
Agnosia is a neurological disorder characterized by an inability to process sensory information. Often there is a loss of ability to recognize objects, persons, sounds, shapes, or smells while the specific sense is not defective nor is there any significant memory loss. It is usually associated with brain injury or neurological illness, particularly after damage to the occipitotemporal border, which is part of the ventral stream. Agnosia only affects a single modality, such as vision or hearing. More recently, a top-down interruption is considered to cause the disturbance of handling perceptual information.

The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.

The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations to language switching. It is located bilaterally, roughly at the upper sides of the temporal lobes – in humans, curving down and onto the medial surface, on the superior temporal plane, within the lateral sulcus and comprising parts of the transverse temporal gyri, and the superior temporal gyrus, including the planum polare and planum temporale.
Auditory neuropathy (AN) is a hearing disorder in which the outer hair cells of the cochlea are present and functional, but sound information is not transmitted sufficiently by the auditory nerve to the brain. The cause may be several dysfunctions of the inner hair cells of the cochlea or spiral ganglion neuron levels. Hearing loss with AN can range from normal hearing sensitivity to profound hearing loss.
Amusia is a musical disorder that appears mainly as a defect in processing pitch but also encompasses musical memory and recognition. Two main classifications of amusia exist: acquired amusia, which occurs as a result of brain damage, and congenital amusia, which results from a music-processing anomaly present since birth.

In psycholinguistics, language processing refers to the way humans use words to communicate ideas and feelings, and how such communications are processed and understood. Language processing is considered to be a uniquely human ability that is not produced with the same grammatical understanding or systematicity in even human's closest primate relatives.

Neurofibromatosis type II is a genetic condition that may be inherited or may arise spontaneously, and causes benign tumors of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. The types of tumors frequently associated with NF2 include vestibular schwannomas, meningiomas, and ependymomas. The main manifestation of the condition is the development of bilateral benign brain tumors in the nerve sheath of the cranial nerve VIII, which is the "auditory-vestibular nerve" that transmits sensory information from the inner ear to the brain. Besides, other benign brain and spinal tumors occur. Symptoms depend on the presence, localisation and growth of the tumor(s). Many people with this condition also experience vision problems. Neurofibromatosis type II is caused by mutations of the "Merlin" gene, which seems to influence the form and movement of cells. The principal treatments consist of neurosurgical removal of the tumors and surgical treatment of the eye lesions. Historically the underlying disorder has not had any therapy due to the cell function caused by the genetic mutation.
Auditory verbal agnosia (AVA), also known as pure word deafness, is the inability to comprehend speech. Individuals with this disorder lose the ability to understand language, repeat words, and write from dictation. Some patients with AVA describe hearing spoken language as meaningless noise, often as though the person speaking was doing so in a foreign language. However, spontaneous speaking, reading, and writing are preserved. The maintenance of the ability to process non-speech auditory information, including music, also remains relatively more intact than spoken language comprehension. Individuals who exhibit pure word deafness are also still able to recognize non-verbal sounds. The ability to interpret language via lip reading, hand gestures, and context clues is preserved as well. Sometimes, this agnosia is preceded by cortical deafness; however, this is not always the case. Researchers have documented that in most patients exhibiting auditory verbal agnosia, the discrimination of consonants is more difficult than that of vowels, but as with most neurological disorders, there is variation among patients.

