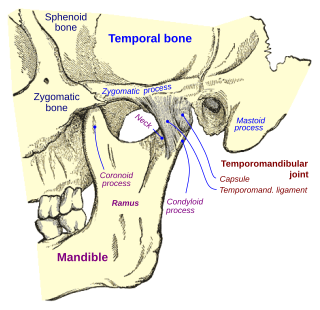
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the condylar process of mandible below; it is from these bones that its name is derived. The joints are unique in their bilateral function, being connected via the mandible.

In vertebrates, an ear is the organ that enables hearing and body balance using the vestibular system. In humans, the ear is described as having three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of the auricle and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear, the word "ear" often refers to the external part (auricle) alone. The middle ear includes the tympanic cavity and the three ossicles. The inner ear sits in the bony labyrinth, and contains structures which are key to several senses: the semicircular canals, which enable balance and eye tracking when moving; the utricle and saccule, which enable balance when stationary; and the cochlea, which enables hearing. The ear canal is cleaned via earwax, which naturally migrates to the auricle.

The middle meningeal artery is typically the third branch of the first portion of the maxillary artery. After branching off the maxillary artery in the infratemporal fossa, it runs through the foramen spinosum to supply the dura mater and the calvaria. The middle meningeal artery is the largest of the three (paired) arteries that supply the meninges, the others being the anterior meningeal artery and the posterior meningeal artery.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.

The tympanic cavity is a small cavity surrounding the bones of the middle ear. Within it sit the ossicles, three small bones that transmit vibrations used in the detection of sound.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.

The stylomastoid artery enters the stylomastoid foramen and supplies the tympanic cavity, the tympanic antrum and mastoid cells, and the semicircular canals. It is a branch of the posterior auricular artery, and thus part of the external carotid arterial system.
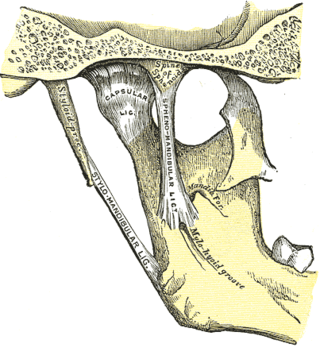
The sphenomandibular ligament is one of the three ligaments of the temporomandibular joint. It is situated medially to - and generally separate from - the articular capsule of the joint. Superiorly, it is attached to the spine of the sphenoid bone; inferiorly, it is attached to the lingula of mandible. The SML acts to limit inferior-ward movement of the mandible.
The pterygoid plexus is a fine venous plexus upon and within the lateral pterygoid muscle. It drains by a short maxillary vein.

The posterior auricular artery is a small artery that arises from the external carotid artery. It ascends along the side of the head. It supplies several muscles of the neck and several structures of the head.

The inferior alveolar artery is an artery of the head. It is a branch of the maxillary artery. It descends through the infratemporal fossa as part of a neurovascular bundle with the inferior alveolar nerve and vein to the mandibular foramen where it enters and passes anteriorly inside the mandible, supplying the body of mandible and the dental pulp of the lower molar and premolar teeth. Its terminal incisor branch supplies the rest of the lower teeth. Its mental branch exits the mandibula anteriorly through the mental foramen to supply adjacent lip and skin.

The ascending pharyngeal artery is an artery of the neck that supplies the pharynx.

The squamous part of temporal bone, or temporal squama, forms the front and upper part of the temporal bone, and is scale-like, thin, and translucent.

The anterior tympanic artery is a branch of the maxillary artery. It passes through the petrotympanic fissure to entre the middle ear where it contributes to the formation of the circular anastomosis around the tympanic membrane. It provides arterial supply to part of the lining of the middle ear. It is accompanied by the chorda tympani nerve.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

The petrotympanic fissure is a fissure in the temporal bone that runs from the temporomandibular joint to the tympanic cavity.

The mastoid cells are air-filled cavities within the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the cranium. The mastoid cells are a form of skeletal pneumaticity. Infection in these cells is called mastoiditis.

The anterior auricular branches of the superficial temporal artery are distributed to the anterior portion of the auricula, the lobule, and part of the external meatus, anastomosing with the posterior auricular. They supply the external acoustic meatus and the visible part of the ear.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
The parotid fascia is a tough fascia enclosing the parotid gland. It has a superficial layer and a deep layer.
















