This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(May 2015) |
| Depressor anguli oris | |
|---|---|
 Scheme showing arrangement of fibers of Orbicularis oris (triangularis labeled at bottom right). | |
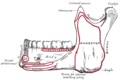
 Muscles of the head, face, and neck (labeled as triangularis near chin). | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Tubercle of mandible |
| Insertion | Modiolus of mouth |
| Artery | Facial artery |
| Nerve | Marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve |
| Actions | Depresses angle of mouth |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus depressor anguli oris |
| TA98 | A04.1.03.026 |
| TA2 | 2076 |
| FMA | 46828 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The depressor anguli oris muscle (triangularis muscle) is a facial muscle. It originates from the mandible and inserts into the angle of the mouth. It is associated with frowning, as it depresses the corner of the mouth.