
In anatomy, the palatine bones are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxilla, they comprise the hard palate.

The pterygopalatine ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck,.

The greater petrosal nerve is a nerve of the head mainly containing pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres which ultimately synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion.

In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve (V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (CN V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxilla, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face, and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.

The right gastroepiploic artery is one of the two terminal branches of the gastroduodenal artery. It runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the splenic artery.

The left gastroepiploic artery, the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger's breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic.

The right colic artery is an artery of the abdomen, a branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the ascending colon. It divides into two terminal branches - an ascending branch and a descending branch - which form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and ileocolic artery (respectively).

The right gastric artery usually arises from the proper hepatic artery. It descends to the pyloric end of the stomach before passing from right to left along its lesser curvature, supplying it with branches, and finally anastomosing with the left gastric artery.
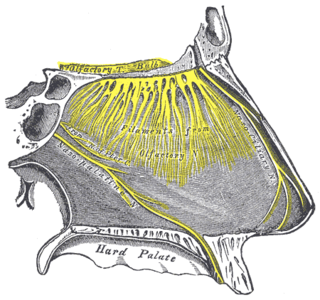
The nasopalatine nerve (also long sphenopalatine nerve) is a nerve of the head. It is a sensory branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) that passes through the pterygopalatine ganglion (without synapsing) and then through the sphenopalatine foramen to enter the nasal cavity, and finally out of the nasal cavity through the incisive canal and then the incisive fossa to enter the hard palate. It provides sensory innervation to the posteroinferior part of the nasal septum, and gingiva just posterior to the upper incisor teeth.

The suprascapular artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk on the neck.

The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible.
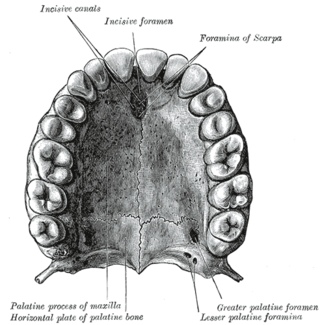
The incisive canals are two bony canals of the anterior hard palate connecting the nasal cavity and the oral cavity. An incisive canal courses through each maxilla. Below, the two incisive canals typically converge medially.
The greater palatine artery is a branch of the descending palatine artery and contributes to the blood supply of the hard palate and nasal septum.

The ascending palatine artery is an artery is a branch of the facial artery which ascends along the neck before splitting into two terminal branches; one branch supplies the soft palate, and the other supplies the palatine tonsil and pharyngotympanic tube.

The infraorbital artery is a small artery in the head that arises from the maxillary artery and passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit, then passes forward along the floor of the orbit, finally exiting the orbit through the infraorbital foramen to reach the face.

The greater palatine nerve is a branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion. This nerve is also referred to as the anterior palatine nerve, due to its location anterior to the lesser palatine nerve. It carries both general sensory fibres from the maxillary nerve, and parasympathetic fibers from the nerve of the pterygoid canal. It may be anaesthetised for procedures of the mouth and maxillary (upper) teeth.

The greater palatine canal is a passage in the skull that transmits the descending palatine artery, vein, and greater and lesser palatine nerves between the pterygopalatine fossa and the oral cavity.
The lesser palatine arteries are arteries of the head. It is a branch of the descending palatine artery. They supply the palatine tonsils and the soft palate.

The lesser palatine nerves (posterior palatine nerve) are branches of the maxillary nerve (CN V2). They descends through the greater palatine canal alongside the greater palatine nerve, and emerge (separately) through the lesser palatine foramen to pass posteriorward. They supply the soft palate, tonsil, and uvula.
















