Articles related to anatomy include:

The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.
Superficial muscular aponeurotic system (SMAS) is a thin yet tough unitary tissue plane of the face formed by facial fasciae, subcutis connective tissue, and facial muscles. Its composition varies, containing muscle fibres in some areas, and fibrous or fibroaponeurotic tissue in others. It connects to the dermis via vertical septa. It does not attach to bone. In most areas, a distinct plane can be defined deep to the SMAS.

In anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication. Found only in mammals, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter. The most obvious muscle of mastication is the masseter muscle, since it is the most superficial and one of the strongest.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.
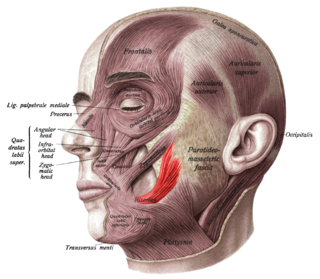
The risorius muscle is a highly variable muscle of facial expression. It has numerous and very variable origins, and inserts into the angle of the mouth. It receives motor innervation from branches of facial nerve. It may be absent or asymmetrical in some people. It pulls the angle of the mouth sidewise, such as during smiling.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

The transverse facial artery is an artery that branches from the superficial temporal artery and runs across the face.

The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible.

The retromandibular vein is a major vein of the face. It is formed within the parotid gland by the confluence of the maxillary vein, and superficial temporal vein. It descends in the gland and splits into two branches upon emerging from the gland. Its anterior branch then joins the (anterior) facial vein forming the common facial vein, while its posterior branch joins the posterior auricular vein forming the external jugular vein.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

The deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.

The temporal fascia is a fascia of the head that covers the temporalis muscle and structures situated superior to the zygomatic arch.
The buccal space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the cheek, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the buccinator muscle and deep to the platysma muscle and the skin. The buccal space is part of the subcutaneous space, which is continuous from head to toe.
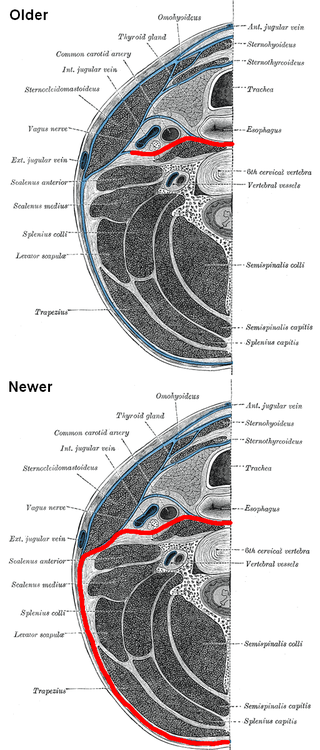
The prevertebral fascia is the layer of deep cervical fascia that surrounds the vertebral column. It is the deepest layer of deep cervical fascia.

The investing layer of deep cervical fascia is the most superficial part of the deep cervical fascia, and encloses the whole neck.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
Fascial spaces are potential spaces that exist between the fasciae and underlying organs and other tissues. In health, these spaces do not exist; they are only created by pathology, e.g. the spread of pus or cellulitis in an infection. The fascial spaces can also be opened during the dissection of a cadaver. The fascial spaces are different from the fasciae themselves, which are bands of connective tissue that surround structures, e.g. muscles. The opening of fascial spaces may be facilitated by pathogenic bacterial release of enzymes which cause tissue lysis. The spaces filled with loose areolar connective tissue may also be termed clefts. Other contents such as salivary glands, blood vessels, nerves and lymph nodes are dependent upon the location of the space. Those containing neurovascular tissue may also be termed compartments.

The submasseterric space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the face over the angle of the jaw, and is paired on each side. It is located between the lateral aspect of the mandible and the medial aspect of the masseter muscle and its investing fascia. The term is derived from sub- meaning "under" in Latin and masseteric which refers to the masseter muscle. The submasseteric space is one of the four compartments of the masticator space. Sometimes the submasseteric space is described as a series of spaces, created because the masseter muscle has multiple insertions that cover most of the lateral surface of the ramus of the mandible.
The parotid fascia is a tough fascia enclosing the parotid gland. It has a superficial layer and a deep layer.















