Articles related to anatomy include:

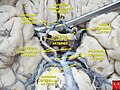
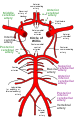
The circle of Willis is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including humans. It is named after Thomas Willis (1621–1675), an English physician.

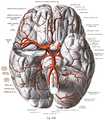
The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face, brain and neck.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain.

The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. The internal capsule contains both ascending and descending axons, going to and coming from the cerebral cortex. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.

The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid. Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right lateral ventricle, respectively.

The basilar artery is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood.

The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system, the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and posterior part of brain.
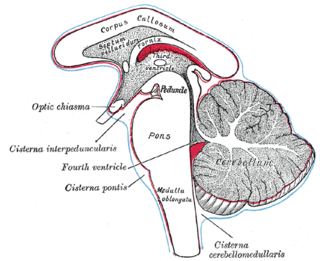
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space is situated between the two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

The anterior choroidal artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the brain. It is typically a branch of the internal carotid artery which supplies the choroid plexus of lateral ventricle and third ventricle as well as numerous structures of the brain.

The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries.

In human anatomy, the left and right posterior communicating arteries are small arteries at the base of the brain that form part of the circle of Willis.

In human anatomy, the anterior communicating artery is a blood vessel of the brain that connects the left and right anterior cerebral arteries.

The cerebral arteries describe three main pairs of arteries and their branches, which perfuse the cerebrum of the brain. The three main arteries are the:

Anterior cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is restricted, leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel: the medial aspects of the frontal and parietal lobes, basal ganglia, anterior fornix and anterior corpus callosum.

The leptomeningeal collateral circulation is a network of small blood vessels in the brain that connects branches of the middle, anterior and posterior cerebral arteries, with variation in its precise anatomy between individuals. During a stroke, leptomeningeal collateral vessels allow limited blood flow when other, larger blood vessels provide inadequate blood supply to a part of the brain.
The recurrent artery of Heubner, Heubner's artery or distal medial striate artery is an artery in the head. It is named after the German paediatrician Otto Heubner. It is a branch of the anterior cerebral artery. Its vascular territory is the anteromedial section of the caudate nucleus and the anterioinferior section of the internal capsule, as well as parts of the putamen and septal nuclei.

The orbitofrontal artery is one of the branches of the anterior cerebral artery, that supplies blood to the cerebrum. The orbitofrontal artery is usually the first cortical branch of the A2 segment, arising from the subcallosal segment to supply the inferior and inferomedial surfaces of the frontal lobe including the gyri recti.