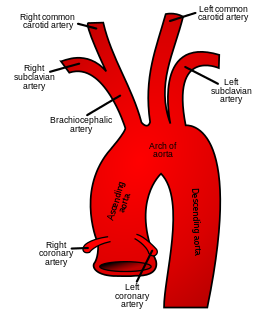
The brachiocephalic artery is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck.

The Palatine Chapel, is the royal chapel of the Norman palace in Palermo, Sicily. This building is a mixture of Byzantine, Norman and Fatimid architectural styles, showing the tricultural state of Sicily during the 12th century after Roger II's father and uncle conquered the island.

In human anatomy, the greater pancreatic artery, is the largest artery that supplies the pancreas. It arises from the splenic artery.

The descending palatine artery is a branch of the third part of the maxillary artery supplying the hard and soft palate.
The greater palatine artery is a branch of the descending palatine artery and contributes to the blood supply of the hard palate and nasal septum.
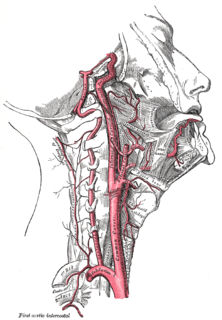
The ascending palatine artery is an artery in the head that branches off the facial artery and runs up the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.

The deep artery of arm is a large vessel which arises from the lateral and posterior part of the brachial artery, just below the lower border of the teres major.
Gluteal artery can refer to:

The princeps pollicis artery, or principal artery of the thumb, arises from the radial artery just as it turns medially towards the deep part of the hand; it descends between the first dorsal interosseous muscle and the oblique head of the adductor pollicis, along the medial side of the first metacarpal bone to the base of the proximal phalanx, where it lies beneath the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus muscle and divides into two branches.

The nutrient artery or medullary, usually accompanied by one or two veins, enters the bone through the nutrient foramen, runs obliquely through the cortex, sends branches upward and downward to the bone marrow, which ramify in the endosteum–the vascular membrane lining the medullary cavity–and give twigs to the adjoining canals. Nutrient arteries are the most apparent blood vessels of the bones.

The plantar metatarsal arteries are four in number, arising from the convexity of the plantar arch. They run forward between the metatarsal bones and in contact with the Interossei. They are located in the fourth layer of the foot.
The thyroid ima artery is an artery of the head and neck. It is an anatomical variant that, when present, supplies blood to the thyroid gland primarily, or the trachea, the parathyroid gland and the thymus gland in rare cases. It has also been reported to be a compensatory artery when one or both of the inferior thyroid arteries are absent and in a few cases the only source of blood to the thyroid gland. It varies in origin, size, blood supply, and termination, and occurs in only 3–10% of the population. Because of the variations and rarity, it may lead to surgical complications.
Suprarenal artery may refer to:
The lesser palatine arteries go through the lesser palatine foramina, and supply the soft palate.
Communicating artery may refer to:
Cecal artery, caecal artery or arteria caecalis can refer to:
Choroidal artery can refer to:
Tympanic artery can refer to:
Volar arteries may refer to:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.








