The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract.

The lips are a horizontal pair of soft appendages attached to the jaws and are the most visible part of the mouth of many animals, including humans. Vertebrate lips are soft, movable and serve to facilitate the ingestion of food and the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are also a somatosensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy.

The zygomaticus major muscle is a muscle of the face. It arises from either zygomatic arch (cheekbone); it inserts at the corner of the mouth. It is innervated by branches of the facial nerve.

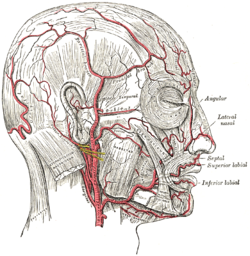
The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

Kiesselbach's plexus is an anastomotic arterial network (plexus) of four or five arteries in the nose supplying the nasal septum. It lies in the anterior inferior part of the septum known as Little's area, Kiesselbach's area, or Kiesselbach's triangle. It is a common site for anterior nosebleeds.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.
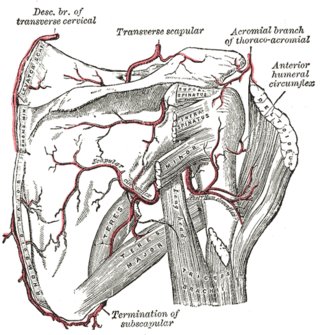
The circumflex scapular artery is a branch of the subscapular artery and part of the scapular anastomoses.

The inferior alveolar artery is an artery of the head. It is a branch of the maxillary artery. It descends through the infratemporal fossa as part of a neurovascular bundle with the inferior alveolar nerve and vein to the mandibular foramen where it enters and passes anterior-ward inside the mandible, suplying the body of mandible and the dental pulp of the lower molar and premolar teeth. Its terminal incisor branch supplies the rest of the lower teeth. Its mental branch exits the mandibula anteriorly through the mental foramen to supply adjacent lip and skin.
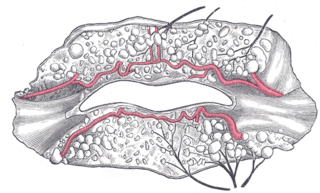
The inferior labial artery arises near the angle of the mouth as a branch of the facial artery; it passes upward and forward beneath the triangularis and, penetrating the orbicularis oris, runs in a tortuous course along the edge of the lower lip between this muscle and the mucous membrane.

The angular vein is a vein of the face. It is the upper part of the facial vein, above its junction with the superior labial vein. It is formed by the junction of the supratrochlear vein and supraorbital vein, and joins with the superior labial vein. It drains the medial canthus, and parts of the nose and the upper lip. It can be a route of spread of infection from the danger triangle of the face to the cavernous sinus.

The lacrimal artery is an artery of the orbit. It is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It accompanies the lacrimal nerve along the upper border of the lateral rectus muscle, travelling forward to reach the lacrimal gland. It supplies the lacrimal gland, two rectus muscles of the eye, the eyelids, and the conjunctiva.

The infraorbital artery is a small artery in the head that arises from the maxillary artery and passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit, then passes forward along the floor of the orbit, finally exiting the orbit through the infraorbital foramen to reach the face.

The superior labial branches, the largest and most numerous, descend behind the quadratus labii superioris, and are distributed to the skin of the upper lip, the mucous membrane of the mouth, and labial glands.

The infraorbital nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve. It arises in the pterygopalatine fossa. It passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit. It travels through the orbit, then enters and traverses the infraorbital canal, exiting the canal at the infraorbital foramen to reach the face. It provides sensory innervation to the skin and mucous membranes around the middle of the face.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The submental artery is the largest branch of the facial artery in the neck. It first runs forward under the mouth, then turns upward upon reaching the chin.

The superior suprarenal artery is an artery in the abdomen. It is a branch of the inferior phrenic artery, itself a branch of the aorta. It supplies the adrenal gland.
Lip reconstruction may be required after trauma or surgical excision. The lips are considered the beginning of the oral cavity and are the most common site of oral cancer. Any reconstruction of the lips must include both functional and cosmetic considerations. The lips are necessary for speech, facial expression, and eating. Because of their prominent location on the face, even small abnormalities can be apparent.

The human nose is the most protruding part of the human face. It bears the nostrils and is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two.

In human anatomy, the mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and produces saliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth.