well studied of their species according to a number of extinction studies which emphasize regional differences, usually claiming the Iberian Peninsula partially acted as a “refuge” for the shrinking Neanderthal populations and the Gibraltar population of Neanderthals as having been one of many dwindling populations of archaic human populations, existing just until around 42,000 years ago. Many other Neanderthal populations went extinct around the same time.
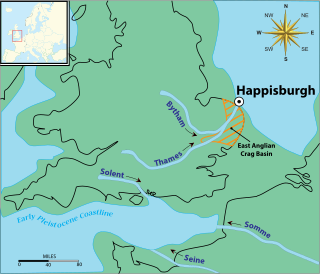
The Happisburgh footprints were a set of fossilized hominid footprints that date to the end of the Early Pleistocene, around 950–850,000 years ago. They were discovered in May 2013 in a newly uncovered sediment layer of the Cromer Forest Bed on a beach at Happisburgh in Norfolk, England, and carefully photographed in 3D before being destroyed by the tide shortly afterwards.

The Hadži-Prodan's Cave is an archaeological site of the Paleolithic period and a national natural monument, located in the village Raščići around 7 km (4.3 mi) from Ivanjica in western central Serbia. The rather narrow and high entrance with at an altitude of 630 m (2,070 ft) above sea level sits about 40 m (130 ft) above the Rašćanska river valley bed and is oriented towards the south. The 345 m (1,132 ft) long cave was formed during the Late Cretaceous in "thick-bedded to massive" Senonian limestone. Prehistoric pottery shards and Pleistocene faunal fossils had already been collected by Zoran Vučićević from Ivanjica. Animal fossils especially Cave bear and Iron Age artifact discoveries during an unrelated areal survey were reportedly made at the cave entrance and in the main cavern. The site is named in honor of Hadži-Prodan, a 19th century Serbian revolutionary.

Scladina, or Sclayn Cave, is an archaeological site located in Wallonia in the town of Sclayn, in the Andenne hills in Belgium, where excavations since 1978 have provided the material for an exhaustive collection of over thirteen thousand Mousterian stone artifacts and the fossilized remains of an especially ancient Neanderthal, called the Scladina child were discovered in 1993.

Mundafan was a former lake in Saudi Arabia, within presently desert-like areas. It formed during the Pleistocene and Holocene, when orbitally mediated changes in climate increased monsoon precipitation in the peninsula, allowing runoff to form a lake with a maximum area of 300 square kilometres (120 sq mi). It was populated by fishes and surrounded by reeds and savanna, which supported human populations.


















