Articles related to anatomy include:
Blinking is a bodily function; it is a semi-autonomic rapid closing of the eyelid. A single blink is determined by the forceful closing of the eyelid or inactivation of the levator palpebrae superioris and the activation of the palpebral portion of the orbicularis oculi, not the full open and close. It is an essential function of the eye that helps spread tears across and remove irritants from the surface of the cornea and conjunctiva.

An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. "Palpebral" means relating to the eyelids. Its key function is to regularly spread the tears and other secretions on the eye surface to keep it moist, since the cornea must be continuously moist. They keep the eyes from drying out when asleep. Moreover, the blink reflex protects the eye from foreign bodies. A set of specialized hairs known as lashes grow from the upper and lower eyelid margins to further protect the eye from dust and debris.

The procerus muscle is a small pyramidal slip of muscle deep to the superior orbital nerve, artery and vein. Procerus is Latin, meaning tall or extended.

The ophthalmic artery (OA) is an artery of the head. It is the first branch of the internal carotid artery distal to the cavernous sinus. Branches of the ophthalmic artery supply all the structures in the orbit around the eye, as well as some structures in the nose, face, and meninges. Occlusion of the ophthalmic artery or its branches can produce sight-threatening conditions.

The corrugator supercilii muscle is a small, narrow, pyramidal muscle of the face. It arises from the medial end of the superciliary arch; it inserts into the deep surface of the skin of the eyebrow.

The frontalis muscle is a muscle which covers parts of the forehead of the skull. Some sources consider the frontalis muscle to be a distinct muscle. However, Terminologia Anatomica currently classifies it as part of the occipitofrontalis muscle along with the occipitalis muscle.

The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, as well as other structures of the head.

The tarsi or tarsal plates are two comparatively thick, elongated plates of dense connective tissue, about 10 mm (0.39 in) in length for the upper eyelid and 5 mm for the lower eyelid; one is found in each eyelid, and contributes to its form and support. They are located directly above the lid margins. The tarsus has a lower and upper part making up the palpebrae.

The lacrimal artery is an artery of the orbit. It is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It accompanies the lacrimal nerve along the upper border of the lateral rectus muscle, travelling forward to reach the lacrimal gland. It supplies the lacrimal gland, two rectus muscles of the eye, the eyelids, and the conjunctiva.
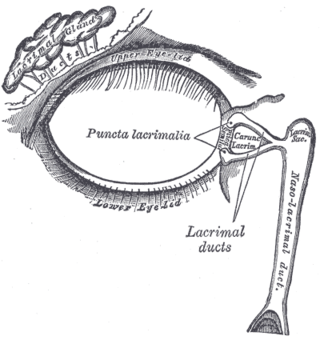
The lacrimal canaliculi are the small channels in each eyelid that drain lacrimal fluid, from the lacrimal puncta to the lacrimal sac. This forms part of the lacrimal apparatus that drains lacrimal fluid from the surface of the eye to the nasal cavity.

The lacrimal sac or lachrymal sac is the upper dilated end of the nasolacrimal duct, and is lodged in a deep groove formed by the lacrimal bone and frontal process of the maxilla. It connects the lacrimal canaliculi, which drain tears from the eye's surface, and the nasolacrimal duct, which conveys this fluid into the nasal cavity. Lacrimal sac occlusion leads to dacryocystitis.
The anterior lacrimal crest is a bony projection on the frontal process of the maxilla. It creates the lateral margin of the lacrimal sac fossa and is continuous with the orbital margin. The medial palpebral ligament is attached to anterior lacrimal crest. It is an important structure to avoid damaging during rhinoplasty.

The medial palpebral ligament is a ligament of the face. It attaches to the frontal process of the maxilla, the lacrimal groove, and the tarsus of each eyelid. It has a superficial (anterior) and a deep (posterior) layer, with many surrounding attachments. It connects the medial canthus of each eyelid to the medial part of the orbit. It is a useful point of fixation during eyelid reconstructive surgery.

The frontal process of the maxilla is a strong plate, which projects upward, medialward, and backward from the maxilla, forming part of the lateral boundary of the nose.

The angular artery is an artery of the face. It is the terminal part of the facial artery. It ascends to the medial angle of the eye's orbit. It is accompanied by the angular vein. It ends by anastomosing with the dorsal nasal branch of the ophthalmic artery. It supplies the lacrimal sac, the orbicularis oculi muscle, and the outer side of the nose.

The medial palpebral arteries are arteries of the head that contribute arterial blood supply to the eyelids. They are derived from the ophthalmic artery; a single medial palpebral artery issues from the ophthalmic artery before splitting into a superior and an inferior medial palpebral artery, each supplying one eyelid.

The zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (malar branches) are nerves of the face. They run across the zygomatic bone to the lateral angle of the orbit. Here, they supply the orbicularis oculi muscle, and join with filaments from the lacrimal nerve and the zygomaticofacial branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).

The lateral palpebral raphe is a ligamentous band near the eye. Its existence is contentious, and many sources describe it as the continuation of nearby muscles. It is formed from the lateral ends of the orbicularis oculi muscle. It connects the orbicularis oculi muscle, the frontosphenoidal process of the zygomatic bone, and the tarsi of the eyelids.

The accessory visual structures are the protecting and supporting structures (adnexa) of the eye, including the eyebrow, eyelids, and lacrimal apparatus. The eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes, lacrimal gland and drainage apparatus all play a crucial role with regards to globe protection, lubrication, and minimizing the risk of ocular infection. The adnexal structures also help to keep the cornea moist and clean.