Foix–Chavany–Marie syndrome (FCMS), also known as bilateral opercular syndrome, is a neuropathological disorder characterized by paralysis of the facial, tongue, pharynx, and masticatory muscles of the mouth that aid in chewing. The disorder is primarily caused by thrombotic and embolic strokes, which cause a deficiency of oxygen in the brain. As a result, bilateral lesions may form in the junctions between the frontal lobe and temporal lobe, the parietal lobe and cortical lobe, or the subcortical region of the brain. FCMS may also arise from defects existing at birth that may be inherited or nonhereditary. Symptoms of FCMS can be present in a person of any age and it is diagnosed using automatic-voluntary dissociation assessment, psycholinguistic testing, neuropsychological testing, and brain scanning. Treatment for FCMS depends on the onset, as well as on the severity of symptoms, and it involves a multidisciplinary approach.
The auditory brainstem response (ABR), also called brainstem evoked response audiometry (BERA) or brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEPs) or brainstem auditory evoked responses (BAERs) is an auditory evoked potential extracted from ongoing electrical activity in the brain and recorded via electrodes placed on the scalp. The measured recording is a series of six to seven vertex positive waves of which I through V are evaluated. These waves, labeled with Roman numerals in Jewett and Williston convention, occur in the first 10 milliseconds after onset of an auditory stimulus. The ABR is considered an exogenous response because it is dependent upon external factors.
Auditory agnosia is a form of agnosia that manifests itself primarily in the inability to recognize or differentiate between sounds. It is not a defect of the ear or "hearing", but rather a neurological inability of the brain to process sound meaning. While auditory agnosia impairs the understanding of sounds, other abilities such as reading, writing, and speaking are not hindered. It is caused by bilateral damage to the anterior superior temporal gyrus, which is part of the auditory pathway responsible for sound recognition, the auditory "what" pathway.

Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science.
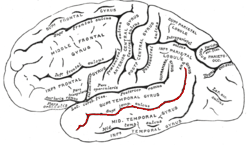
In the human brain, the superior temporal sulcus (STS) is the sulcus separating the superior temporal gyrus from the middle temporal gyrus in the temporal lobe of the brain. A sulcus is a deep groove that curves into the largest part of the brain, the cerebrum, and a gyrus is a ridge that curves outward of the cerebrum.
The neuroscience of music is the scientific study of brain-based mechanisms involved in the cognitive processes underlying music. These behaviours include music listening, performing, composing, reading, writing, and ancillary activities. It also is increasingly concerned with the brain basis for musical aesthetics and musical emotion. Scientists working in this field may have training in cognitive neuroscience, neurology, neuroanatomy, psychology, music theory, computer science, and other relevant fields.
Neuroscientists have learned much about the role of the brain in numerous cognitive mechanisms by understanding corresponding disorders. Similarly, neuroscientists have come to learn much about music cognition by studying music-specific disorders. Even though music is most often viewed from a "historical perspective rather than a biological one" music has significantly gained the attention of neuroscientists all around the world. For many centuries music has been strongly associated with art and culture. The reason for this increased interest in music is because it "provides a tool to study numerous aspects of neuroscience, from motor skill learning to emotion".
Phonagnosia is a type of agnosia, or loss of knowledge, that involves a disturbance in the recognition of familiar voices and the impairment of voice discrimination abilities in which the affected individual does not suffer from comprehension deficits. Phonagnosia is an auditory agnosia, an acquired auditory processing disorder resulting from brain damage. Other auditory agnosias include cortical deafness and auditory verbal agnosia also known as pure word deafness.
Spatial hearing loss refers to a form of deafness that is an inability to use spatial cues about where a sound originates from in space. Poor sound localization in turn affects the ability to understand speech in the presence of background noise.

Sign language refers to any natural language which uses visual gestures produced by the hands and body language to express meaning. The brain's left side is the dominant side utilized for producing and understanding sign language, just as it is for speech. In 1861, Paul Broca studied patients with the ability to understand spoken languages but the inability to produce them. The damaged area was named Broca's area, and located in the left hemisphere’s inferior frontal gyrus. Soon after, in 1874, Carl Wernicke studied patients with the reverse deficits: patients could produce spoken language, but could not comprehend it. The damaged area was named Wernicke's area, and is located in the left hemisphere’s posterior superior temporal gyrus.

Identification of a hearing loss is usually conducted by a general practitioner medical doctor, otolaryngologist, certified and licensed audiologist, school or industrial audiometrist, or other audiometric technician. Diagnosis of the cause of a hearing loss is carried out by a specialist physician or otorhinolaryngologist.

Auditosensory cortex is the part of the auditory system that is associated with the sense of hearing in humans. It occupies the bilateral primary auditory cortex in the temporal lobe of the mammalian brain. The term is used to describe Brodmann area 42 together with the transverse temporal gyri of Heschl. The auditosensory cortex takes part in the reception and processing of auditory nerve impulses, which passes sound information from the thalamus to the brain. Abnormalities in this region are responsible for many disorders in auditory abilities, such as congenital deafness, true cortical deafness, primary progressive aphasia and auditory hallucination.











