The superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. It gives passage to multiple structures, including the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, ophthalmic nerve, abducens nerve, ophthalmic veins, and sympathetic fibres from the cavernous plexus.

The nasalis muscle is a sphincter-like muscle of the nose. It has a transverse part and an alar part. It compresses the nasal cartilages, and can "flare" the nostrils. It can be used to test the facial nerve (VII), which supplies it.

In human anatomy, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), also known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurcation as the superior epigastric and musculophrenic arteries.
In human anatomy, the dorsalis pedis artery is a blood vessel of the lower limb. It arises from the anterior tibial artery, and ends at the first intermetatarsal space. It carries oxygenated blood to the dorsal side of the foot. It is useful for taking a pulse. It is also at risk during anaesthesia of the deep peroneal nerve.

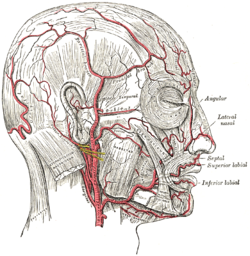
The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

In human anatomy, the superior epigastric artery is a terminal branch of the internal thoracic artery that provides arterial supply to the abdominal wall, and upper rectus abdominis muscle. It enters the rectus sheath to descend upon the inner surface of the rectus abdominis muscle. It ends by anastomosing with the inferior epigastric artery.
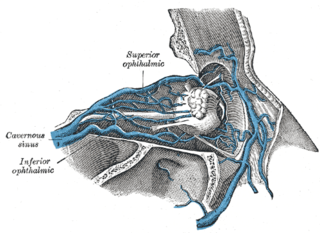
The superior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that drains venous blood from structures of the upper orbit. It is formed by the union of the angular vein, and supraorbital vein. It passes backwards within the orbit alongside the ophthalmic artery, then exits the orbit through the superior orbital fissure to drain into the cavernous sinus.

The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue.

The supratrochlear nerve is a branch of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) from the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the forehead and the upper eyelid.

The zygomatic nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve. It arises in the pterygopalatine fossa and enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure before dividing into its two terminal branches: the zygomaticotemporal nerve and zygomaticofacial nerve.

The inferior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that - together with the superior ophthalmic vein - represents the principal drainage system of the orbit. It begins from a venous network in the front of the orbit, then passes backwards through the lower orbit. It drains several structures of the orbit. It may end by splitting into two branches, one draining into the pterygoid venous plexus and the other ultimately into the cavernous sinus.

The angular vein is a vein of the face. It is the upper part of the facial vein, above its junction with the superior labial vein. It is formed by the junction of the supratrochlear vein and supraorbital vein, and joins with the superior labial vein. It drains the medial canthus, and parts of the nose and the upper lip. It can be a route of spread of infection from the danger triangle of the face to the cavernous sinus.

The retromandibular vein is a major vein of the face. It is formed within the parotid gland by the confluence of the maxillary vein, and superficial temporal vein. It descends in the gland and splits into two branches upon emerging from the gland. Its anterior branch then joins the (anterior) facial vein forming the common facial vein, while its posterior branch joins the posterior auricular vein forming the external jugular vein.

The lacrimal artery is an artery of the orbit. It is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It accompanies the lacrimal nerve along the upper border of the lateral rectus muscle, travelling forward to reach the lacrimal gland. It supplies the lacrimal gland, two rectus muscles of the eye, the eyelids, and the conjunctiva.

The infraorbital artery is a small artery in the head that arises from the maxillary artery and passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit, then passes forward along the floor of the orbit, finally exiting the orbit through the infraorbital foramen to reach the face.

The lacrimal sac or lachrymal sac is the upper dilated end of the nasolacrimal duct, and is lodged in a deep groove formed by the lacrimal bone and frontal process of the maxilla. It connects the lacrimal canaliculi, which drain tears from the eye's surface, and the nasolacrimal duct, which conveys this fluid into the nasal cavity. Lacrimal sac occlusion leads to dacryocystitis.

The supraorbital artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It passes anteriorly within the orbit to exit the orbit through the supraorbital foramen or notch alongside the supraorbital nerve, splitting into two terminal branches which go on to form anastomoses with arteries of the head.

The medial palpebral arteries are arteries of the head that contribute arterial blood supply to the eyelids. They are derived from the ophthalmic artery; a single medial palpebral artery issues from the ophthalmic artery before splitting into a superior and an inferior medial palpebral artery, each supplying one eyelid.

The anterior ciliary arteries are seven arteries in each eye-socket that arise from muscular branches of the ophthalmic artery and supply the conjunctiva, sclera, rectus muscles, and the ciliary body. The arteries end by anastomosing with branches of the long posterior ciliary arteries to form the circulus arteriosus major.

The zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (malar branches) are nerves of the face. They run across the zygomatic bone to the lateral angle of the orbit. Here, they supply the orbicularis oculi muscle, and join with filaments from the lacrimal nerve and the zygomaticofacial branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).