In the human skull, the zygomatic bone, also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. It is situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek, part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit, and parts of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal fossa. It presents a malar and a temporal surface; four processes, and four borders.

In anatomy, the zygomatic arch, or cheek bone, is a part of the skull formed by the zygomatic process of the temporal bone and the temporal process of the zygomatic bone, the two being united by an oblique suture ; the tendon of the temporal muscle passes medial to the arch, to gain insertion into the coronoid process of the mandible (jawbone).

In anatomy, the temporalis muscle, also known as the temporal muscle, is one of the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is a broad, fan-shaped convergent muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic arch so it covers much of the temporal bone.Temporal refers to the head's temples.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.

The procerus muscle is a small pyramidal slip of muscle deep to the superior orbital nerve, artery and vein. Procerus is Latin, meaning tall or extended.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.

The temporal fossa is a fossa on the side of the skull bounded by the temporal lines above, and the zygomatic arch below. Its floor is formed by the outer surfaces of four bones of the skull. The fossa is filled by the temporalis muscle.

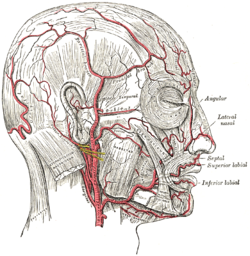
In human anatomy, the superficial temporal artery is a major artery of the head. It arises from the external carotid artery when it splits into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery.

The transverse facial artery is an artery that branches from the superficial temporal artery and runs across the face.

The zygomaticotemporal nerve (zygomaticotemporal branch, temporal branch) is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the head. It is a branch of the zygomatic nerve (itself a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2)). It arises in the orbit and exits the orbit through the zygomaticotemporal foramen in the zygomatic bone to enter the temporal fossa. It is distributed to the skin of the side of the forehead. It also contains a parasympathetic secretomotor component for the lacrimal gland which it confers to the lacrimal nerve (which then delivers it to the gland).

The squamous part of temporal bone, or temporal squama, forms the front and upper part of the temporal bone, and is scale-like, thin, and translucent.

The lacrimal artery is an artery of the orbit. It is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It accompanies the lacrimal nerve along the upper border of the lateral rectus muscle, travelling forward to reach the lacrimal gland. It supplies the lacrimal gland, two rectus muscles of the eye, the eyelids, and the conjunctiva.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

The deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.

The temporal fascia is a fascia of the head that covers the temporalis muscle and structures situated superior to the zygomatic arch.

The zygomatic processes are three processes (protrusions) from other bones of the skull which each articulate with the zygomatic bone. The three processes are:

The deep temporal arteries are two arteries of the head. They ascend between the temporalis muscle and the pericranium. They anastomose with the middle temporal artery, among other vessels. They supply the temporalis muscle.

The temporal branches of the facial nerve crosses the zygomatic arch to the temporal region, supplying the auriculares anterior and superior, and joining with the zygomaticotemporal branch of the maxillary nerve, and with the auriculotemporal branch of the mandibular nerve.
The middle temporal artery occasionally gives off a zygomatico-orbital branch, which runs along the upper border of the zygomatic arch, between the two layers of the temporal fascia, to the lateral angle of the orbit.

The parotid plexus or plexus parotideus is the branch point of the facial nerve (extratemporal) after it leaves the stylomastoid foramen. This division takes place within the parotid gland.