A transient ischemic attack (TIA), commonly known as a mini-stroke, is a minor stroke whose noticeable symptoms usually end in less than an hour. TIA causes the same symptoms associated with strokes, such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, sudden dimming or loss of vision, difficulty speaking or understanding language, slurred speech, or confusion.

Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. The most common presentation of cerebrovascular disease is an ischemic stroke or mini-stroke and sometimes a hemorrhagic stroke. Hypertension is the most important contributing risk factor for stroke and cerebrovascular diseases as it can change the structure of blood vessels and result in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis narrows blood vessels in the brain, resulting in decreased cerebral perfusion. Other risk factors that contribute to stroke include smoking and diabetes. Narrowed cerebral arteries can lead to ischemic stroke, but continually elevated blood pressure can also cause tearing of vessels, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke.
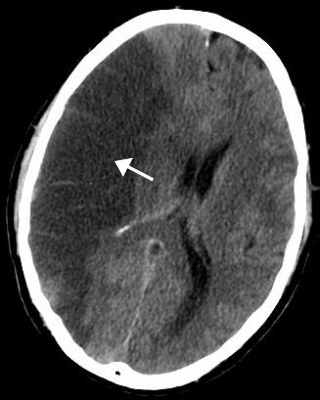
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly.
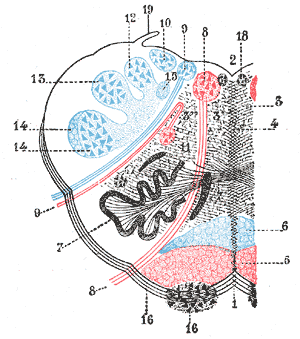
Lateral medullary syndrome is a neurological disorder causing a range of symptoms due to ischemia in the lateral part of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. The ischemia is a result of a blockage most commonly in the vertebral artery or the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Lateral medullary syndrome is also called Wallenberg's syndrome, posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) syndrome and vertebral artery syndrome.

Moyamoya disease is a disease in which certain arteries in the brain are constricted. Blood flow is blocked by constriction and blood clots (thrombosis). A collateral circulation develops around the blocked vessels to compensate for the blockage, but the collateral vessels are small, weak, and prone to bleeding, aneurysm and thrombosis. On conventional angiography, these collateral vessels have the appearance of a "puff of smoke".

The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery.

Intraparenchymal hemorrhage (IPH) is one form of intracerebral bleeding in which there is bleeding within brain parenchyma. The other form is intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH).

The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries.

Cerebral infarction, also known as an ischemic stroke, is the pathologic process that results in an area of necrotic tissue in the brain. In mid to high income countries, a stroke is the main reason for disability among people and the 2nd cause of death. It is caused by disrupted blood supply (ischemia) and restricted oxygen supply (hypoxia). This is most commonly due to a thrombotic occlusion, or an embolic occlusion of major vessels which leads to a cerebral infarct. In response to ischemia, the brain degenerates by the process of liquefactive necrosis.

The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) is one of three pairs of arteries that supplies blood to the cerebellum.

A watershed stroke is defined as a brain ischemia that is localized to the vulnerable border zones between the tissues supplied by the anterior, posterior and middle cerebral arteries. The actual blood stream blockage/restriction site can be located far away from the infarcts. Watershed locations are those border-zone regions in the brain supplied by the major cerebral arteries where blood supply is decreased. Watershed strokes are a concern because they comprise approximately 10% of all ischemic stroke cases. The watershed zones themselves are particularly susceptible to infarction from global ischemia as the distal nature of the vasculature predisposes these areas to be most sensitive to profound hypoperfusion.

Weber's syndrome, also known as midbrain stroke syndrome or superior alternating hemiplegia, is a form of stroke that affects the medial portion of the midbrain. It involves oculomotor fascicles in the interpeduncular cisterns and cerebral peduncle so it characterizes the presence of an ipsilateral lower motor neuron type oculomotor nerve palsy and contralateral hemiparesis or hemiplegia.
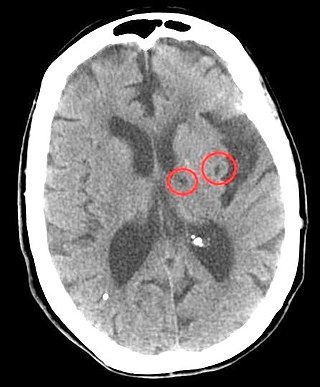
Lacunar stroke or lacunar cerebral infarct (LACI) is the most common type of ischemic stroke, resulting from the occlusion of small penetrating arteries that provide blood to the brain's deep structures. Patients who present with symptoms of a lacunar stroke, but who have not yet had diagnostic imaging performed, may be described as having lacunar stroke syndrome (LACS).

Posterior cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is restricted, leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel: the occipital lobe, the inferomedial temporal lobe, a large portion of the thalamus, and the upper brainstem and midbrain.

Middle cerebral artery syndrome is a condition whereby the blood supply from the middle cerebral artery (MCA) is restricted, leading to a reduction of the function of the portions of the brain supplied by that vessel: the lateral aspects of frontal, temporal and parietal lobes, the corona radiata, globus pallidus, caudate and putamen. The MCA is the most common site for the occurrence of ischemic stroke.

The leptomeningeal collateral circulation is a network of small blood vessels in the brain that connects branches of the middle, anterior and posterior cerebral arteries, with variation in its precise anatomy between individuals. During a stroke, leptomeningeal collateral vessels allow limited blood flow when other, larger blood vessels provide inadequate blood supply to a part of the brain.
Benedikt syndrome, also called Benedikt's syndrome or paramedian midbrain syndrome, is a rare type of posterior circulation stroke of the brain, with a range of neurological symptoms affecting the midbrain, cerebellum and other related structures.
Claude's syndrome is a form of brainstem stroke syndrome characterized by the presence of an ipsilateral oculomotor nerve palsy, contralateral hemiparesis, contralateral ataxia, and contralateral hemiplegia of the lower face, tongue, and shoulder. Claude's syndrome affects oculomotor nerve, red nucleus and brachium conjunctivum.
A silent stroke is a stroke that does not have any outward symptoms associated with stroke, and the patient is typically unaware they have suffered a stroke. Despite not causing identifiable symptoms, a silent stroke still causes damage to the brain and places the patient at increased risk for both transient ischemic attack and major stroke in the future. In a broad study in 1998, more than 11 million people were estimated to have experienced a stroke in the United States. Approximately 770,000 of these strokes were symptomatic and 11 million were first-ever silent MRI infarcts or hemorrhages. Silent strokes typically cause lesions which are detected via the use of neuroimaging such as MRI. The risk of silent stroke increases with age but may also affect younger adults. Women appear to be at increased risk for silent stroke, with hypertension and current cigarette smoking being amongst the predisposing factors.
A migrainous infarction is a rare type of ischaemic stroke which occurs in correspondence with migraine aura symptoms. Symptoms include headaches, visual disturbances, strange sensations and dysphasia, all of which gradually worsen causing neurological changes which ultimately increase the risk of an ischaemic stroke. Typically, women under the age of 45 who experience migraine with aura (MA) are at the greatest risk for developing migrainous infarction, especially when combined with smoking and use of oral contraceptives.












