Related Research Articles

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.
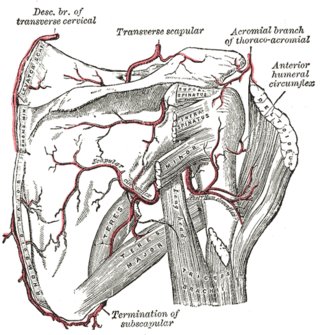
The circumflex scapular artery is a branch of the subscapular artery and part of the scapular anastomoses.

The right gastroepiploic artery is one of the two terminal branches of the gastroduodenal artery. It runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the splenic artery.

The left gastroepiploic artery, the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger's breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic.

The sigmoid arteries are 2–5 branches of the inferior mesenteric artery that are distributed to the distal descending colon and the sigmoid colon.

The right colic artery is an artery of the abdomen, a branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the ascending colon. It divides into two terminal branches - an ascending branch and a descending branch - which form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and ileocolic artery (respectively).

The left colic artery is a branch of the inferior mesenteric artery distributed to the descending colon, and left part of the transverse colon. It ends by dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch; the terminal branches of the two branches go on to form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and a sigmoid artery (respectively).

The transverse cervical artery is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery.
The esophageal arteries four or five in number, arise from the front of the aorta, and pass obliquely downward to the esophagus, forming a chain of anastomoses along that tube, anastomosing with the esophageal branches of the inferior thyroid arteries above, and with ascending branches from the left inferior phrenic and left gastric arteries below. These arteries supply the middle third of the esophagus.
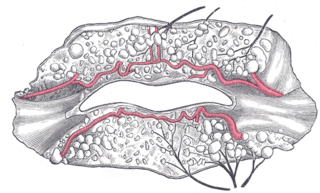
The superior labial artery is larger and more egregious than the inferior labial artery.

The suprascapular artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk on the neck.

The descending palatine artery is a branch of the third part of the maxillary artery supplying the hard and soft palate.
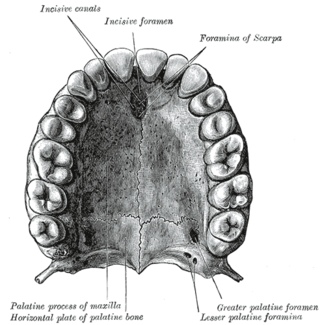
The incisive canals are two bony canals of the anterior hard palate connecting the nasal cavity and the oral cavity. An incisive canal courses through each maxilla. Below, the two incisive canals typically converge medially.

The sphenopalatine artery is an artery of the head, commonly known as the artery of epistaxis. It passes through the sphenopalatine foramen to reach the nasal cavity. It is the main artery of the nasal cavity.

The ascending palatine artery is an artery is a branch of the facial artery which ascends along the neck before spliting into two terminal branches; one branch supplies the soft palate, and the other supplies the palatine tonsil and pharyngotympanic tube.

The inferior ulnar collateral artery is an artery in the arm. It arises about 5 cm. above the elbow from the brachial artery.

The deep artery of arm is a large artery of the arm which arises from the brachial artery. It descends in the arm before ending by anastomosing with the radial recurrent artery.

The infraorbital artery is a small artery in the head that arises from the maxillary artery and passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit, then passes forward along the floor of the orbit, finally exiting the orbit through the infraorbital foramen to reach the face.

The lateral nasal branch of facial artery is derived from the facial artery as that vessel ascends along the side of the nose.

The descending branch of occipital artery, the largest branch of the occipital, descends on the back of the neck, and divides into a superficial and deep portion.
References
- ↑ Gray, Henry (1924). Anatomy of the Human Body. Lea & Febiger. p. 569.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 562 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 562 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)